Nuclear
-
Coal
POWER Digest (September 2011)
Australia Pursues Carbon Tax. Australia’s Prime Minister Julia Gillard on July 10 laid out an ambitious plan to cut national greenhouse gas emissions by 5% of 2000 levels by 2020 by imposing a A$23 (US$23.4) per metric ton carbon tax, starting next year. If parliament approves the plan before year-end, the carbon tax will increase […]
-
Coal
Best Practices for Natural Gas Line Cleaning
As barriers to new coal-fired generation expand and enthusiasm for nuclear plants wanes, the commissioning of natural gas–fired plants promises to increase. However, gas plants pose hazards, too. An explosion last year that was caused by unsafe use of natural gas to blow residue from a gas pipeline during commissioning of a gas-fired power plant has focused regulator and industry attention on finding safer alternatives for this task. Fluor shares its gas pipeline cleaning best practices.
-
Commentary
Advancing America’s Nuclear Infrastructure
It is fair to say that 2011 is bringing some uncertainty into the nuclear energy industry. The tsunami and subsequent events at Fukushima present Japan and our industry with new challenges but also serve as a catalyst for continuous improvement. In the U.S., we are learning from these events and improving our operations, designs, and emergency response approaches to make our plants safer, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly.
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Nuclear
The Fukushima Fallout: Six Months After the Nuclear Crisis
(WEB EXCLUSIVE) Much has transpired during the nearly six months following the Great East Japan Earthquake—a 3-minute, magnitude 9.0 temblor that generated a series of tsunami waves as tall as 38.9 meters (130 feet), killed more than 25,000 people, and set off the worst nuclear disaster in 25 years.
-
Nuclear
THE BIG PICTURE: Underground Nuclear Waste Disposal
According to the International Atomic Energy Commission, deep disposal in stable geological formations is the only sustainable way to safely manage spent fuel and high-level waste (HLW) from nuclear power reactors. No permanent geological repository has yet been built, but some countries have found a location for a future repository. Others are researching the option…
-
Nuclear
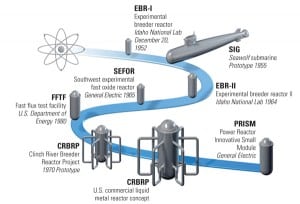
PRISM: A Promising Near-Term Reactor Option
PRISM is an advanced sodium-cooled reactor that simultaneously reduces proliferation concerns by consuming transuranics and weapons-grade plutonium and closes the nuclear fuel cycle. PRISM’s passive safety systems, successfully demonstrated in earlier liquid metal reactor programs, combined with modern design requirements, make PRISM invulnerable to most serious accidents that can affect light water reactors.
-
Nuclear
Nuclear Power in the Shadow of Fukushima
Risk, risk management, and the specter of Fukushima ran through the nuclear track at May’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference in Chicago. The reality of risk, driven home by the horrendous events in Japan, was a recurring theme in many presentations, in questions to speakers, and in the conversations among delegates during informal moments.
-
Nuclear
Germany to Shut Down All Nuclear Reactors
Germany’s Chancellor Angela Merkel at the end of May officially endorsed a plan to shut down all 17 of the nation’s nuclear power plants by 2022. The decision, which gives the power-intensive nation just over a decade to find new sources of power for 23% of its energy needs, has had reverberations all over the world, though the future of nuclear—through growth in developing nations—continues to look sturdy.
-
Nuclear
TEPCO: Most Fuel at Daiichi 1 Melted
Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO) in May discovered—after calibrating water gauges—that the water level in the reactor pressure vessel of Unit 1 at the quake- and tsunami-ravaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant may have dropped to such low levels that the fuel was completely uncovered. This caused almost all the fuel pellets to melt and fall to the bottom of the vessel at a relatively early stage in the accident—roughly 15 hours after the March 11 earthquake that killed an estimated 28,000.
-
Nuclear
Holtec, Westinghouse Roll Out Small Modular Reactor Designs
As the Daiichi nuclear crisis has governments around the world reconsidering their nuclear-heavy energy plans and scrutinizing the safety of existing reactors and third-generation designs, several developers are touting the merits of small modular reactors (SMRs).
-
O&M
Defeating Concrete Reinforcing Steel Corrosion
Four concrete cooling towers at a coal-fired electrical generation plant exhibited reinforcing steel corrosion that was causing concrete deterioration. This case study follows the repairs to those towers—how the corrosion control solution was selected, how repairs were made, and how follow-up tests found the repairs to be effective three years later.
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.
-
Nuclear
Recovery Efforts Continue at Fukushima Daiichi
In April, Japan’s Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency provisionally raised the accident rating for three reactors at the crippled six-unit Daiichi nuclear plant in Fukushima Prefecture to Level 7—making it a “major accident” and putting it on par with the 1986 Chernobyl accident in the Ukraine. Recovery efforts continue at the nuclear plant with workers […]
-
Nuclear
Germany Considers Accelerated Nuclear Exit on Fukushima Worries
In the wake of the devastating nuclear crisis afflicting the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant in Japan, Germany has embarked on an abrupt shift away from nuclear power, shutting down eight reactors for safety checks and ditching concerted efforts to keep nuclear power plants open in the long term. In mid-April, Chancellor Angela Merkel told reporters that leaders of Germany’s 16 states all want to “exit nuclear energy as soon as possible and make the switch to supplying via renewable energy.” The policy reversal has incited ardent opposition from the energy sector and industry.
