Water
-
Coal
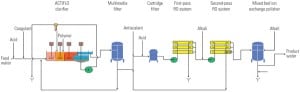
Fundamentals of Zero Liquid Discharge System Design
Power plants often produce wastewaters that contain salts, such as those from wet gas scrubbing, coal pile run-off, and leachate from gypsum stacks. Evaporation of those liquid wastes in a modern zero liquid discharge system produces clean water that is recycled into the plant plus a solid product suitable for landfill disposal. Here are the options to consider.
-
O&M
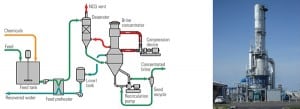
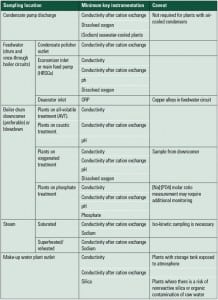
The New Water Lab
Recent advances in water laboratory instrumentation—from improved sample conditioning to advanced online instruments—have reached the market. Here’s a look at the equipment you’ll find in the best-equipped power plant laboratory this year.
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
O&M
Systems Integration, Flexible Control Reduce Makeup Water Cost
Longview Power, a 695-MW coal-fired power plant now under construction in Maidsville, W.Va., is scheduled to begin commercial operation later this year. The $2 billion project reached 580 MW in early June, just a month after completing the “first fire on coal” schedule milestone. Testing and tuning of the controls and various systems continue.
-
Water
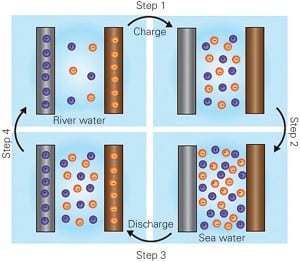
Battery That Extracts Energy from Water Salinity Difference
A rechargeable battery developed by researchers from Stanford University employs the difference in salinity between freshwater and saltwater to generate a current.
-
Water
Readers Write
In the September and October 2010 issues, POWER Contributing Editor David Daniels explored the causes and damage mechanisms of condenser tube leaks (“Taming Condenser Tube Leaks,” Part I and Part II). Dennis J. Schumerth, Valtimet’s director of business development, took issue with several of Daniels’ statements regarding the proper use of titanium condenser tubes. We have given Schumerth the opportunity to express his concerns and for Daniels to reply.
-
Hydro
Massive Energy Storage Facility Planned for Mexico-U.S. Border
Dubai-based energy firm Rubenius in October proposed to build a $4 billion energy storage facility based on sodium sulfur (NaS) technology on a 345-acre site in the Mexican state of Baja California, close to the U.S. border. If it comes to fruition, the facility—dubbed a “mega region energy warehouse” by Mexico’s President Felipe Calderon—will feature 1,000 MW of battery storage and offer “storage space” to energy companies and utilities in both Mexico and the U.S.
-
Gas
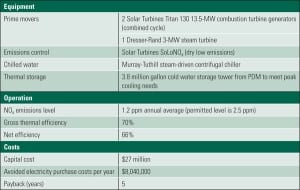
Smart Power Generation at UCSD
The University of California, San Diego has been accumulating awards for its savvy use of a constellation of power generation and energy-saving technologies. The campus already controls a fully functioning microgrid—including a cogeneration plant—and, as befits a research institution, is constantly looking for new ways to make its energy system smarter. This “living laboratory,” as campus leaders like to call it, demonstrates what it takes to build a smarter grid and why the effort is worth it.
-
Commentary
The Nexus of Energy and Water
The age-old adage “water and electricity don’t mix” does not apply to 21st-century infrastructure planning. The two entities can no longer be viewed as separate commodities. The demands on both are intertwined, so solutions for meeting new and growing challenges associated with water scarcity and carbon regulations must also be integrated. Water is essential to […]
-
Water
Mine Drainage: An Alternative Source of Water
Although mining practices often vary greatly according to the material produced and the value of the deposit, one common denominator is that mining of materials containing sulfide minerals creates acid mine drainage (AMD). AMD is one of the mining industry’s major environmental challenges.