Waste to Energy
-
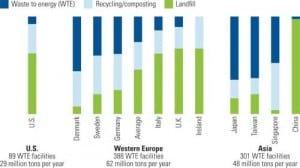
Waste to Energy
The Growing Role of Waste-to-Energy in the U.S.
Using nonhazardous waste for power generation is a trend that’s gaining steam for several reasons. Though there are several environmental reasons, another is the reliability of the fuel supply.
-
Coal
Biomass Cofiring: Another Way to Clean Your Coal
Demand for renewable power is burgeoning as state governments (and maybe soon the U.S. federal government) impose increasingly rigorous environmental and procurement standards on the energy industry. Surprisingly, biomass cofiring has yet to attract much attention, even though it could help many utilities meet their renewable portfolio requirements, reduce carbon emissions, and solve other regional environmental problems. U.S. developers, investors, and regulators should consider including cofiring as part of the energy mix going forward.
-
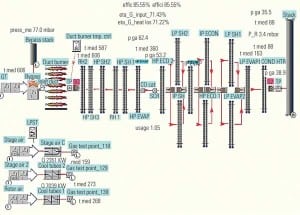
O&M
Computer Simulation of HRSGs Can Improve O&M
Obtaining accurate data about the performance of a plant’s heat-recovery steam generator is crucial to ensuring the smooth operation and maintenance of the equipment. Software designed to model and simulate HRSG operations can provide valuable information about corrosion and other operational problems.
-
O&M
Solving Fouling Problems with an HRSG Upgrade
Despite being located on the beautiful Hawaiian island of Oahu, the Kalaeloa Cogeneration Plant had trouble in paradise: Large amounts of ash from #6 low-sulfur fuel oil coated the finned tubes of its heat-recovery steam generators (HRSGs). The fouling added an extra $5 million dollars a year to the plant’s fuel bill. By retrofitting the HRSG with new panels and improved fin design, the plant overcame the fouling problems, stopped tube leaks, and cut fuel costs.
-
Waste to Energy
Microbe Turns Carbon Dioxide into Methane
Microbe Turns Carbon Dioxide into Methane A team of Penn State engineers say that a tiny self-perpetuating microbe can take electricity and directly convert carbon dioxide and water into methane, potentially producing a portable energy source with a carbon-neutral footprint. Methanogenic microorganisms produce methane in marshes and dumps, but scientists thought that the organisms turned […]
-
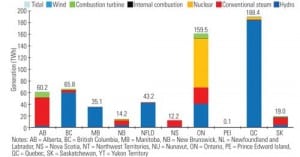
Coal
Canada Moves to Rebalance Its Energy Portfolio
Though Canada is rich in fossil fuels, nuclear power may fuel a significant portion of the nation’s future electrical generation needs, especially in provinces that have traditionally relied on hydropower and fossil fuels.
-
Coal
CHP: Helping to Promote Sustainable Energy
Because combined heat and power (CHP) plants optimize energy use, they cut fuel costs and pollution. Even though U.S. power plants have been using CHP for decades, today’s energy experts have a newfound appreciation for its ability to promote sustainable energy use.
-
Hydro
Renewable Project Finance Options: ITC, PTC, or Cash Grant?
Dozens of institutional investors in U.S. renewable energy projects pulled out of the market when the nation’s liquidity reserves dried up late last year. Some left the renewable market sector in search of more lucrative investment opportunities. Others found themselves unable to take advantage of the attractive tax credits because they themselves lacked profits against which to use the credits. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, approved February 13, changed the investor ground rules — again.
-
Coal
Firstenergy to Convert Coal-Fired Burger Plant to Biomass
Confronted with a district court ultimatum that would have forced it to install expensive pollution controls or close two coal-fired units at its R.E. Burger Plant in Shadyside, Ohio, Akron-based FirstEnergy Corp. announced in April that it would convert them to biomass. When the $200 million retrofit is complete, as is expected by 2013, the Burger Plant will likely be one of the largest biomass facilities in the U.S.
