News
-
News
Ameren, Dominion Spend Billions on Plant, Reliability Improvements
Last week, Ameren Corp. and Dominion Virginia Power separately issued statements claiming the utilities had spent billions on improvements to existing power plants.
-
News
EPA Proposes Stricter Ozone Standard
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Thursday proposed to lower ground-level ozone standards from those set in March 2008. The tighter so-called “smog” regulations would require power plants to cut their emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other volatile organic compounds.
-
News
UK Parcels Out Coastal Zones to Jumpstart £75B Offshore Wind Industry
The UK government’s Crown Estate on Friday parceled out rights to develop 32-GW worth of offshore wind energy in nine coastal zones. The announcement was part of the government’s ambitious plans to develop a £75 billion offshore wind industry by 2020.
-
News
Coal Plant Conversion to Biomass Delayed on EPA Rule Uncertainty
Georgia Power will delay the conversion of its coal-fired 155-MW Plant Mitchell in Albany, Ga., to run on wood waste until the Environmental Protection Agency better defines rules governing industrial boiler emissions in April 2010.
-
News
CPS Energy Receives New Toshiba Cost Estimate for STP Expansion
San Antonio’s CPS Energy said on Monday it had received the contractually mandated cost estimate for the proposed South Texas Project Units 3 and 4 from contractor Toshiba—but it stressed it would make no decisions on the project until “rigorous analysis” of price and methodology was completed.
-
News
Historic Label Deals New Hurdle for Cape Wind Offshore Project
The National Park Service ruled Monday that Nantucket Sound—the Massachusetts site proposed for Cape Wind, the nation’s first offshore wind farm—is eligible for listing in the National Register of Historic Places. The decision deals a new hurdle for the long-disputed proposal because it requires consideration of archaeological, historic, and cultural values in the review of the project by the Minerals Management Service (MMS).
-
News
Council Strikes Down French Carbon Emissions Tax
France’s Constitutional Council, the nation’s highest constitutional authority, last week annulled a tax on carbon emissions hailed by President Nicolas Sarkozy, saying that the tax that was due to become effective Jan. 1 would have allowed for too many exemptions.
-
News
BLM Fast-Tracks 31 Renewable Projects to Meet Stimulus Funding Deadline
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) last week put 31 renewable energy projects on a list for expedited processing so they could receive incentive funding under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act before its December 2010 deadline.
-
News
NRC Approves Final Rule on Nuclear Reactor Vessel Protection Requirements
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) on Monday issued a final rule to provide alternate requirements for protection against pressurized thermal shock events in nuclear power plant reactor vessels.
-
News
Obama to Honor UTEP Engineering Professor
President Barack Obama will honor 22 mentors and 80 educators across the country for their efforts to mentor minorities studying science and engineering at a White House reception today. Ben Flores, PhD, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP), will be a recipient of the Presidential Award for Excellence in Science, Technology, Mathematics and Engineering Mentoring (STEM).
-
News
Miniature Stainless Steel Pressure Switch
Ashcroft A-Series pressure switches are designed for tough OEM and industrial applications that require a durable, high-quality miniature switch. Available with explosion-proof and watertight enclosures, the pressure switch features a refined piston actuator that can be ranged up to 2,000 psi while enduring a working pressure of 5,000 psi. Small dimensions, a choice of connections, […]
-
News
Flowmeters for Steam Measurement
Racine Vortex released its RNS Series (Insertion) and RWS Series (Wafer) Vortex Steam Flow Meters to measure noncondensing steam and saturated process steam at pressures up to 150 psi for applications such as boiler monitoring. Both meters have no moving parts and are loop-powered devices with standard HART communication for ease of field programming and […]
-
News
Low-Noise Remote Charge Converter
Endevco Corp. launched Model 2771C-XX, an ultra-low-noise remote charge converter (RCC) designed for use with charge output piezoelectric sensors within applications such as nuclear power plant/regenerative energy and environmental testing. The model offers a rugged two-wire (IEPE), single-ended design that operates from constant current power (4-20 mA). Both RCC signal output and current to the […]
-
News
Predicting Hurricane-Related Outages
Researchers from John Hopkins and Texas A&M universities say that they have found a way to accurately predict power outages in advance of a hurricane. Computer models developed using data from Hurricane Katrina and four other destructive storms could save utilities substantial amounts of money and help facilitate rapid restoration of power after a storm, they say.
-
News
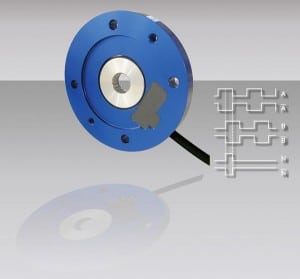
Thin, Flange-Style Magnetic Encoders
Baumer introduced the new MOR 90 and MOR 105 magnetic incremental encoders for improved speed and position control on electric motors, drives, gearboxes, and conveyors. Measuring just 14 mm thick, these extremely thin, flange-style encoders are virtually imperceptible when positioned between the motor and the gearbox and have little effect on the overall size of […]
-
News
Mich. DEQ Approves Air Permit for Consumers’ 830-MW Coal-Fired Plant
Michigan’s Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) on Tuesday approved an air permit for an 830-MW coal-fired power plant in Hampton Township—with the condition that its proposer, Consumers Energy, will retire up to 958 MW of coal-fired generating capacity from seven of the company’s oldest existing coal plants in the state.
