In This Issue
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Power Generation: Automation Today and Tomorrow
Handheld smart devices providing custom applications and Internet access at the touch of a virtual button are common today. Hidden beneath their touchscreens is a global network of digital technologies that respond to each command. Will these familiar commercial technologies and apps make their way to industrial digital control systems?
-
Nuclear
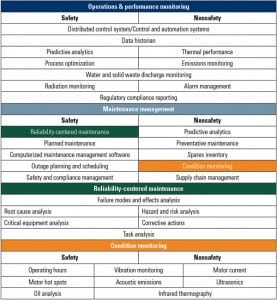
Comprehensive Asset Management for Nuclear Plant
Asset management means different things to different people. But it boils down to converting raw data and observations about equipment and components into information and knowledge that is then used, propagated, and shared by workers and digital components to manage performance. Nuclear plants have special asset management needs, given the level of their safety, reliability, and regulatory requirements.
-
Coal
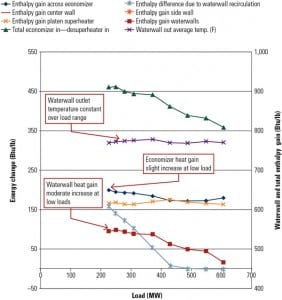
Enhanced Load Dispatch Rate and Furnace Protection Through Model Predictive Control
The enhanced plant performance achieved at the 1,477-MW Morgantown Generating Station shows the value of model predictive control in conjunction with intelligent distributed control algorithms. This project update looks at how the project team moved from ramp rate improvements to reducing tube metal temperatures to improved component life.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
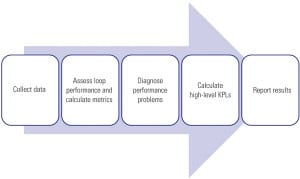
Monitoring Control Loop Performance
Control loop performance-monitoring software can help to improve loop performance at electric power plants by automatically collecting data, assessing several aspects of loop performance, and providing the results in reports and user interfaces.
-
News
Battle of the Bulb
When then-President George W. Bush signed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007, he noted that, “New technologies will help usher in a better quality of life for our citizens.” One provision of the act required an increase in the efficiency of newly manufactured lightbulbs, starting with 100-watt incandescent bulbs in 2012.
-
Nuclear
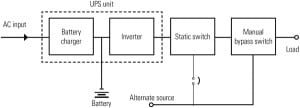
Specifying Nuclear DCS Power Supplies
The consideration of power supplies has become critical to the success of converting analog instrumentation and control systems to digital control systems (DCSs). Careful planning is particularly necessary for nuclear power plants, where instrumentation systems are required for safely shutting down a reactor, mitigating the consequences of an accident, and performing post-accident analysis.
-
Nuclear
The Big Picture: DOE Loan Guarantees
Of the $35.9 billion in loan guarantees awarded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) since 2009, roughly $26.5 billion have financed nuclear and renewable power projects across the nation through the Section 1703 and 1705 loan guarantee programs.
-
Coal
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Wind
European Firms Complete Wind-to-Hydrogen Power Plant
A consortium of European developers, with funding from the German federal government, have completed a power plant in Prenzlau, near Berlin, Germany, that uses excess wind energy to convert water into oxygen and hydrogen in a process called hydrolysis, and then uses hydrogen and biogas to generate power and heat.
-
Coal
Colstrip’s Cure for Mercury
In January 2012 a new mercury control system at the Colstrip power plant in Montana reached its first major milestone: two years of operation with mercury emissions below the state regulatory limit. The plant uses Alstom’s unique Mer-Cure technology to capture up to 90% of the mercury leaving the stack.
-
News
Cost-Cutting Nanoparticle Electrode for Batteries
Using nanoparticles of a copper compound to develop an inexpensive and durable high-powered battery electrode could be the breakthrough solution to the problem of sharp drop-offs in the output of wind and solar systems, scientists at Stanford University say.
-
O&M
Condenser Backpressure High? Check Vacuum System Sizing
In a power plant, the primary use of vacuum systems is to remove air and other noncondensable gases from the shell side of the condenser in order to maintain design heat transfer and thus design vacuum. If holding condenser vacuum is a persistent problem, one often-overlooked cause is an inadequately sized vacuum system.
-
Wind
Novel Floating Wind Turbine Deployed in the Atlantic
A semi-submersible structure supporting a 2-MW wind turbine was towed nearly 350 kilometers (217.5 miles) to water depths of about 35 meters (114.8 feet) into open Atlantic waters and deployed off the coast of Aguçadoura, Portugal, last November.
