Plant Design
-
O&M
Constructing and Managing Coal Ash Landfills
Creating a landfill to hold dry boiler ash is a challenging proposition these days. There’s more to the project than you might imagine, as you’ll learn from this article about the development of a typical new ash landfill.
-
O&M
Wet Booster Fans Optimize Power Station Performance with FGD and Wet Stack
A Romanian lignite-fired power station wanted to minimize the operating cost of the flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system by placing the booster fans in the "wet position," between the wet FGD scrubber and the wet stack, where they would consume significantly less power. A number of combined environmental effects must be considered in this design.
-
O&M
Improved Performance from Priority-Based Intelligent Sootblower Systems
When sootblower operation frequency is too high, a plant risks losing power generation from tube leaks; but when sootblower frequency is too low, there is a risk of boiler pluggage. Intelligent sootblowing finds the right balance between tube erosion and plant economic operation.
-
O&M
Enhanced Capture of Mercury Using Unique Baghouse Filter Media
Several states have already instituted mercury emission limits in expectation of tightening mercury emission rules that will require reductions of up to 91%. Coal-fired plants searching for an economical way to meet the new limits may need to look no further than replacing their baghouse filter elements.
-
O&M
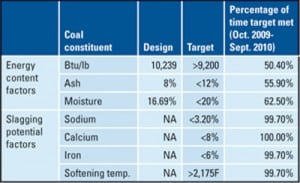
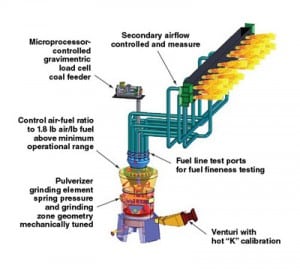
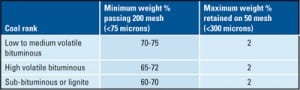
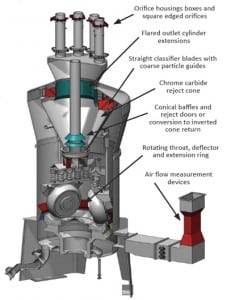
Pulverizers 101: Part II
Pulverizers prepare the raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of this three-part report, we examined the essentials of pulverizer design and performance. In the second part, we discuss the importance of fuel fineness. In the final article, we will discuss the importance of air and fuel measurement.
-
O&M
Improved Coal Fineness Improves Performance, Reduces Emissions
Utilizing engineering ingenuity and today’s developing computational fluid dynamics tools, a new classifier design is now available that significantly improves fineness from pulverizers without the heavy costs associated with dynamic classification or any downsides on pulverizer capacities, maintenance, and parasitic power. Instead, operational flexibility and improved emission control options are enhanced.
-
Coal
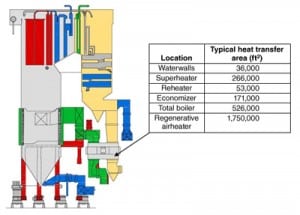
Innovations in Air Heater Design Produce Performance and Reliability Improvements
The regenerative air heater on a typical steam generator usually accounts for over 10% of a coal-fired plant’s thermal efficiency. A poorly performing air heater will cause an increase in the gas outlet temperature, often reducing the electrostatic precipitator collection efficiency and baghouse reliability. Recent design innovations enable restoration of this lost performance.
-
O&M
Pulverizers 101: Part I
Pulverizers prepare raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of three parts, we’ll examine the essentials of pulverizer capacity, what should be done after a coal pulverizer fire or other incident, and how to tune up pulverizer performance. In future articles we’ll discuss measuring pulverizer performance and performance optimization.
-
O&M
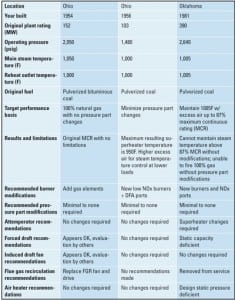
Natural Gas Conversions of Existing Coal-Fired Boilers
Why should utilities consider converting existing coal-fired plants to burn gas? We explore the rationale for fuel switching, some of the options available for the conversion of coal-fired units, technical considerations related to conversion, and some of the financial considerations that will impact the final decision.
-
Coal
Biomass Boiler Market Remains Unpredictable
Utilities struggling to meet renewable portfolio standards requirements have studied the conversion of existing coal-fired boilers to burn biomass. The results of those studies have been mixed, although test burns continue; the results of one such test are included. Overall, the market is tending toward smaller biomass projects, and the low price of natural gas is perhaps the biggest reason utility-scale projects are now few and far between.