-
News
Luminant Puts Oak Grove Coal Plant Unit Online in Texas
The first of two 800-MW units at Luminant’s new Oak Grove Power Plant in Robertson County, Texas, is now online, the Dallas-based company said on Monday. The coal-fired unit is the second Luminant has entered into service in Texas in the past six months. two
-
News
Application to Build Major Transmission Line Through Va. Withdrawn
Allegheny Energy and American Electric Power (AEP) on Tuesday said they had requested withdrawal of an application to run parts of the proposed Potomac-Appalachian Transmission Highline (PATH) through Virginia because data from a regional grid operator showed that the project would not be needed in 2014 to resolve reliability problems on the grid.
-
News
S. Korean Consortium Wins $20B Deal to Build Nukes in UAE
A South Korean consortium last week won a $20.4 billion deal to build four nuclear power plants in the United Arab Emirates—beating bids from a French consortium including Areva, GdF Suez, Électricité de France, and Total and a U.S.-Japanese consortium including General Electric and Hitachi. The consortium that won the first nuclear project awarded by […]
-
News
DOE to Fund Three “Energy Innovation Hubs” for Speedy Commercial Deployment
The U.S. Energy Department last week outlined plans to invest $366 million in three key energy areas: production of fuels directly from sunlight; improving energy-efficient building systems design; and computer modeling and simulation for the development of advanced nuclear reactors.
-
News
EPA Delays Coal Ash Regulations, Citing “Complexity” of Analysis
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) last week said that its decision to regulate coal ash waste from power plants, expected this month, will be delayed for a “short period” because of the “complexity of the analysis” underway at the agency.
-
News
Duke to Spend $93 Million to Settle Clean Air Act Violations at Ind. Plant
Duke Energy this week agreed under a settlement with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) to spend $93 million to resolve Clean Air Act violations at its coal-fired 560-MW Gallagher Station in New Albany, Ind.
-
News
Seminole Scraps Plans for $1.4 Billion Coal-Fired Unit in Florida
A motion submitted to an administrative judge last week by Seminole Electric Cooperative states that the Florida-based electricity supplier has decided “not to go forward with construction and operation” of a 750-MW coal-fired unit planned for the Seminole Generating Station—a 2009 POWER Top Plant—in Palatka, Fla. The company cited regulatory and legal uncertainties.
-
News
Postcombustion Capture Test at R.E. Burger Plant is Successful, Powerspan Says
A year-long 1-MW pilot test demonstrating postcombustion carbon capture technology for coal-fired power plants has reportedly captured more than 90% of carbon dioxide from a slipstream of flue gas at FirstEnergy Corp.’s R.E. Burger Plant near Shadyside, Ohio.
-
News
ERCOT: Texas Added More Than 3,100 MW of New Capacity Since May
Texas has added some 3,140 MW of new generation capacity since May, mostly from coal and natural gas–fired power plants, the grid operator for most of the state said in a capacity, demand, and reserve update released last week.
-
News
California PUC Approves SCE’s Renewable Transmission Line Segments
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) last week approved Southern California Edison’s (SCE’s) application to build segments of the Tehachapi Renewable Transmission (TRTP), a major transmission project and the first in that state specifically designed to access multiple renewable generation sources from remote renewable-rich resource areas.
-
News
Slow Progress at UN Copenhagen Conference
World leaders have begun arriving in Copenhagen days before the international conference’s close on Dec. 18 to sign a comprehensive pact to curb climate change, but disagreements—mostly on rich-poor lines—among the 193 attending nations on issues from emissions reductions to technologies such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) could mean there may be nothing to sign.
-
News
Murkowski to Act Against EPA’s Endangerment Finding
Sen. Lisa Murkowski (R-Alaska) on Monday said she would file a disapproval resolution to stop the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from regulating greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) under the Clean Air Act.
-
News
More Bipartisan Senatorial Measures to Curb Climate Change
Last week, Sens. John Kerry (D-Mass.), Lindsey Graham (R-S.C.), and Joe Lieberman (I-Conn.) unveiled a “basic framework for climate action” that combines caps on greenhouse gas (GHG) with offshore oil and gas exploration and an emphasis on nuclear power. At the same time, Sens. Maria Cantwell (D-Wash.) and Susan Collins (R-Maine.) introduced legislation to cap the amount of fossil carbon sold but reduce the role of Wall Street in carbon markets.
-
News
TCEQ Grants Air Permit to NRG’s 744-MW Coal-Fired Limestone Expansion
NRG Energy’s $1.2 billion plan to build a 744-MW pulverized coal unit at its Limestone Electric Generating Station near Jewett, Texas, got a boost last week as the Texas Commission on Environment Quality (TCEQ) approved air permits for the plant.