-
Waste to Energy
Compact, Portable System Converts Trash to Energy
Post-consumer waste could be the newest, ubiquitous fuel source for distributed energy generation if a mobile waste-to-energy conversion system launched this January finds its way onto the parking lots of facilities that produce more than two tons of waste daily. According to its developer, Massachusetts-based IST Energy, the GEM system can process up to 3 tons of waste daily — which can include paper, plastic, food, wood, and agricultural materials — and produce up to 120 kWe and 240 kWth.
-
Waste to Energy
New Biogas Plant Runs Purely on Nonedible Materials
German researchers in February said they had developed the first-ever biogas plant to run purely on waste instead of edible raw materials. The team from the Fraunhofer Institute for Ceramic Technologies and Systems IKTS (Institut Keramische Technologien und Systeme) in Dresden said that the plant, which uses a fuel cell to convert the gas into electricity, exclusively uses agricultural waste such as corn stalks — and it generates 30% more biogas than conventional plants.
-
Waste to Energy
Power Generators Turn to Diverse Fuels
Like the airline industry, power generators all over the world have been seeking alternative fuels with which to produce electricity, and the blends are bound to get stranger. One company is looking to make liquid fuels from chicken fat, beef tallow, and pork lard, for example. Here’s a list of innovative fuels that generators could use in the near future.
-
Hydro
International Organization to Push Renewable Energy
Seventy-five countries from around the world joined a new political agency dedicated to the acceleration of green energy this January, but several notable nations — including the U.S., Canada, Australia, UK, Japan, and China — were not among them.
-
Waste to Energy
Landfills: From Trash to Treasure
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has described landfills as an "effectively untapped resource" for renewable energy. The agency estimates that landfills are the source of about 12% of global methane emissions. (Methane is about 21 times more powerful as a greenhouse gas than CO2.) The EPA estimated that there were some 1,000 projects around […]
-
Waste to Energy
Top Plants: Covanta Onondaga Waste-to-Energy Plant, Jamesville, New York
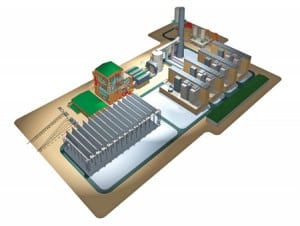
Covanta Energy Corp. doesn’t believe in wasting waste. Since 1995 the Covanta Onondaga waste-to-energy (WTE) plant has converted approximately 4 million tons of solid waste into 3 million MWh of clean electricity. Additionally, unlike power plants that use wind or solar energy, this 39-MW WTE facility operates 24/7, making it and similar WTE plants among the most continuously reliable sources of renewable electricity generation currently in operation.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Texas loses “food vs. fuel” biofuel feud
How often do you get a clash between two great Lone Star icons?
-
Coal
Global Monitor (September 2008)
Cost hikes for all things nuclear in the U.S. and UK / North Americans plan liquid makeover for coal / California balloon bill deflates in legislative process / The Lego skyscraper / Of manure and methane / U.S. small wind turbine market moving slowly / Israeli desert center tests solar thermal tech for California desert / POWER digest / Correction
-
Nuclear
Global Monitor (August 2008)
Australia considers seabed sequestration legislation / ElectraTherm installs its first commercial waste-heat generator / Mass. researchers achieve dramatic increase in thermoelectric efficiency / Nuclear power option for developing nations gaining steam / The great green wall of China / POWER digest / Correction
-
Coal
Global Monitor (July 2008)
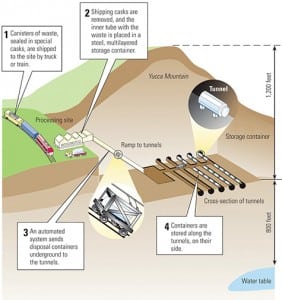
Yucca Mountain plan sent to NRC/ CPV cells get cooling chips from IBM/ StatoilHydro to pilot test first offshore floating wind turbine/ U.S. rivers next massive power source?/ Siemens delivers 500-MW gasifiers/ Algae: A green solution/ POWER digest
-
Coal
Global Monitor (June 2008)
