Hydro
-
History
Modernization of Century-Old Hydro Facility Yields Rich History
When the Boulder Canyon Hydroelectric Facility was built in the steep, forested mountains between Boulder and Nederland, Colo., in 1910, it was the highest head hydroelectric facility in the western U.S.
-
Hydro
TOP PLANT: Three Gorges Dam, Yangtze River, Hubei Province, China
After nine years of construction, installation, and testing, the Three Gorges Dam is now complete. On May 23, 2012, the last main generator finished its final test, increasing the facility’s capacity to 22.5 GW and making it the world’s largest capacity hydroelectric power plant.
-
Hydro
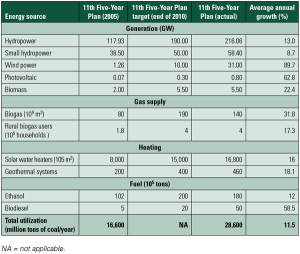
Renewable Energy Development Thrives During China’s 12th Five-Year Plan
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan calls for expanding the use of renewable energy in all forms throughout the country. From solar and wind to biomass gas and briquettes, China has a true “all of the above” renewable energy policy.
-
Hydro
Hawaii’s Largest Wind Project Online as State Struggles to Integrate Renewables
On Monday, as First Wind announced its 69-MW Kawailoa Wind Project had gone into commercial operations on Oahu, other news underscored the difficulty the island state faces in trying to substitute renewables for expensive, imported fossil fuels.
-
Hydro
Trend Shows Growth of Renewables on Contaminated Lands
Renewable energy projects installed on potentially contaminated lands, landfills, and mine sites have increased by 40% since 2008, a new list released last week by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems make up the bulk of about 184.7 MW installed at 60 sites in 25 U.S. states.
-
Hydro
Three Gorges Dam Completed Amid Technical Victories, Controversy
China in early July installed the 32nd and final turbine of its mammoth Three Gorges Dam, virtually completing the controversial 1994-initiated hydropower project on the middle reaches of the Yangtze River.
-
Coal
Chile’s Power Challenge: Reliable Energy Supplies
Droughts, unreliable gas imports, and protests against proposed projects have hampered the Chilean power sector and its largest economic driver, the copper-mining industry. Recent policies designed to foster more reliable supplies are a move in the right direction, but remaining obstacles are formidable.
-
Hydro
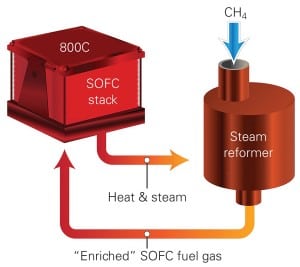
Major Developments for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which oxidize a fuel to produce electricity, have received much attention of late for the technology’s myriad benefits, including high efficiency, long-term stability, fuel flexibility, and low carbon emissions—all at a relatively low cost.
-
Hydro
Tubular Turbine Hydropower Plant Comes Online
Albania this June inaugurated its first major hydropower project since the early 1980s, bringing online Ashta I, the first of two run-of-river plants with a combined capacity of 53 MW. At the inauguration ceremony, Albania’s Prime Minister Sali Berisha called the plant “a novelty” because it is the largest in the world to use advanced tubular turbines technology.
-
Hydro
FERC Rule 1000: What Does It Mean?
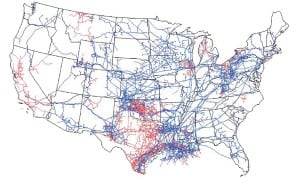
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has the responsibility for ensuring just and reasonable rates and preventing undue discrimination by public utility transmission providers. Last year FERC defined a new framework for public utilities and regional transmission organizations planning new transmission networks. The framework is provided in Order No. 1000—Transmission Planning and Allocation by Transmission Owning and Operating Public Utilities. The Final Rule was issued on July 21, 2011, and reaffirmed by Order No. 1000-A on May 17, 2012.
-
Coal
Power in India: Opportunities and Challenges in a Fast-Growing Market
India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth. India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth.
-
Hydro
Utility Perspectives on Ramping Up Renewable Power
Panelists at ELECTRIC POWER discussed how U.S. utilities choose renewable power generation technologies based on their geographic locations, state requirements, economics, and other criteria—including reliability and federal regulations.
-
Commentary
Incentives Provide Boon to Hydropower Industry
The U.S. hydropower industry has undergone a renaissance in recent years. One of the major drivers of the industry’s growth, the establishment of the production tax credit (PTC) for hydro, has seen strong policy support from our elected officials in Washington, D.C. More than any other federal policy, tax incentives, particularly the PTC, have sparked a level of growth in the industry not seen in nearly two decades.
-
History
Japan Scrambles to Revamp Its Electricity Sector
The March 2011 Japanese earthquake and tsunami that destroyed a number of Japanese power plants—most notably, four nuclear units—hit quickly. Almost as speedy were calls to take all other nuclear units out of service for safety reviews. What will take much longer is developing a new, sustainable energy plan to fill the generation gap left by a potential total lack of nuclear power.
