A coalition of large energy users—including Google, Amazon, Meta, Occidental, and Dow—have pledged their support for tripling global nuclear capacity by 2050. The cross-industry commitment, announced on the sidelines of CERAWeek by S&P Global in Houston, marks the first time large energy users beyond the nuclear sector have collectively backed such an extensive expansion of nuclear power.
The Large Energy Users Pledge is facilitated by the World Nuclear Association (WNA), the international organization representing the global nuclear industry, in collaboration with its partners under the Net Zero Nuclear initiative—a WNA-led effort to promote nuclear energy as a key solution for achieving net-zero emissions.
It essentially champions nuclear energy’s crucial role in ensuring energy security, resiliency, and a continuous supply of firm clean power. Recognizing the growing energy demands of industries and the need for reliable, weather-independent electricity, the signatories support nuclear as a key solution for sustaining cost-competitive operations across sectors, including high-temperature industrial processes, hydrogen production, and synthetic fuels.
The pledge notably also calls for equitable financial access for nuclear projects, government commitments to mobilize investment, and broader corporate participation to accelerate nuclear expansion as part of a diversified and resilient energy strategy.
Founding signatories at CERAWeek include hyperscalers Amazon, Google, and Meta. Industry signatories include chemical giant Dow; oil and gas major Occidental; offshore engineering firm Allseas; IHI Corporation, a Japanese multinational in heavy industry and energy; and ORLEN Synthos Green Energy (OSGE), a Polish joint venture focused on deploying GE Hitachi’s BWRX-300 small modular reactors. “The pledge is expected to gain more support over the coming months, reflecting growing interest in nuclear power from industries as diverse as maritime, aviation, and oil & gas,” WNA said in a statement.
A Crucial Market Signal
The Large Energy Users Pledge arrives as demand for firm, carbon-free power surges amid electrification, AI-driven data center growth, and industrial decarbonization efforts. As POWER recently reported in detail, while recent years have marked significant policy and market momentum for nuclear, challenges such as high capital costs, regulatory bottlenecks, and financing hurdles remain formidable.
Experts have told POWER scaling deployment to even double capacity—as projected by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)—will require stronger investment signals and policy frameworks. The IAEA’s latest outlook suggests nuclear capacity could reach between 458 GWe and 890 GW by 2050, depending on market conditions, policy support, and investment in new and existing reactors.
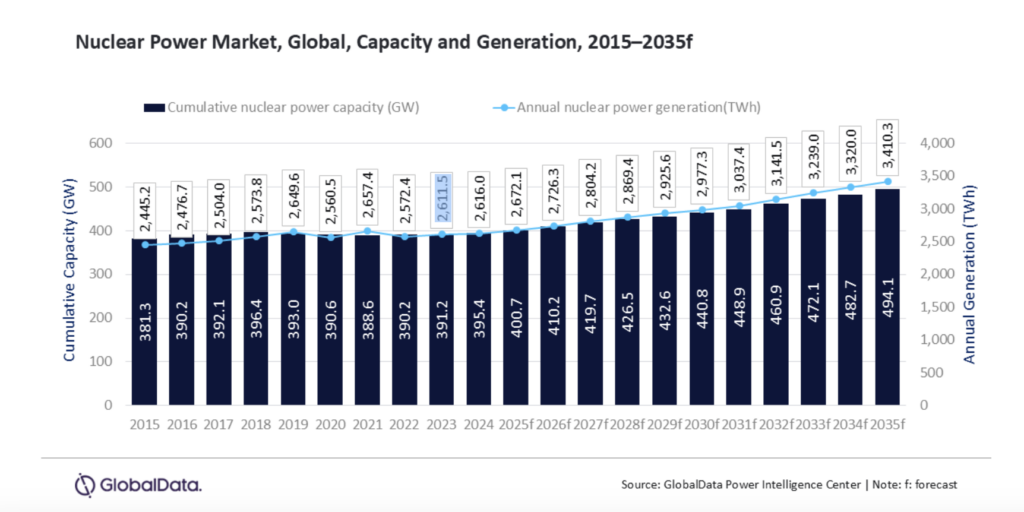
The pledge ambitiously envisions expanding global nuclear capacity from 377 GW, currently generated by 417 operational reactors, to 1,131 GW by 2050. Beyond its scale, its core significance lies in signaling alignment among global corporations across diverse industries. This growing private sector commitment is expected to mobilize capital, expand supply chains, and accelerate the deployment of small modular reactors (SMRs) and advanced nuclear technologies.
Momentum for Efforts to Triple Nuclear
Notably, the pledge by large energy users echoes the Declaration to Triple Nuclear Energy, which was endorsed by 25 countries at COP28 in Dubai in December 2023. Six more countries joined the declaration at COP29 in Azerbaijan in November 2024, bringing the total number of countries to 31.
Signatory countries committed to ensuring the safe and responsible operation of nuclear power plants, mobilizing investment in nuclear energy—including through innovative financing mechanisms—and promoting resilient supply chains. The declaration also encourages financial institutions, including the World Bank and regional development banks, to support nuclear power, and underscores the importance of extending the lifetimes of existing reactors where feasible. Additionally, it calls for advancing new nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs) and advanced reactors for power generation, hydrogen production, and industrial decarbonization. Progress on these commitments is reviewed annually at the COP climate conferences, with signatories urging other nations to join the initiative.
In September 2024, at New York Climate Week, 14 of the world’s largest banks and financial institutions from five countries also signaled their support for tripling global nuclear capacity, pledging to explore greater access to sustainable finance mechanisms for nuclear projects.
Wright: U.S. Remains Committed to Nuclear Expansion
Under the Biden administration, the U.S, a key endorser of the declaration, in November 2024 set deployment targets to add 35 GW of new capacity by 2035 and achieve a sustained pace of 15 GW per year by 2040. The country also joined with Canada, France, Japan, and the UK to mobilize $4.2 billion to boost enriched uranium production capacity “free from Russian material and establish a resilient uranium supply market free from Russian influence.”
At CERAweek on Monday, while Energy Secretary Chris Wright emphasized a shift away from what he called the previous administration’s “myopic” focus on climate change, he outlined a strategy centered on energy security, affordability, and industrial revitalization. Signaling that the Trump administration will continue to champion nuclear energy, he said: “We are working to launch the long-awaited American nuclear renaissance—fission and fusion.”
More details about the large energy user pledge at a formal launch ceremony on Wednesday, cohosted by nuclear fuel giants Urenco Group and Cameco Corp.
—Sonal Patel is a POWER senior editor (@sonalcpatel, @POWERmagazine).
Editor’s Note: This story is currently evolving and subject to change. We encourage you to revisit this article or check our website for the latest updates.