-
Coal
Spain: A Renewable Kingdom
Spain has served as both exemplar and scapegoat when it comes to renewable energy policy. Though power policy must necessarily accommodate specific national resources and goals, Spain’s experience as an early and eager adopter of renewable energy technologies and subsidies is a cautionary tale of how the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
-
Nuclear
The Battle to Stabilize Daiichi
Weeks after a massive magnitude 9.0 earthquake and subsequent 14-meter-high tsunami devastated Fukushima Prefecture in northeastern Japan, workers from the Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO) were still struggling to regain control of four severely damaged reactors at the six-unit Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant.
-
Coal
China’s Five-Year Plan Is Heavy on Non-Fossil Generation
The People’s Republic of China’s Congress approved a much-anticipated draft of the country’s 12th Five-Year Plan (2011–2015) on March 14. Along with key objectives that included boosting its gross domestic product (GDP) by 7% annually on average, the country for the first time in a five-year plan established targets to tackle climate change. It plans to reduce carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by 17% from 2010 levels by 2015 and to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 16% from 2010 levels by 2015.
-
Nuclear
Chernobyl: Twenty-Five Years of Wormwood
Twenty-five years ago last month, engineers and technicians were running low-power tests at the 1,000-MW Reactor No. 4 of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant outside Kiev. They quickly, inexplicably, lost control of the light-water-cooled, graphite-moderated reactor. In an instant, the critical chain reaction flared out of control. The plant exploded like a small, dirty bomb, the graphite caught fire, and the worst catastrophe in civilian nuclear power was under way.
-
Nuclear
The Battle to Control Quake-Stricken Japanese Reactors
As POWER closes this issue (March 15), 6,000 people have been confirmed dead and 10,000 others are still missing as a result of the magnitude 9.0 earthquake and ensuing tsunami that destroyed Japan’s eastern shore on March 11. At this writing, the country is battling a third cataclysm—the potential meltdown of several reactors at Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO’s) Daiichi nuclear power plant in Fukushima Prefecture.
-
Nuclear
Nuclear Monitor: News from France, Japan, U.S., Belgium, Germany
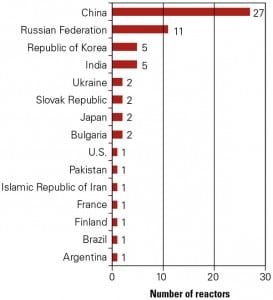
Five new nuclear reactors were connected to the grid while construction of 14 others began in 2010, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) reported in early March. Around the world, a total 65 reactors with a net power capacity of 62.9 GW were in various stages of construction—almost half of them in China.
-
Nuclear
Nuclear Fever Breaks
Excitement over an expected nuclear renaissance reached fever pitch over the past decade. Today, the original volume of announced projects has been sifted, leaving just a few serious ones that may match well with the level of loan guarantees recently announced as part of the president’s budget proposal. The pace of progress is slow, yet progress is almost certainly unavoidable.
-
Nuclear
Small Nuclear Reactor Concept Goes Underwater
France in January announced its contribution to the wave of small and modular reactors (SMRs): a submarine-like nuclear plant that can be submerged in waters 60 meters (m) to 100 m deep and several kilometers offshore.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Nuclear
Major Milestones for the AP1000 Reactor
Westinghouse’s AP1000 reactor design hit several milestones in recent months, prompting speculation that it could take the coveted lead in the charge to deploy the world’s third-generation nuclear power plants.
-
Nuclear
Ukraine Opens Chernobyl to Visitors
The Ukraine will on April 26 mark 25 years after explosions at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (then in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic) resulted in a fire that sent a plume of radioactive fallout into the atmosphere and over an extensive area.
-
Nuclear
I&C Update on Plant Vogtle Units 3 and 4
Development of Vogtle Electric Generating Station Units 3 and 4—the first new nuclear power plant units in the U.S. in decades—has generated considerable excitement. The next generation of nuclear plants, represented by these units, includes at least two major improvements: the use of passive safety systems and a reliance on digital control systems. The latter represents a gigantic leap in modernization and a fundamental change in control of the plant.
-
Coal
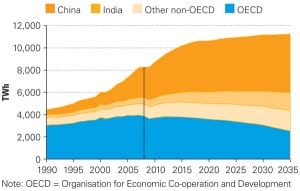
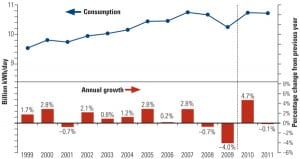
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.
-
Coal
The U.S. Power Industry 2011: The Sequel
If Hollywood were scripting the power industry story for 2011, it would be a sequel to 2010—more of the same, but just not quite as good. Natural gas gets top billing and the accolades, wind power drops to a supporting role, and new nuclear answers the casting call but has yet to get a speaking part. Coal is like Mel Gibson—a talented Oscar winner unlikely to get another leading role. In this, our fifth annual industry forecast report, the story may be familiar, but the price of admission is going way up.
-
Nuclear
Russia Powers On, Boosting Nuclear Reactor Sales
Atomstroyexport, the Russian Federation’s nuclear power equipment and services export monopoly, in September signed a US$1.8 billion contract with the Chinese government for development of the second stage of the Tianwan nuclear power plant in Lianyungang City. Under the agreement, Units 3 and 4 are to be built in a way similar to construction of the first stage of Tianwan—two Russian-designed VVER-1000 reactors that came online in 2007, each with a rated capacity of 1,060 MW.