Gas
-
Gas
ISO-NE: Possible Summer Nat. Gas Constraints, but Supply Will Be Reliable
Natural gas pipeline maintenance this summer could affect natural gas supplies to some power plants in the six-state New England region, but forecasts suggest that summer electricity supplies will adequately meet consumer demand under normal weather conditions, ISO New England (ISO-NE) said on Monday.
-
Gas
FERC’s Moeller to Address Natural Gas Issues at ELECTRIC POWER 2013
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) hearings on issues related to natural gas and its use for electric power generation continue this month. The next hearing is set for May 16, two days after Commissioner Philip D. Moeller addresses the natural gas/electric power generation nexus in keynote remarks delivered to the 15th annual ELECTRIC POWER Conference in Chicago. POWER is a media affiliate of the conference.
-
Coal
Ontario Goes Coal-Free in a Decade
By the end of 2013, one year ahead of its goal, the province of Ontario will be virtually coal-free—a first for a North American jurisdiction. How did the most populous part of Canada go from 25% to 0% coal-fired generation in just a decade, and what does this phaseout mean for the rest of the world?
-
Coal
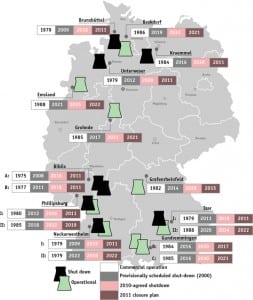
Germany’s Energy Transition Experiment
Germany has chosen to transform its energy system within a few decades—an ambition that has evoked equal admiration and confusion. Has Europe’s largest economy embarked on a rational path to an energy future that will make it the bellwether for global acceptance of renewables, or will the complex array of current challenges encumber its grand transformation?
-
Gas
New York State PSC Approves $2B Transmission Line from Canada
The New York State Public Service Commission (PSC) last week approved the construction and operation of a 1-GW transmission line that could stretch 330 miles from the Canadian border to Astoria, Queens, through Lake Champlain and the Hudson River.
-
Coal
Lawmakers Push for Financing Parity for Renewable Projects
Bipartisan legislation introduced on Wednesday by a bicameral group of lawmakers seeks to give renewable energy project investors access to an existing corporate structure whose tax benefits are now only available to investors in fossil fuel–based energy projects.
-
Gas
NRG Buying Texas Cogen Plant
On Monday, NRG Energy Inc. announced that it has entered into an agreement to acquire the Gregory cogeneration plant in Corpus Christi, Texas. The transaction with a consortium of affiliates of Atlantic Power Corp., John Hancock Life Insurance Co. (U.S.A.), and Rockland Capital LLC is expected to close in the third quarter.
-
Coal
EIA Projects Coal Generation Gains Due to Increasing Gas Prices
The increasing cost of natural gas relative to coal is expected to increase coal’s share of total generation from 37.4% in 2012 to 39.9% in 2013, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) April release of its Short-Term Energy Outlook (STEO). Though that would leave coal’s percentage below its 42.3% share in 2011, it indicates that gas may not be on an inevitable path to overtake a significantly greater share of the generation pie.
-
Coal
DOE Nominee Moniz Gets Bipartisan Support in Senate Hearing
Dr. Ernest Moniz, President Obama’s nominee for the next Secretary of Energy, appears poised for easy confirmation after responding to questions from the Senate Energy & Natural Resources Committee on April 9. His remarks indicated support for, among other things, small modular reactors, carbon capture technology research, and moving forward with the recommendations of the Blue Ribbon Commission on America’s Nuclear Future.
-
Coal
Proposed 2014 Budget: More Funds for the DOE, Less for the EPA
The proposed 2014 federal budget that President Obama submitted to Congress on Wednesday includes increases for the Department of Energy in general and for DOE-sponsored research and development (R&D) in particular. It also shows a slight decrease in funding for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
-
Coal
Shifting Sands
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is made up of seven emirates, yet two dominate the demographic, economic, and geopolitical landscape. Download the report.
-
Gas
Europe Embraces Shale Gas
Several European governments have so far this year bucked a reluctance to extract shale gas via hydraulic fracking even as the practice continues to be strongly opposed in countries like France and Bulgaria.
-
Gas
The Second Anniversary of Fukushima: Daiichi, Japan, and the World’s Nuclear Sector
On the second anniversary of the 9.0-magnitude Great Tohuku Earthquake that killed more than 25,000 people and set off the worst nuclear disaster in 25 years, Tokyo Electric Power Co.’s (TEPCO’s) devastated Fukushima Daiichi Units 1 through 4 were in cold shutdown and set to be abolished. All Japan’s nuclear reactors remain shuttered for safety inspections, and the rattled nation has yet to finalize a future energy roadmap. Meanwhile, as panelists at the IHS CERAWeek noted, the world’s global nuclear sector seems to have made a slow but determined recovery.
-
Coal
Four Major EPA Air and Water Rules Forthcoming Through May, Agency Schedule Shows
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates final regulations curbing greenhouse gas (GHG), mercury, and air toxics emissions from new sources could appear in the Federal Register over the next six weeks. Also forthcoming are final cooling water intake rules and proposed effluent guidelines. The coal ash rule, which has no target date for a final rule, may not be issued this year, the agency said.
