Water
-
O&M
Avoid These 10 Mistakes When Selecting Your New Water Treatment System
There are a number of reasons why your plant might be looking at new water pretreatment equipment in the near future. One common reason is the addition of new generating capacity. Regardless of the type of new generation, you can be sure that it will require additional high-purity water for processes ranging from direct steam generation to power augmentation, NOx control, and washing the blades of the combustion turbines.
-
O&M
Accurate Online Silica Analyzers Ensure Boiler Performance, Add Boiler Life
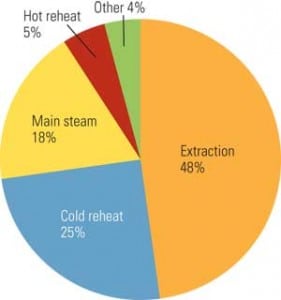
One key area at the 800-MW Michoud power station where O&M excellence is evident is in maintaining plant water quality.
-
Water
Improved FGD Dewatering Process Cuts Solid Waste
In 2007, Duke Energy’s W.H. Zimmer Station set out to advance the overall performance of its flue gas desulfurization (FGD) dewatering process. The plant implemented a variety of measures, including upgrading water-solids separation, improving polymer program effectiveness and reliability, optimizing treatment costs, reducing solid waste sent to the landfill, decreasing labor requirements, and maintaining septic-free conditions in clarifiers. The changes succeeded in greatly reducing solid waste generation and achieving total annual savings of over half a million dollars per year.
-
O&M
Preventing Turbine Water Damage: TDP-1 Updated
ASME’s latest revision of its Recommended Practices for the Prevention of Water Damage to Steam Turbines Used for Electric Power Generation: Fossil-Fuel Plants, ASME TDP-1-2006, contains much important design and operating advice that is proven to protect steam turbines. However, many in the industry are not as familiar with the update as they should be. This article provides a concise overview of this critical design standard.
-
Gas
Qatar Starts Construction on Middle East’s Largest Power and Water Plant
The gas-rich Persian Gulf state of Qatar in May commenced construction of the region’s largest power and water plant, a massive project comprising eight gas turbine generators, eight heat-recovery steam generators, four steam turbine generators, and 10 desalination units.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Looking Downstream After the Cooling Water Case
In the wake of the recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling related to cooling water intake practices at large power plants, many utilities are relieved to be off the hook as far as implementing expensive control upgrades to protect fish and other aquatic organisms.
-
O&M
Focus on Organics in Steam
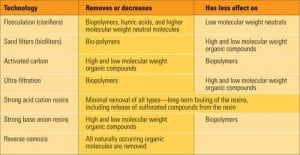
Organic compounds can enter the steam cycle from a number of sources, including water treatment chemicals, or as part of a manufacturing process. Regardless of the source of the organics, their effects range from fouling polisher resins to causing significant steam turbine damage. Conventional water pretreatment systems are available to remove organics from water, but removing organic compounds at their source is the best place to start addressing the problem.
-
Water
Reconsider Start-up Controls to Avoid Boiler Deposits and Underdeposit Corrosion
Water treatment programs for boilers and heat-recovery steam generator (HRSG) units appropriately focus on chemistry controls during normal operation. However, rates of corrosion product transport and deposition can be much greater in boilers and HRSG units during start-up than during routine operation. For that reason, in addition to standard programs for monitoring and control of corrosion product transport, deposition, and underdeposit corrosion, consider adding contingency plans for boiler water chemistry holds in the start-up process.
-
Water
How to Measure Corrosion Processes Faster and More Accurately
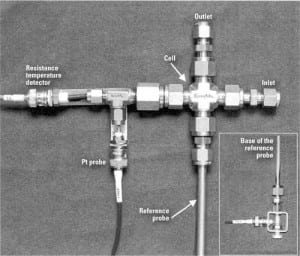
Maintaining reliable and efficient plant operations requires good control of corrosion and corrosion product transport in power plant water systems. The Electric Power Research Institute recommends oxidation-reduction potential for passivator control in feedwater systems, as do many industry experts. Here’s how to turn that recommendation into a robust feedwater monitoring program.
-
Water
Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment Primer
Purge water from a typical wet flue gas desulfurization system contains myriad chemical constituents and heavy metals whose mixture is determined by the fuel source and combustion products as well as the stack gas treatment process. A well-designed water treatment system can tolerate upstream fuel and sorbent variation over time and consists of multiple process treatment steps arranged in just the right order to produce wastewater acceptable for discharge.