In This Issue
-
Solar
Epic Fail
Over the past 18 months, four solar energy equipment companies have closed their doors. Each one blamed poor market conditions for its economic woes, even though each had fundamental weaknesses that went unaddressed. It now appears that the Department of Energy (DOE) did insufficient due diligence before backstopping one of those four companies, Solyndra, with a $535 million loan guarantee.
-
Coal
Top Plant: St. Johns River Power Park, Jacksonville, Florida
A recent NOx reduction project added selective catalytic reduction equipment to each of the two 640-MW, mixed coal–fired units at the St. Johns River Power Park. The selection of precisely the right catalyst required extensive long-term testing with “mini” reactors. Once the right catalyst formula was identified, the actual retrofit project was completed in a mere 23 months, an aggressive project schedule that required overcoming many design and construction challenges.
-
Nuclear
Germany’s Nuclear Phase-Out Has Widespread Implications
The German government in July finalized a package of bills that will phase out nuclear’s 23% contribution to the country’s power supply by 2022 and increase renewable generation from the current 17% to 35%. In August, the Federal Network Agency ( Bundesnetzagentur) said it wouldn’t rely on power from seven of the nation’s oldest reactors […]
-
Coal
CWA 316(b) Update: Fish Guidance and Protection
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed new Clean Water Act section 316(b) regulations for once-through cooling water intake structures. Comments on the proposed rules closed in August, and a final rule is expected mid-2012. The EPA estimates that at least half of the power plants using once-through cooling will be required to implement a best technology available solution in coming years. That typically means barriers and screens, but you may want to consider other options.
-
Nuclear
Ling Ao 4 Starts Up While Sanmen Gets First AP1000 Reactor Vessel
In China this August, as Ling Ao Unit 4—the second unit of the Ling Ao Phase II nuclear plant—started commercial operation, Westinghouse and its consortium partners marked the milestone of receiving the reactor vessel for the Sanmen nuclear power plant—the world’s first AP1000—in China’s Zhejiang province. The start-up of Ling Ao Unit 4 in Guangdong […]
-
Coal
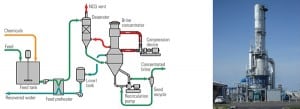
Fundamentals of Zero Liquid Discharge System Design
Power plants often produce wastewaters that contain salts, such as those from wet gas scrubbing, coal pile run-off, and leachate from gypsum stacks. Evaporation of those liquid wastes in a modern zero liquid discharge system produces clean water that is recycled into the plant plus a solid product suitable for landfill disposal. Here are the options to consider.
-
Gas
New Peaking Plant to Balance California’s Renewables
As utilities in California are scrambling to meet the state’s 33% renewable mandate by 2020, a 49.6-MW peaking plant in Modesto, Calif., built by Finnish firm Wärtsilä for the Modesto Irrigation District, has been commissioned to provide flexible, fast-start peaking generation to balance the state’s increase in intermittent renewable generation (Figure 4). 4. Flexible peaking. […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
New EPA Rule Calls for Flexibility
Quin Shea, vice president, environment for the Edison Electric Institute, comments on the Utility MACT rule that is expected to be finalized in November.
-
Gas
Kuwait Starts First Turbines of 2,000-MW Gas Plant
Kuwait put online the first 1,400 MW of its massive 2,000-MW combined cycle gas turbine Sabiya facility in June to mitigate looming power shortages it faces each summer. The plant—Kuwait’s largest power plant and one of the largest in the Gulf region—is now operating six GE 9FA gas turbines; the remaining 600 MW are expected […]
-
Coal
An SCR Can Provide Mercury Removal Co-Benefits
Complying with various state (and expected federal) requirements governing mercury removal from the stack gas of coal-fired power plants has usually been achieved by adding an expensive activated carbon injection system. Now there is another alternative: a catalyst that features higher mercury oxidization activity than conventional catalysts while maintaining the same SO2 to SO3 conversion activity—and all at a lower operating cost. Full-scale installations are under way at several Southern Company plants that burn a variety of coals.