-
Renewables
The Spotlight on a Mexican Success Story
Energy demand in Mexico, according to the Secretary of Energy (SENER), will increase by approximately 4% each year for the next ten years, and with it the potential for private sector growth in the industry. Download the report.
-
Commentary
Biogas: An Alternative Energy Source
Most professionals in the energy industry know about biomass; fewer of us are conversant with biogas. This commentary explains the basics of biogas, with a focus on its current use and future potential as a source of electrical power.
-
Gas
Japan Banks on LNG
Japan’s scramble to replace generation lost from nuclear power plants that were shuttered after the March 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident has forced it to rely on pricey imports of fossil fuels—and soaring energy costs are hammering the world’s third-largest economy.
-
Gas
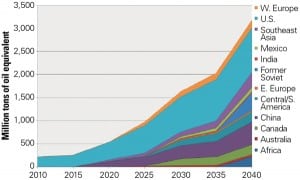
Should the U.S. Export Natural Gas?
Controversy concerning natural gas exports flared the day the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) released its estimate that U.S. natural gas exports could begin in 2021.
-
Gas
THE BIG PICTURE: Stretching the Pipeline
Here are some of the longest pipelines recently built as well as noteworthy ones in the pipeline.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Align Generation Reliability and Fuel Supply Firmness
More and more electricity is generated by natural gas. This trend is likely to persist. Hydraulic fracturing technology is increasing domestic supplies and enabling natural gas prices to remain at historic lows.
-
Gas
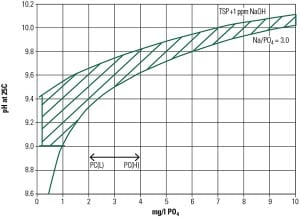
Selecting a Combined Cycle Water Chemistry Program
The lifeblood of the combined cycle plant is its water chemistry program. This is particularly true for plants designed for high pressures and temperatures as well as fast starts and cycling. Even though such plants are increasingly common, no universal chemistry program can be used for all of them.
-
O&M
Steam Turbine Blade Reverse Engineering, Upgrade, and Structural Design
Steam turbine blade cracking often suggests the need for an upgraded blade design. Follow the process of reversing engineering a failed blade to produce a more reliable and efficient design.
-
Coal
EPA Directs 36 States to Revise SIPs for Emissions during Plant Startup, Shutdown, Malfunction
A rule proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) directs 36 states to revise their Clean Air Act State Implementation Plans (SIPs) to eliminate exemptions for excess emissions of air pollutants at power plants during startup, shutdown, or when the plant malfunctions.
-
Coal
Senators Introduce “Carbon Fee” Bill, House Dems Call for Blue Ribbon Climate Panel
Boosted by President Obama’s inaugural address commitment to mitigate climate change, congressional Democrats have initiated several more climate measures. A legislative packet that seeks to mitigate climate change by enacting a carbon "fee" of $20 per ton of emitted carbon or methane equivalent was introduced last week by Sens. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) and Barbara Boxer (D-Calif.). In the House, as several Democratic amendments for climate change hearings were voted down, more than 40 lawmakers urged President Obama to create a panel that would help communities deal with climate change events.
-
Coal
Obama Calls for Market-Based Climate Change Solution in SOTU
President Obama outlined a number of key energy-related measures in his State of the Union speech on Tuesday night, urging Congress to pursue legislation to mitigate climate change and calling for an expansion of clean energy and reduced red-tape for natural gas and oil permits.
-
Coal
Low Gas Prices Prompt Duke to Retire Coal Units Two Years Early
Citing low natural gas prices, Duke Energy announced on Feb. 1 that it would shutter its 1920s-built Buck and Riverbend stations two years before the coal-fired plants were slated for retirement. The company had chosen to retire the plants just before April 2015, which is the compliance deadline for recently enacted federal environmental rules.
-
Coal
Minn. Power Considers Fuel Switch, Coal Unit Retirement to Comply with Fed, State Mercury Rules
A newly announced resource strategy could require Duluth, Minn.–based Minnesota Power to convert its 110-MW Laskin Energy Center in Hoyt Lakes, Minn., to a natural gas peaking facility in 2015, install environmental upgrades at its 558-MW Clay Boswell Energy Center Unit 4 in Itasca County, and retire one of three coal-fired units at its 225-MW Taconite Harbor facility in Schroeder.
-
O&M
Layup Practices for Fossil Plants
Improper layup practices are a major contributor to boiler tube failures and to steam turbine pitting and cracking in U.S. fossil plants. EPRI’s research into identifying damage mechanisms, utility best practices, and innovative new methods to protect plant equipment during outages will aid plant operators in achieving a successful layup.
-
Commentary
The Shale Gas Revolution Continues
The electricity industry is being transformed by the so-called “shale gas revolution” in the United States. Production of natural gas from shale rock using hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”) has boosted supply and reduced prices, making gas-fired power competitive with coal-fired power on price. Historically, coal-fired electricity generation has dwarfed generation from gas-fired plants in the U.S. […]
-
Gas
EIA: Natural Gas Generators in New England See Supply Constraints, Highest Prices
Average spot natural gas prices in New England have surged to $3 per million British thermal units (MMBtu) higher than natural gas prices at the Henry Hub since November, driven up by supply constraints from natural gas pipelines that haven’t kept up with demand, high international prices, and declining production in eastern Canada, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) says in a report released last week.