Plant Design
-
Coal
The Coal Pile: Steam Blast Rocks Big Apple
This July, an underground steam pipe near Manhattan’s Grand Central Terminal ruptured and spewed a scalding brown geyser of steam and debris higher than the nearby 77-story Chrysler Building. The blast, which injured 30 people, created a 40-foot crater at street level that swallowed a tow truck. A similar explosion in 1989 killed three people. […]
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: Smart Sootblower Tailors Cleaning to Need for It / Blending’s Impact on Coal Quality
The 1990 amendments to the Clean Air Act require coal-fired power plants to reduce their emissions of the pollutant SO2. To do so, many have switched to, or are considering switching to, Powder River Basin (PRB) coal. Unfortunately, PRB coal has a tendency to leave excessive and tenacious deposits on boiler heat-exchange surfaces. Complicating the problem, the distribution of the deposits is far from uniform.
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Coal to Synfuels: Deal or No Deal?
Synfuels’ political bubble has burst in Washington, but the market may step in where Congress fears to tread. When coal industry interests, in the form of the CTL Coalition, got a bill with strong federal support for coal-to-liquids technology before the Senate this spring, it appeared that the political skids were greased for some kind […]
-
O&M
Lignite Drying: New Coal-Drying Technology Promises Higher Efficiency Plus Lower Costs and Emissions
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Great River Energy are testing a new coal-drying technology that could dramatically reduce the emissions of lignite-burning power plants. The project was selected for funding during Round I of the DOE’s Clean Coal Power Initiative (CCPI), a series of competitions to demonstrate a range of promising clean-coal technologies. […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: IGCC Sticker Shock
Former Illinois Senator Everett Dirksen once observed, "A billion here and a billion there, and pretty soon you’re talking real money." The same can be said about skyrocketing estimated costs of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants as their designs are fleshed out. The higher price tags shouldn’t be a surprise — the more you learn […]
-
O&M
PRB Tech Notes: Lawrence Energy Center Showcases Winning Plant
Lawrence Energy Center (LEC) proudly hosted about 60 representatives of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) at its July 24th open house, luncheon, and plant tour. LEC was named the PRBCUG’s 2007 Plant of the Year at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference and Exhibition in Chicago, May 1 – 3. Traditionally, the winning […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: Pay Me Now or Pay Me Later
Money is always spent with the best intentions. We look for the best deal, often identifying it by the lowest price. Sometimes, our choice works out and we save money and get a great product. When it doesn’t work out, however, we find ourselves spending more and more money to repair or replace our "great […]
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: River Locks and Barges Are an Aging Workforce, Too
During 2005, about 150 million tons of coal were transported to power plants by hopper barges plying U.S. inland waterways. With coal-fired plants expected to continue producing 50% of America’s electricity, coal barge traffic is not likely to fall off. In fact, it may increase, for two reasons. One is cost. Shipping coal by barge […]
-
O&M
Pollution Control: LCRA Fayette Lowers NOx Below 0.10 lb/mmBtu
The Fayette Power Project (FPP, aka the Sam K. Seymour Power Station) is a three-unit, coal-fired generating plant sited near La Grange, Texas (Figure 1). Units 1 and 2, each with a nominal rating of 600 MW, are co-owned by the Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) and Austin Energy (AE). LCRA is a conservation and […]
-
O&M
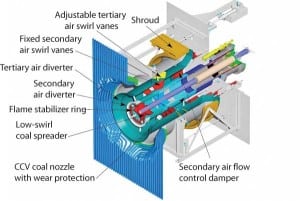
Pollution Control: Low-NOx Combustion Retrofit Options
Reducing NOx emissions from large utility coal-fired boilers has been a primary focus of the U.S. power generation industry since passage of the 1970 Clean Air Act and subsequent legislation. By the early 1990s, nearly all such boilers had installed some form of low-NOx burner (LNB) technology and/or overfire air (OFA) — the least expensive […]