Artificial photosynthesis for solar power? / Poultry litter to fuel 55-MW N.C. plan / First fuel cell-powered plane takes flight / First HTS transmission cable energized / PTC powers wind power industry / Renewing Greensburg / GAO deems coal-to-gas switch impractical / Assessing the Congo River’s power potential / POWER digest / Corrections
-
Coal
Global Monitor (April 2008)
Tenaska proposes first new coal-fired plant with carbon capture/ Concerns raised over growth of China’s CO2 emissions/ Sandia, Stirling Energy Systems set new world record/ Indonesia orders first Wärtsilä Gas Cubes/ First wind turbines on Galapagos Islands cut oil imports/ Harnessing waste heat for electricity/ POWER digest/ Correction
-
Coal
Global Monitor (February 2008)
FutureGen picks Mattoon, Ill./Duke applies for first greenfield COL/PPL to work with UniStar on another COL
/Areva seeks NRC certification of its reactor/Mitsubishi also in line at the NRC/PV project shines in Nevada/SunEdison commissions Colorado PV plant/Big concentrating solar plant proposed/Super Boiler celebrates first anniversary/Small fuel cell uses JP-8 jet fuel/POWER digest -
Coal
Regulatory risks paralyzing power industry while demand grows
In our second annual report on the state and future of the U.S. power generation industry, we combine the considerable experience of POWER’s editorial staff with the market savvy of Industrial Info Resources Inc. (see next story) to preview the industry’s direction in 2008. We anticipate that the specter of carbon control legislation will hobble coal and make renewables the hot ticket while nukes continue to inch forward in a generation market that is basically treading water.
-
Waste to Energy
Central Vermont Public Service, Cow Power Program
Central Vermont Public Service developed the nation’s first farm-to-consumer renewable energy choice by using cow manure to generate electricity. CVPS gave beleaguered farms new economic hope; developed a generation system that provides clean, renewable energy; and helped solve numerous manure management environmental challenges. CVPS and Cow Power’s four member dairies are recognized as a 2007 Top Plant for generating renewable energy one cow at a time.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (September 2007)
Constellation files partial COL / IAEA scrutinizes shaken Japanese nuke / Wave energy of the future? / New GE plant reigns in Spain / Solar house competition heats up / Oxygen-blown IGCC, at micro-scale / Turning corncobs into ethanol / Court blocks gas attack on coal project / New advanced energy initiatives / POWER digest
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (May 2007)
Cyber security and the grid; Harnessing the Yangtze;
Hydraulic system overhaul;
O&M problems not caused by cycling;
-
Waste to Energy
Experts ponder future of biomass industry
This month we officially commemorate the 125th anniversary of the magazine that has been essential reading for owners and operators of power generating plants. As you read this brief history, you’ll see that—although we’re looking back at an illustrious past—the secret of POWER’s success has been its commitment to the future. As we look forward to the next milestone anniversary, we anticipate covering the latest developments in a new generation of power technologies. As always, our mission is to provide the best information and advice in the service of safely and efficiently powering the global energy industry.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (April 2007)
Npower plans big coal plant in UK / Berkeley boffins make thermoelectric discovery / Rinspeed’s roadster: Fast, fun, and green / Dead chickens, the weirdest renewable / Siemens celebrating three big deals / Nevada Power picks P&W, CH2M Hill / Scuderi’s air-hybrid engine / Ovation for huge new Chinese coal plant / PG&E dips toe into wave power / POWER digest
-
Gas
Global Monitor (March 2007)
Winter storms ravage Nebraska grid / Waste-fired plant coming to Arizona / Wartsila lands jobs in Azerbaijan, Sweden / Yet another controversial LNG project / Siemens lands two-gasifier order in China / IndyCars drink nothing but ethanol / New Otto/diesel engine to debut in Russia / POWER digest / Readers talk back