Coal
-
Coal
Explosion Devastates Major Cypriot Power Plant
A brush fire that spread and detonated explosives stored at the Evangelos Florakis naval base in Mari on the southern coast of Cyprus on July 11 killed 13 people, injured 62 others, and severely damaged the Vassilikos Power Station—an oil- and gas-fired plant that supplied almost 60% of the island nation’s power. Cyprus, which was once considered an “economic miracle,” has been battling crippling power shortages that have beleaguered its financial and tourism sectors since the blast and left it on the verge of economic collapse.
-
Coal
POWER Digest (September 2011)
Australia Pursues Carbon Tax. Australia’s Prime Minister Julia Gillard on July 10 laid out an ambitious plan to cut national greenhouse gas emissions by 5% of 2000 levels by 2020 by imposing a A$23 (US$23.4) per metric ton carbon tax, starting next year. If parliament approves the plan before year-end, the carbon tax will increase […]
-
O&M
Advanced Coatings Protect Plant FGD Systems
Now that many flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems are reaching middle age, corrosion repairs of structural and process vessels are becoming more common. Corrosion is caused by condensates of acids formed during the FGD process, which accelerate pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in scrubbers where high sulfate solutions are present. Scrubbers lined with 2205 duplex stainless steel are among the most vulnerable to pit or crevice corrosion, from both chlorides and fluorides.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Critics Get Crossways with New Cross-State Air Rule
From the East Coast to the Lone Star State, a number of elected officials and power industry representatives are bashing the new aggressive regulation aimed at controlling specific power plant emissions. Complying with a federal court mandate, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) on July 6. The new […]
-
Coal
Best Practices for Natural Gas Line Cleaning
As barriers to new coal-fired generation expand and enthusiasm for nuclear plants wanes, the commissioning of natural gas–fired plants promises to increase. However, gas plants pose hazards, too. An explosion last year that was caused by unsafe use of natural gas to blow residue from a gas pipeline during commissioning of a gas-fired power plant has focused regulator and industry attention on finding safer alternatives for this task. Fluor shares its gas pipeline cleaning best practices.
-
O&M
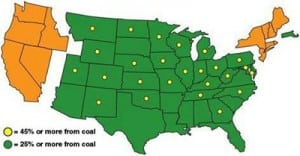
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Coal
Dominion to Convert Three Coal Plants to Biomass
Dominion Virginia Power has asked the Virginia Corporation Commission for approval to convert three aging and relatively small coal-fired plants to biomass, saying the move would provide substantial long-term savings to customers while cutting air emissions and creating hundreds of forest-related and trucking jobs in the state.
-
O&M
Natural Gas Conversions of Existing Coal-Fired Boilers
Why should utilities consider converting existing coal-fired plants to burn gas? We explore the rationale for fuel switching, some of the options available for the conversion of coal-fired units, technical considerations related to conversion, and some of the financial considerations that will impact the final decision.
-
Coal
Largest CCS Project in Operation
Companies continue to increase the size of carbon capture and sequestration test projects. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has launched operation of what it calls the world’s largest demonstration of carbon capture on a pulverized coal plant.
-
Coal
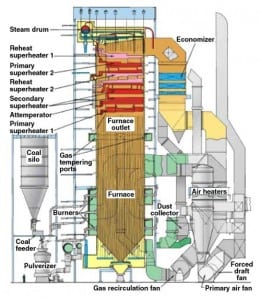
Plant of the Year: KCP&L’s Iatan 2 Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
Kansas City Power & Light (KCP&L) began engaging stakeholders in 2003 to develop consensus on a regional energy plan designed to balance customers’ desire for low electricity costs with system reliability needs and environmental requirements. The culmination of that plan was the completion of Iatan 2, which entered service in August 2010. For executing an innovative energy plan that reduced overall fleet emissions, ensuring the region’s future electricity supply, and completing an approximately $2 billion project in time for the summer 2010 peak load by using innovative contracting and project controls, KCP&L’s Iatan 2 is awarded POWER’s 2011 Plant of the Year Award.
-
O&M
Make Your Plant Ready for Cycling Operations
Cycling your steam power plant is inevitable, so now is the time to learn how to minimize equipment damage and assess the true costs of cycling. Whether cycling is required by the grid operator because of renewable integration or other factors, you must be proactive about updating operating processes and upgrade equipment so the transition to cycling operation goes smoothly.
-
O&M
Mitigating the Effects of Flexible Operation on Coal-Fired Power Plants
As coal-fired power plants increasingly operate in cycling modes, many plants are confronting the potential for higher levels of component damage and degraded performance of environmental control equipment. Generators and EPRI are working together to find ways to mitigate the effects of cycling operation and to manage the transition of formerly baseload plants to flexible operation.
-
Coal
Innovations in Air Heater Design Produce Performance and Reliability Improvements
The regenerative air heater on a typical steam generator usually accounts for over 10% of a coal-fired plant’s thermal efficiency. A poorly performing air heater will cause an increase in the gas outlet temperature, often reducing the electrostatic precipitator collection efficiency and baghouse reliability. Recent design innovations enable restoration of this lost performance.
-
O&M
Pulverizers 101: Part I
Pulverizers prepare raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of three parts, we’ll examine the essentials of pulverizer capacity, what should be done after a coal pulverizer fire or other incident, and how to tune up pulverizer performance. In future articles we’ll discuss measuring pulverizer performance and performance optimization.
-
Coal
Is AEP Exaggerating Impact of Air Rules?