-
Hydro
Hydro Reservoir GHG Emissions Lower Than Estimated
A new analysis of 85 hydroelectric reservoirs distributed around the world suggests that these systems emit about 48 million metric tons of carbon annually. That figure is much lower than earlier estimates of 64 million metric tons that were based on studies relying on more limited data and which cautioned that reservoirs of all types […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Managing Equipment Data Through Asset Virtualization
Asset “virtualization” extends and combines the technologies of 3-D visualization and virtual reality to a new, practical level for the life-cycle management of power industry equipment. All pertinent data for a component, subsystem, or plant is associated with, stored, and accessed through as-built 3-D digital models of the actual plant that are constructed using laser scanning techniques.
-
News
POWER Digest
Siemens Gets $1 Billion Order to Build Gas Power Plants in Thailand. Siemens on Aug. 17 said it received two orders worth $1 billion from Thailand for the engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) of combined cycle power plants. The firm will build Chana Block 2 in the province of Songkhla and Wang Noi Block 4 […]
-
Coal
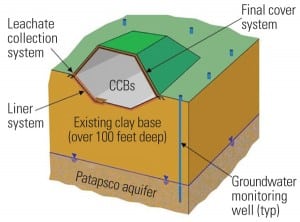
Constructing Maryland’s First Permitted Landfill for Coal Combustion By-products
Constellation Power Source Generation Inc., which owns and operates three coal-fired power plants in Maryland, has contracted with Charah Inc., an ash management company, to build a landfill to strict environmental requirements for the disposal of its plants’ coal combustion by-products that can’t be recycled for other uses.
-
Solar
THE BIG PICTURE: A Solar Switch
The plummeting cost of photovoltaic (PV) panels—resulting from lower costs for high-grade silicon and advancements in thin-film technology, solar storage, and electronic control technologies—has a slew of firms rethinking concentrating solar power (CSP) projects. Although there is a CSP project pipeline (including both CSP and concentrating PV) of more than 9 GW in the U.S., […]
-
News
NERC CIP Information and Security E-Learning Series
Global Training Solutions Inc. released an interactive, self-paced, and fully customizable electronic training program to achieve compliance with the North American Electric Reliability Corp.’s (NERC’s) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) security standards. The company designed its NERC CIP Information Security E-Learning Series on open-web standards, sharable content object reference model (SCORM) compliance, and advanced technical concepts. […]
-
O&M
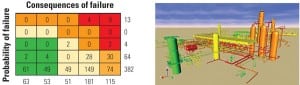
JEA Increases Power Output Through CFB Improvements
JEA’s Northside Generating Station in Jacksonville, Fla., Units 1 and 2 were built in 1966 and 1972, respectively, although the Unit 2 boiler had not operated since 1983. Both were heavy oil– and natural gas–fired steam units rated at about 300 MW. The utility “repowered” those two units by removing the old boilers and adding new circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers (Figure 1) that entered service in 2002. At that time, they were the world’s two largest CFBs, and the plant won POWER’ s Plant of the Year Award.
-
News
High-Horsepower, High-Pressure Water Jet Pumps
The new NLB 605 series of water jet pump units from NLB Corp. gives users a powerful combination of ultra-high pressure and high horsepower in a rugged unit they can convert to a variety of operating pressures. The range of the NLB 605 Series has been expanded to include eight operating pressures from 4,000 psi […]
-
O&M
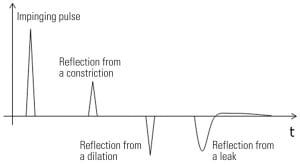
Applying Acoustic Pulse Reflectometry in a Geothermal Plant
Acoustic pulse reflectometry (APR) is a tube inspection method that has been gradually gaining acceptance as a tool for heat exchanger inspection. Different types of heat exchangers operating in different operating environments have different failure mechanisms, making some of them more suited than others for inspection by APR. Finned tube heat exchangers are a typical example of heat exchangers particularly conducive to APR inspection.
-
News
High-Flow Gas Regulators for Pipeline Monitoring
The BelGAS division of Marsh Bellofram Corp. introduced Type P627, a high-performance, spring-loaded, direct-operating high-flow gas regulator that is designed to control both low- and high-output pressure in oil and gas applications. Designed for maximum durability, Marsh Bellofram BelGAS Type P627 regulators are compact and offered in multi-position body and spring case configurations. Units offer […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Too Much of a Good Thing Creates Legal Havoc
As last winter’s abundant snowfall in the Pacific Northwest melted, rivers swelled and hydroelectric operators enjoyed substantial increases in generation. That bountiful clean and cheap power generation was a blessing, but it also triggered a host of legal issues.
