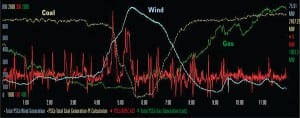
Wind
-
Coal
Vietnam Works Hard to Power Economic Growth
For the past 15 years, Vietnam has enjoyed enviable gross domestic product increases, averaging 7% annually. That kind of economic growth increases power demand, but financing new capacity remains a challenge. Reaching its ambitious capacity growth goals will require Vietnam to expand its financing and vendor base, attract foreign investment, and ensure future fuel supplies in a region thick with competition for those resources.
-
Nuclear
The Big Picture: DOE Loan Guarantees
Of the $35.9 billion in loan guarantees awarded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) since 2009, roughly $26.5 billion have financed nuclear and renewable power projects across the nation through the Section 1703 and 1705 loan guarantee programs.
-
Wind
European Firms Complete Wind-to-Hydrogen Power Plant
A consortium of European developers, with funding from the German federal government, have completed a power plant in Prenzlau, near Berlin, Germany, that uses excess wind energy to convert water into oxygen and hydrogen in a process called hydrolysis, and then uses hydrogen and biogas to generate power and heat.
-
Wind
Novel Floating Wind Turbine Deployed in the Atlantic
A semi-submersible structure supporting a 2-MW wind turbine was towed nearly 350 kilometers (217.5 miles) to water depths of about 35 meters (114.8 feet) into open Atlantic waters and deployed off the coast of Aguçadoura, Portugal, last November.
-
Coal
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Coal
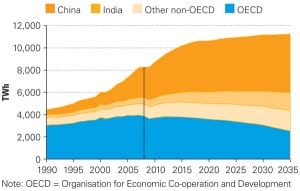
World Energy Outlook Forecasts Great Renewables Growth
Driven by policies to limit carbon emissions, as well as government subsidies, the share of worldwide nonhydro renewable power is set to grow from just 3% in 2009 to 15% in 2035, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its recently released World Energy Outlook 2011. Under the same scenario—which assumes that carbon pricing, explicit […]
-
Coal
U.S. Confronts Pipeline Gaps While Europe Juggles Renewables and Debt
U.S. optimism has been restored by reports of abundant, reasonably priced natural gas to fuel most new generation; however, huge gaps in the fuel delivery system (thousands of miles of pipelines are needed) will soon challenge gas plant development. Meanwhile, the cloud of sovereign debt hangs over all major capital projects in Europe, where the UK moves ahead with new nuclear projects while many of its neighbors shut the door on nuclear and struggle to finance their commitment to renewables.
-
O&M
EPRI Bridges Industry R&D Gaps
The technologies used to generate and distribute electricity will be radically transformed during the coming decade. Amid that change, the power industry must continue to meet customer reliability, safety, and cost-of-service expectations. Achieving the right balance among these often-conflicting goals is the primary focus of every utility. The Electric Power Research Institute is helping utilities achieve that balance with R&D programs for many new and emerging technologies.
-
Coal
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan Pushes Power Industry in New Directions
The Five-Year Plan is the expression of the centralized planning goals for China’s economy. The 12th Five-Year Plan, approved by the Chinese Government on March 14, 2011, established many social and economic goals, including significant expansion of the country’s power generation industry in many new directions.
-
Coal
Editors Select Top Five Stories of 2011
The POWER editorial staff’s picks for the most significant stories of 2011.
-
Wind
Top Plant: EnBW Baltic 1, Darss-Zingst Peninsula, Mecklenburg Province, Germany
Owner/operator: EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg AG/EnBW Renewables GmbH Germany’s first commercial offshore wind farm—the 48.3-MW EnBW Baltic 1—consists of 21 Siemens wind turbines, each with a capacity of 2.3 MW and a rotor diameter of 93 meters. Siemens constructed the facility in an area covering about 7 square kilometers in the Baltic Sea.
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.
-
Wind
AMSC Former Employee Convicted in Sinovel Intellectual Property Case
An intellectual property battle between Massachusetts-based American Superconductor Corp. (AMSC) and China’s giant wind turbine maker Sinovel in late September culminated with an Austrian court conviction of a former AMSC employee, who was arrested in Austria and who pled guilty to corporate espionage charges. The court charged Dejan Karabasevic, a 38-year-old Serbian engineer, with stealing AMSC’s software, modifying it, and secretly selling it to Sinovel.
-
Gas
Nordic Nations Provide Clean Energy Leadership
In the past few years, nuclear concerns, rising oil prices, and a growing understanding of our environmental impact has given energy issues a higher profile worldwide. In this report on the Continental Nordic countries, we look at the efforts being made in much of the Nordic region to secure a sustainable energy supply for the future and at the extent to which the innovative solutions of these countries can be exported around the globe.