American Electric Power recently announced plans to retire over 6,000 MW of coal-fired generation in response to two looming Environmental Protection Agency air quality regulations. Is AEP exaggerating the impact of these regulations? Some members of Congress believe that to be the case. AEP disagrees.
-
Coal
House GOP Moves to Block EPA from Regulating Coal Ash as Toxic Waste
Continuing the House Republicans’ aggressive attack on Obama administration environmental proposals, a House subcommittee approved legislation in June to prevent the Environmental Protection Agency from regulating coal ash as a hazardous waste—one of two options the EPA is considering for tightening coal ash management regulations in response to a disastrous leak from a Tennessee Valley Authority ash impoundment in 2008.
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.
-
O&M
Solid Fuels: Moving Material and Managing Emissions
In today’s solid-fueled power plant, managing emissions and moving materials more defines the task than the traditional work of making megawatts. That’s the message that emerged from the coal and solid fuels track at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER.
-
Coal
Using Fossil-Fueled Generation to Accelerate the Deployment of Renewables
It may seem counterintuitive, but the strategic coupling of simple- and combined- cycle technologies with renewable generation could establish the conditions necessary for adding more renewable megawatts to transmission grids around the world.
-
Coal
Underground Coal Gasification: Another Clean Coal Option
Underground coal gasification (UCG) is the gasification of coal in-situ, which involves drilling boreholes into the coal and injecting water/air or water/oxygen mixtures. It combines an extraction process and a conversion process into one step, producing a high-quality, affordable synthetic gas, which can be used for power generation. Still in the early stage of commercialization, UCG is poised to become a future major contributor to the energy mix in countries around the world.
-
Coal
The Better Environmental Option: Dry Ash Conversion Technology
After the 2008 incident involving the failure of a large surface impoundment containing wet coal ash, the EPA began investigating all coal-fired power plants employing this wet coal ash management method. Now a new dry ash management technology offers coal-fired power plants an environmentally suitable alternative for handling coal ash that also increases energy efficiency.
-
Coal
Biomass Boiler Market Remains Unpredictable
Utilities struggling to meet renewable portfolio standards requirements have studied the conversion of existing coal-fired boilers to burn biomass. The results of those studies have been mixed, although test burns continue; the results of one such test are included. Overall, the market is tending toward smaller biomass projects, and the low price of natural gas is perhaps the biggest reason utility-scale projects are now few and far between.
-
Coal
Re-Industrializing America with Clean Coal Technologies
Balancing the rising energy needs of a globally expanding population (most of which lives in poverty) against the need to reduce increases in atmospheric emissions is a monumental problem. What role can clean coal technologies play?
-
O&M
Applying CFD to Optimize Furnaces Cofiring Biomass, and the Impact of Cofiring on SCR
The international policy framework regulating the emissions of greenhouse gases from industrial and utility boilers is in flux. Meanwhile, most boiler owners are evaluating potential strategies for when, not if, more stringent emissions reduction regulations are put in place. One of the most attractive compliance options is the cofiring of biomass in existing coal-fired boilers.
-
Coal
ERCOT Predicts No Coal Retirements from EPA Rules
In surprising findings, given the state’s often-contentious relationship with the Environmental Protection Agency, a study released May 11 by the Texas grid operator concludes that a suite of looming EPA rules to reduce conventional and hazardous air pollution from power plants and to tighten power plant cooling water regulations likely would not force the retirement of any Texas coal plants.
-
Coal
Southern CEO Sees Federal "War on Coal"; Questions Dash to Gas
In a wide-ranging speech on U.S. electricity policy, Southern Co. Chairman, President, and Chief Executive Officer Thomas Fanning said that coal is "under attack" by the federal government, that natural gas may not be the panacea seen by some utilities facing environmental constraints on their coal plants, and that federal proposals to sharply reduce utility hazardous air pollution have unreasonable compliance deadlines that should be extended.
-
Coal
Proposed Clean Energy Agency Has Cost Issue
Even as Senate energy leaders gear up to re-introduce widely supported legislation to create the Clean Energy Deployment Administration, they have acknowledged that the bill faces a heightened problem this term: the need to find nearly $10 billion in offsets to pay for the new green energy financing authority at a time of overwhelming concern about the federal debt.
-
Coal
Spain: A Renewable Kingdom
Spain has served as both exemplar and scapegoat when it comes to renewable energy policy. Though power policy must necessarily accommodate specific national resources and goals, Spain’s experience as an early and eager adopter of renewable energy technologies and subsidies is a cautionary tale of how the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
-
Coal
China’s Five-Year Plan Is Heavy on Non-Fossil Generation
The People’s Republic of China’s Congress approved a much-anticipated draft of the country’s 12th Five-Year Plan (2011–2015) on March 14. Along with key objectives that included boosting its gross domestic product (GDP) by 7% annually on average, the country for the first time in a five-year plan established targets to tackle climate change. It plans to reduce carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by 17% from 2010 levels by 2015 and to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 16% from 2010 levels by 2015.
-
Coal
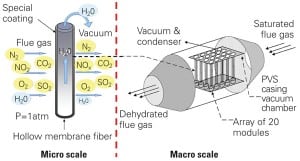
Large-Scale Tests Begin to Convert Flue Gas to Usable Water
Subsidized by the Dutch government, a number of Dutch utilities, the European Membrane Institute at the University of Twente, and Dutch consulting firm KEMA have, for over a decade, been testing membrane technology that promises to directly convert water vapor from power and other industrial plants’ flue gases into drinking water. The technology could provide a new source of large volumes of potable water.