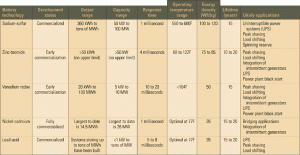
Wind
-
Wind
Atlantic City bets on renewables
New Jersey’s gaming mecca is hosting one of the largest hybrid (solar-wind) power plants in the world (Figure 3). The Jersey-Atlantic Wind Farm, with 7.5 MW of wind capacity and 0.5 MW from photovoltaic (PV) cells, is expected to generate 20,000 MWh annually. That should be enough to power an adjacent wastewater treatment plant operated […]
-
Hydro
Big batteries blooming
Several advanced battery technologies tailored for utility applications have doffed their white coats and donned hard hats. These new bulk energy storage devices, which can almost instantly shave peaks and shift loads, are the answer to the dreams of T&D system designers and operators. Finally, years of R&D in electrochemistry are beginning to pay dividends in the field.
-
Hydro
Roadmap for the all-electric warship
One of the key projects at the U.S. Navy’s Office of Naval Research is developing an integrated ship power system capable of supplying power both to propulsion systems and to advanced electric weapons, launchers, and high-power sensors. It would be the ultimate naval power T&D system. The "all-electric warship," which some predict will have as much of an impact on navies as the nuclear submarine, is still a decade or two away. But the first generation of electric systems is already being installed on U.S. warships currently under construction.
-
Hydro
A new player in backup power
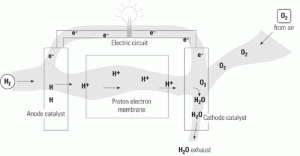
For thousands of U.S. businesses, a lesson learned the hard way over the past few years is the need for an absolutely reliable electricity source. Challenging the standard backup power options, proton exchange membrane fuel cells are making a play for this duty.
-
Hydro
Renewable energy’s growing share
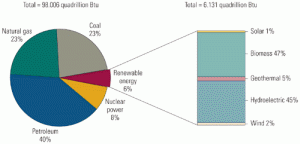
Renewable power development will continue to grow in the U.S., with the nonhydro total reaching 53,121 MW by the end of 2016. So predicts a soon-to-be-released report from Boulder, Colo.–based Platts Analytics (which, like POWER, is a part of Platts, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies). If all that capacity goes on-line, it would […]
-
Wind
Bonus to Siemens
Siemens Power Generation (Erlangen, Germany) announced late last year that it had acquired wind turbine manufacturer Bonus Energy A/S (Brande, Denmark). With a market share of about 9%, Bonus was one of the top five manufacturers of wind turbines in 2004. On paper, Siemens now seems well-positioned to challenge the market leaders (GE Wind, Vestas, […]
-
Hydro
Promoting renewable exports
Promoting renewable exports The DOE is not the only U.S. government department promoting renewable energy. Any U.S. energy firm or supplier looking to export its goods and services can tap the services of the Energy Team at the Commerce Department’s International Trade Administration (ITA), which is part of the U.S Commercial Service (USCS). The […]
-
Hydro
Fuel cells reach MW class
Most people think of fuel cells within a single, "not ready for prime time" context: powering tomorrow's automobiles. But stationary fuel cell power plants are beginning to power some industrial facilities today. The need for heat as well as ultraclean power, and the availability of a renewable fuel, recently came together in a Seattle suburb, site of the world's first commercial megawatt-scale fuel cell power plant—powered entirely by gas produced by anaerobic digestion of municipal wastewater.
-
Hydro
Nowhere to go but up
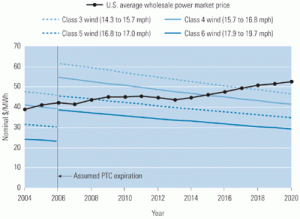
Installations of new renewable energy facilities in the U.S. slowed significantly last year. Why? The short answer is a lack of political will. Compared with the EU, the U.S. has much less progressive renewable energy policies. For example, although the Production Tax Credit was renewed last year, legislators in Washington had let it expire, and prospects for a comprehensive national energy policy are fuzzier than ever. Following is a brief roundup of what’s happening worldwide in the fields of wind, photovoltaic, and hydro power. (For a snapshot of today’s global geothermal industry, see p. 40.)