-
O&M
Avoiding Flow-Induced Sympathetic Vibration in Control Valves
Compressible fluid flow through control valves will inevitably cause some form of flow-induced vibration in the fluid system. Identifying the type and cause of the vibration requires detective work. Determining the design changes required in the valve and fluid system to prevent the vibration from occurring requires advanced analytical techniques.
-
Coal
One Step Forward, Two Steps Back for CCS Projects
Last December, as Spain’s national carbon capture and storage (CCS) research laboratory Fundación Ciudad de la Energía (CIUDEN) began a much-watched testing phase of oxycombustion in its 30-MWth circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boiler in Cubillos del Sil, Vattenfall scrapped the €1.5 billion ($2 billion) Jänschwalde CCS demonstration project that it had planned to build and begin operating by 2015 in the German federal state of Brandenburg.
-
News
Handheld Fluorometer
Turner Designs has introduced the Opti-Check Handheld Fluorometer for performing system verifications for industrial water process control applications. The Opti-Check is a small, lightweight, highly durable handheld fluorometer that is ideal for quick measurements in the field. Configurable for either PTSA or Fluorescein as well as both dyes, the Opti-Check enables monitoring of either cooling […]
-
Coal
Indonesia Inaugurates Three Coal Plants
Indonesian state-owned utility Perusahaan Listrik Negara (PLN) formally launched operations at three new coal-fired power plants on Dec. 28.
-
News
Handheld Vibration Meter
Columbia Research Laboratories’s Model VM-300 is a general purpose vibration measuring instrument designed for periodic routine checks of industrial equipment where portability and ease of use are required. Acceleration, velocity, and displacement measurement modes are provided, along with a number of value-enhancing features. Dual power allows the VM-300 to be powered from its internal battery […]
-
Business
POWER Digest (February 2012)
ANDRITZ to Rebuild Oldest Egyptian Nile Dam. Austrian firm ANDRITZ HYDRO on Dec. 22 won a $138.4 million contract from the Egyptian Ministries of Energy and Water Resources for the supply and installation of four bulb turbines, generators, and the electrical and hydro-mechanical equipment to rebuild the Assiut barrage—the oldest dam in the Egyptian section […]
-
News
Ductile and Flexible Seal Rings
Milan-based ATO S.r.l. has introduced a series of flexible seal rings made of KetaSpire polyetheretherketone (PEEK) resin, which is made by Solvay Specialty Polymers. KetaSpire KT-820 PEEK provides greater flexibility and elasticity than competitive PEEK grades, the company says. The parts can be folded or twisted in half and then twisted again into three or […]
-
Gas
Industry Shift in Gas Line Cleaning Practice
The National Fire Protection Association has issued a new standard for gas line cleaning in response to the urgent recommendations prepared by the U.S. Chemical Safety Board.
-
News
Batch Chemical Reactor Simulation Software
French company ProSim, which provides process simulation and optimization software to the process industries, released a new version of BatchReactor, its software for batch chemical reactors simulation. The new software combines detailed equipment modeling, reaction engineering, and advanced numerical methods to create a state-of-the art simulation environment for chemists and chemical engineers, providing a complete […]
-
O&M
Virtual Co-Driver to Improve Truck Safety
POWER recently talked with Erika Jakobsson, a project manager at Volvo Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden, who is responsible for developing intelligent trucks in response to European Union (EU) directives.
-
News
High-Performance Air Pressure Regulator Series
The Precision Controls Division of Marsh Bellofram Corp. launched the Type 41 high-performance air pressure regulator series, which is designed to support a variety of demanding industrial and original equipment manufacturer flow-monitoring requirements. Available in two different packages with identical performance characteristics, both with ¼-inch NPT BSPT port size, the Type 41 incorporates a patented […]
-
Business
Data Center’s Standby Power System Is “Money in the Bank”
Synovus relies on emergency standby generator sets to prevent any loss of services or data in the event of a utility outage.
-
News
Capacitive Accelerometer Modules
Silicon Designs, a designer and manufacturer of rugged industrial-grade microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) capacitive accelerometer chips and modules, has introduced a ±5 g model to its 2210 accelerometer series. The low-noise, single-axis model 2210-005 accelerometer module incorporates high-quality MEMS capacitive sensing elements. Sensing elements are packaged within a compact, lightweight, anodized epoxy-sealed aluminum housing, occupying a […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Debate Heats Up over New Mercury and Air Toxics Rule
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) new Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) rule for power plants has critics’ tempers flaring. Not surprisingly, a number of electric power representatives, industry groups, and elected officials oppose the rule, which was released on Dec. 21, 2011.
-
Commentary
Clean Air, Jobs, and Power Reliability
The electric power generation system is the backbone of our economy. Recently, however, sudden outages or rolling blackouts have increased.