-
Hydro
THE BIG PICTURE: Dammed Dams
New coal and nuclear power plants aren’t the only ones facing opposition. Several countries that are struggling to alleviate chronic power shortages are facing hurdles as they attempt to build new hydropower plants. Here are some massive projects riddled with setbacks caused by everything from social and environmental protests to funding collapses.
-
Coal
Vietnam Works Hard to Power Economic Growth
For the past 15 years, Vietnam has enjoyed enviable gross domestic product increases, averaging 7% annually. That kind of economic growth increases power demand, but financing new capacity remains a challenge. Reaching its ambitious capacity growth goals will require Vietnam to expand its financing and vendor base, attract foreign investment, and ensure future fuel supplies in a region thick with competition for those resources.
-
Coal
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Coal
World Energy Outlook Forecasts Great Renewables Growth
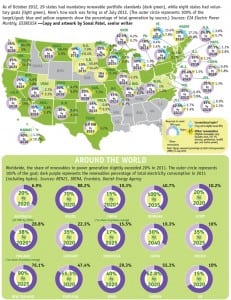
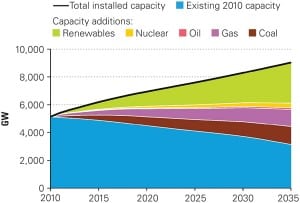
Driven by policies to limit carbon emissions, as well as government subsidies, the share of worldwide nonhydro renewable power is set to grow from just 3% in 2009 to 15% in 2035, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its recently released World Energy Outlook 2011. Under the same scenario—which assumes that carbon pricing, explicit […]
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.
-
Hydro
Burma Halts Massive Chinese-Developed Hydropower Dam
China’s efforts to build the Myitsone Dam—a $3.6 billion hydropower project planned at the confluence of the Mali and N’Mai Rivers at the source of the Irrawaddy River in Burma’s Kachin State—were thwarted in late September after Burma’s President Thein Sein suspended construction “to respect the will of the people.”
-
Hydro
Top Plant: Pelton Round Butte Hydroelectric Project’s Selective Water Withdrawal Project, Oregon
In December 2009, construction of an underwater tower and fish collection structure was successfully completed at the 465-MW Pelton Round Butte Hydroelectric Project. The first-of-its-kind fish bypass and intake structure returns temperatures in the lower Deschutes River to historic patterns and restores downstream passage of Chinook, steelhead, and sockeye salmon while maintaining existing generating capacity.
-
Gas
Nordic Nations Provide Clean Energy Leadership
In the past few years, nuclear concerns, rising oil prices, and a growing understanding of our environmental impact has given energy issues a higher profile worldwide. In this report on the Continental Nordic countries, we look at the efforts being made in much of the Nordic region to secure a sustainable energy supply for the future and at the extent to which the innovative solutions of these countries can be exported around the globe.
-
Hydro
Hydro Reservoir GHG Emissions Lower Than Estimated
A new analysis of 85 hydroelectric reservoirs distributed around the world suggests that these systems emit about 48 million metric tons of carbon annually. That figure is much lower than earlier estimates of 64 million metric tons that were based on studies relying on more limited data and which cautioned that reservoirs of all types […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Too Much of a Good Thing Creates Legal Havoc
As last winter’s abundant snowfall in the Pacific Northwest melted, rivers swelled and hydroelectric operators enjoyed substantial increases in generation. That bountiful clean and cheap power generation was a blessing, but it also triggered a host of legal issues.
-
Hydro
Chart a New Course
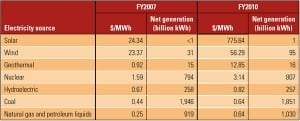
I examined the magnitude of electricity subsidies for renewables compared with conventional generation technologies in my May 2011 editorial, based on data from a 2008 report prepared by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). An updated EIA report released in July determined that federal government subsidies have risen substantially during the past three years. In fact, overall renewable energy subsidies have almost tripled, increasing from $5.1 billion to $14.7 billion. In my opinion, we aren’t getting value for the money spent.
-
Hydro
Commercial Oscillating Water Column Marine Power Plant Commissioned
One of the world’s first breakwater wave power stations was commissioned this July by Ente Vasco de Energia (EVE), an energy agency in the northern Basque region of Spain. The €2.3 million ($3.3 million) project in Mutriku uses oscillating water column technology developed by Voith Hydro’s Wavegen, based in Inverness, Scotland. The technology is integrated into a concrete power station built on a breakwater or coastal protection project.
-
Gas
Who Pays for Firming Up Variable Energy Resources?
The major economic hurdle for renewable power generation technologies continues to be substantial installation costs. But another cost is associated with continuous load-balancing, made possible by backstopping that variable generation with dispatchable generators that typically consume expensive fossil fuels. Bottom line: Who pays for the capacity firming or backstopping resources?
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Hydro
Chile, Peru Put the Brakes on Mega-Hydro Projects
Weeks after Brazil’s environmental agency, IBAMA, granted final approval for construction of the mammoth 11.2-GW Belo Monte Dam in the Amazon region to proceed, an appeals court in Chile suspended plans for the 2.75-GW multi-dam HidroAysen project in the Patagonia region, and Peru’s government terminated a concession for the 1.5-GW Inambari in the Peruvian Amazon area after month-long mass protests (Figure 5).