-
Hydro
Chart a New Course
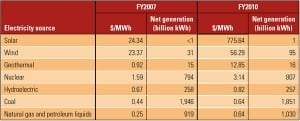
I examined the magnitude of electricity subsidies for renewables compared with conventional generation technologies in my May 2011 editorial, based on data from a 2008 report prepared by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). An updated EIA report released in July determined that federal government subsidies have risen substantially during the past three years. In fact, overall renewable energy subsidies have almost tripled, increasing from $5.1 billion to $14.7 billion. In my opinion, we aren’t getting value for the money spent.
-
Gas
Who Pays for Firming Up Variable Energy Resources?
The major economic hurdle for renewable power generation technologies continues to be substantial installation costs. But another cost is associated with continuous load-balancing, made possible by backstopping that variable generation with dispatchable generators that typically consume expensive fossil fuels. Bottom line: Who pays for the capacity firming or backstopping resources?
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.
-
Solar
Utilities Increase Renewable Energy Capacity
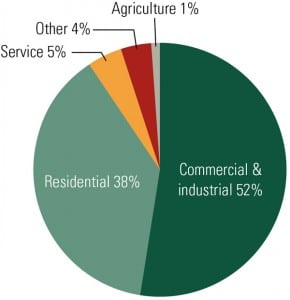
Driven by state RPS requirements and the desire to diversify their energy sources, U.S. utilities continue to add more renewable power to their generation portfolios. As a result, they must deal with a number of important issues, including resource availability that varies geographically.
-
Wind
Charting the Wind: Where the Sector Is Headed
Perhaps the most echoed sentiment at the American Wind Energy Association’s (AWEA’s) WINDPOWER 2011 Conference & Exhibition, which took place May 22 to 25 in Anaheim, Calif., was the call to extend the Production Tax Credit (PTC), the industry’s policy driver, before it expires at the end of 2012. But that wasn’t the only theme. The throngs of companies and organizations that are shaping the rapidly emerging sector around the world had different notions of the factors that help or hinder the growth of wind power, and POWER was there to listen to their perspectives about everything from grid integration, to offshore energy, to technology innovation.
-
Solar
Countries Abandon Subsidies for Renewables en Masse
Stricken by the economic crisis and forced to implement austerity measures, several countries around the world have been forced to abandon or slash subsidies for renewable power producers.
-
Coal
Spain: A Renewable Kingdom
Spain has served as both exemplar and scapegoat when it comes to renewable energy policy. Though power policy must necessarily accommodate specific national resources and goals, Spain’s experience as an early and eager adopter of renewable energy technologies and subsidies is a cautionary tale of how the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
-
Wind
Major Offshore Players Introduce Colossal Wind Turbines
Competition among offshore wind turbine vendors vying for market share went into overdrive in the first three months of 2011 as several key players announced gigantic new turbine models.
-
Wind
Horizontal or Vertical? The Question for Wind Turbine Axis Orientation
This web supplement to "Changing Winds: The Evolving Wind Turbine" examines the debate over the merits of the two most common wind turbine axis orientations.
-
Solar
Energy Storage Enables Just-in-Time Generation
One of the main criticisms of renewable energy facilities is that they are unable to dispatch electricity when it’s needed. The great game-changer is low-cost energy storage, which would enable renewable energy production to be stored and rapidly released when needed. Here are seven promising distributed energy storage technologies that could be commercialized in the near future.
-
Wind
Changing Winds: The Evolving Wind Turbine
As early as the first century A.D., wind energy was harnessed for practical purposes. Since then, turbine designs have come a long way from the archetypal post-mounted four-bladed devices. Today’s ubiquitous three-bladed designs will soon be evolving in many unexpected directions.
-
Wind
European Offshore Wind Turbine Capacity Grows 51% in 2010
Europe installed 308 new offshore wind turbines in 2010—a 51% increase in installed offshore capacity over the previous year, the European Wind Energy Association (EWEA) said in new figures released this January. The 883 MW of new capacity—worth some €2.6 billion—were installed at nine wind farms in five countries, bringing the continent’s total offshore installed wind capacity to 2,964 MW.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Coal
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
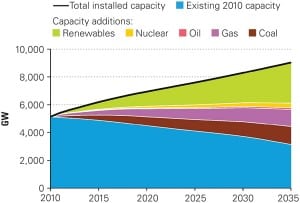
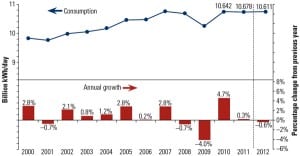
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Solving the Renewable Integration Puzzle
In November, California voters overwhelmingly rejected an initiative that would have put the brakes on AB 32, the state’s ambitious greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction law. Given the role that California has played in climate change policy, that such a vote took place only four years into the law’s implementation process and 10 years before the emissions reduction targets were to be met was a reality check on climate change policy for those on both sides of the issue.