O&M
-
O&M
Managing Minimum Load
Reducing the minimum load at which a steam turbine can reliably operate is one way to increase revenue for marginal base-loaded units during periods of low electrical demand. For this reason, it is not unusual to see merchant plants operating at "super minimum" load levels that are well below the typical 25% rated full-load limits. However, such units are operating well outside the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) design basis, and owners may experience undesirable damage to their turbines for a number of reasons. That’s why it is important for owners to understand the trade-offs and risks that come with such operation.
-
O&M
Extreme Oil Changes
Performing regular oil changes on remote generators is far from simple or cost-effective. Here’s how one firm harnessed technology to extend oil change intervals from one week to two months.
-
O&M
Improved Filler Metal Enables Higher-Temperature Dissimilar Metal Welds
The welding of dissimilar metal joints in new and retrofit power plant boiler tubing has long proved challenging. New plants designed to operate at higher temperatures and pressures require advanced alloys and a filler metal that produces reliable welds. EPRI recently developed and sponsored the commercialization of a new filler metal. Its first application is the fabrication of boiler tubes for American Electric Power’s ultrasupercritical John J. Turk, Jr. Power Plant.
-
O&M
Optimize Gas Turbine Performance Using Acoustic Simulation Software
Increasingly fierce competition driven by deregulation and privatization is putting downward pressure on power plant operations and maintenance (O&M) budgets. Recently, lower natural gas prices have pushed natural gas – fired combined-cycle plants higher up in many utilities’ dispatch order in some regions, a welcome change from the twice-a-day cycling experienced by some plants during the past few years. However, with more operating hours comes more interest in plant operating availability, and that means increased emphasis on reliable gas turbine operation.
-
O&M
Steam Turbines: San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Gets Upgraded Generator Rotors
Southern California Edison’s (SCE) 2,250-MWe San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS) recently took receipt of a new and upgraded generator rotor for one of its two Alstom steam turbine generator units (Figure 1). Following the successful installation and flawless start-up of this new rotor in the Unit 2 generator, the former Unit 2 rotor was […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Looking Downstream After the Cooling Water Case
In the wake of the recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling related to cooling water intake practices at large power plants, many utilities are relieved to be off the hook as far as implementing expensive control upgrades to protect fish and other aquatic organisms.
-
O&M
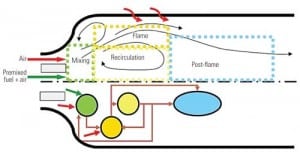
Advanced Modeling Tools Slash Combustor Analysis Chores
Combustor design simulation requires the resolution of complex geometry, turbulent flow patterns, heat transfer, and detailed chemistry. Although computational fluid dynamics (CFD) can simulate the reacting flow in realistic geometries, it requires the use of severely restricted chemistry models that are too simple to accurately simulate emissions and operational stability. A new simulation tool is now available that eliminates this CFD shortcoming while significantly reducing computing time.
-
O&M
Turkey Opens Electricity Markets as Demand Grows
Turkey’s growing power market has attracted investors and project developers for over a decade, yet their plans have been dashed by unexpected political or financial crises or, worse, obstructed by a lengthy bureaucratic approval process. Now, with a more transparent retail electricity market, government regulators and investors are bullish on Turkey. Is Turkey ready to turn the power on?
-
O&M
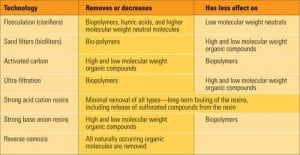
Focus on Organics in Steam
Organic compounds can enter the steam cycle from a number of sources, including water treatment chemicals, or as part of a manufacturing process. Regardless of the source of the organics, their effects range from fouling polisher resins to causing significant steam turbine damage. Conventional water pretreatment systems are available to remove organics from water, but removing organic compounds at their source is the best place to start addressing the problem.
-
O&M
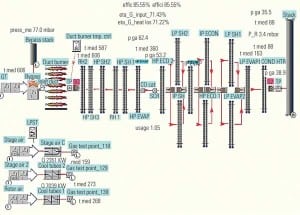
Computer Simulation of HRSGs Can Improve O&M
Obtaining accurate data about the performance of a plant’s heat-recovery steam generator is crucial to ensuring the smooth operation and maintenance of the equipment. Software designed to model and simulate HRSG operations can provide valuable information about corrosion and other operational problems.