-
News
Preventing Dust Accumulation on Beams
BeamCap’s signature product, the BeamCap, prevents dust accumulation on I-beams, structural steel members, pipes, cable trays, and other difficult-to-clean areas. BeamCap pieces completely enclose the structures, eliminating horizontal surfaces where dust consistently builds up. This eliminates the need for cleaning in hard-to-reach places and greatly reduces the potential for fires and secondary explosions. The aluminum […]
-
Coal
Top Plant: Coffeen Energy Center, Montgomery County, Illinois
Situated in predominantly rural central Illinois, the 1,000-MW Coffeen Energy Center has installed a number of controls in recent years and achieved significant environmental performance. For example, in 2010 a new scrubber facility was added that reduces SO2 from combustion gases coming from the plant’s two coal-fired boilers. The plant personnel’s continuing commitment to protecting the environment helps to promote a strong relationship between the plant and the local community.
-
News
Robotic Underwater Debris Remover
Aqua-Vu, a provider of portable underwater viewing systems, introduced the Claw 360, a device designed for the detection and removal of objects in an underwater environment. The Claw 360 incorporates a Sharp 520 color camera that can rotate 360 degrees to scan the environment. Lighting is provided by high-intensity LEDs that rotate with the camera. […]
-
Coal
Top Plant: J.K. Spruce 2, Calaveras Power Station, San Antonio, Texas
CPS Energy, the largest municipally owned utility in the U.S. providing both natural gas and electric service, implemented an energy plan in 2003 that required energy conservation measures, use of available renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, and additional coal-fired generation. The $1 billion 750-MW Spruce 2 fits into that plan by being one of the cleanest coal-fired plants in the country.
-
News
Nut, Bolt, and Flange Face Corrosion Protection
Advance Products & Systems’ new Kleerband Flange Protectors and Radolid Protection caps protect bolts, nuts, and flange faces on raised-face or full-face flanges in conditions where extreme corrosion occurs, such as at gas plants, pump stations, and above- and below- ground installations. Kleerband is a patented transparent polymer band with grease injection fittings and a […]
-
Coal
Top Plant: John Twitty Energy Center Unit 2, Springfield, Missouri
Utilities of Springfield elected to add a 300-MW coal-fired plant to its fleet to meet rising demand for electricity. It was the first coal plant constructed by the utility since 1976. An extremely competitive construction market required the utility to adopt new contracting practices to meet a tight project schedule, an approach that proved very successful. The $555 million plant commissioned in January 2011 is expected to cover system growth at least through 2024.
-
Commentary
Shaping America’s Energy Policy
America’s energy and environmental policies have been dysfunctional for decades. Obsessively moving toward “green” has made America weaker and has damaged our economy. During POWER’ s first 100 years (1882–1982), the magazine chronicled the U.S. growing into the strongest industrialized economy in the world. America designed and built products for the world using raw materials and energy from within our own borders. Now we are in a recession and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) “War on Coal” continues. Does anyone get the connection? Ever-worsening regulations are killing jobs by the thousands.
-
Coal
Top Plant: Masinloc Power Plant, Zambales Province, Philippines
In April 2008, AES Philippines purchased the Masinloc coal-fired power plant in Zambales Province in the Luzon region. Originally constructed in 1998 as a two-unit, 600-MW plant, the facility uses coal from a variety of sources in the Pacific Rim. After AES finished overhauling much of its equipment, the expanded 660-MW (gross) plant’s availability increased from 48% to 74%, which enabled net electricity production to jump by 129% by 2010.
-
Coal
U.S. Coal-Fired Power Development: Full Employment for the Lawyers
The EPA began rolling out its long-anticipated power plant regulations this year, causing some utilities to shutter some older coal-fired plants. Other utilities paused, perhaps hoping that a neighbor’s closure decisions would allow continued operation of some of their own older, smaller, less-efficient plants. As the nation sweated through a scorching summer, air conditioners hummed thanks to coal-fired power plants built 50 or more years ago. How many of them will be retired, and over what timeframe?
-
Coal
Top Plant: Plum Point Energy Station Mississippi County, Arkansas
The new 665-MW Plum Point Energy Station is energizing the Arkansas Delta, an area that is ready to supplement its farming heritage by promoting new jobs that offer residents a higher standard of living. But first, the plant’s construction team had to overcome a number of significant challenges related to building a facility in the New Madrid fault zone.