Environmental
-
O&M
Use predictive techniques to guide your mercury compliance strategy
Several states have mandated faster and/or deeper reductions in plant mercury emissions than those called for by the Clean Air Mercury Rule. Unfortunately, differences between plants make accurate evaluation of control options difficult. In most cases, even statistically based Hg emission models don’t pass muster because they don’t account for the dynamic chemical behavior of Hg species in gas cleaning systems. This article describes one system evaluation tool that has been validated using Hg field test data from 50 full-scale flue gas cleaning systems. It is already being used by TVA and other utilities.
-
Environmental
The bumpy road to federal carbon dioxide caps
There are often five stages to enacting major legislative reforms: Initial enthusiasm, a sobering recognition of the complex issues to be solved, excruciating negotiations over those issues, hand-to-hand combat with supporters of the status quo, and resignation that the final product only deals with part of the problem. Congress has reached Stage 2 as it considers a cap-and-trade system for reducing carbon emissions. Now the real work begins.
-
Coal
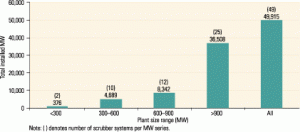
What’s that scrubber going to cost?
The latest benchmarking study by the EUCG examines the technology and costs of 49 flue gas desulfurization systems currently under design or construction by 12 of the nation’s largest utilities. Although the study’s detailed results are proprietary to EUCG members that participated in it, POWER was given access to the top-level findings. To get details at the plant/unit level, you’ll have to join the EUCG and participate in the study, which is ongoing.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Cogeneration qualifying facilities warrant extended contracts
Congress’s enactment of the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 (PURPA) triggered a revolution in the development and construction of power plants. PURPA’s creation of an independent class of generators—qualifying facilities (QFs)—exposed a century-old economic myth that had justified restricting ownership of generating facilities to governmental and investor-owned utilities (IOUs). The success of QFs […]
-
Coal
Navigating a carbon-constrained world
Scientific debate on the validity of global warming science continues, but the issue has yet had little impact on individuals. That impact is being negotiated in Washington, where a regulatory framework that would mandate reductions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) is taking shape. Legislative options under consideration would redefine what power plants must do-and not do-to […]
-
O&M
Lignite Drying: New Coal-Drying Technology Promises Higher Efficiency Plus Lower Costs and Emissions
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Great River Energy are testing a new coal-drying technology that could dramatically reduce the emissions of lignite-burning power plants. The project was selected for funding during Round I of the DOE’s Clean Coal Power Initiative (CCPI), a series of competitions to demonstrate a range of promising clean-coal technologies. […]
-
Coal
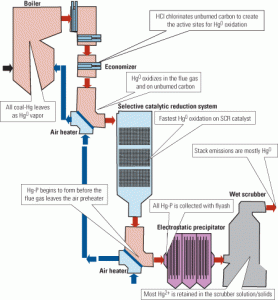
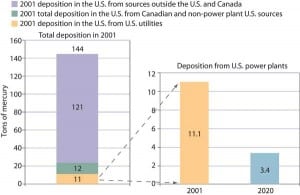
Mercury Control: Capturing Mercury in Wet Scrubbers: Part I
Are you using your flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system to its highest potential? You might not be if you’re not making it do double duty. It seems that million-dollar wet scrubber you installed to rid your flue gases of sulfur dioxide also can do a decent job of capturing mercury — under the right conditions. […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (June 2007)
Siemens, E.ON to test world’s largest GTG / Midwest to add 76-MW peaker in Kansas / Tapping the sun near Phoenix / Georgia Tech developing 3-D PV nanocells / Wind farms with hydrogen backup? / BNSF , union come to terms / IPL to buy 200-MW wind project / India to improve environmental monitoring / POWER digest
-
Coal
Global warming, rising costs complicate capacity additions
If little else is clear about the future of the U.S. power industry, this much is: Electricity rates are going up across the country, and will continue to. None of the esteemed panelists at the CEO session of the ELECTRIC POWER 2007 Conference & Exhibition in Chicago last month actually said those words. But much […]
-
Coal
Climate change concerns drive projects to curb CO2
In a carbon-constrained world, CO2 capture and storage (CCS), although considered the most radical of the carbon abatement technologies (CATs), seems to be favored over combustion and steam cycle improvements alone. However, CCS is the least commercially developed of the CAT options; at present, there are only field prototypes for its various forms. Nonetheless, most […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (May 2007)
World’s largest PV plant now in Portugal; latan 2 construction may resume; Allegheny to scrub Fort Martin plant; TVA will clean up big Dutch CC plant; Connecticut blesses six fuel cell projects; DOE approves IGCC plant in Florida; FERC relicenses Osage hydro plant; A nanotech perpetual motion machine?; POWER digest
-
Legal & Regulatory
States should cede control of renewable power to regional markets
State policy makers are characteristically reluctant to recognize that they have advanced a policy as far as they can, and that they must cede some control to fully realize its ultimate benefits. Ceding control often runs counter to policy makers’ political instinct to serve their constituents. Doing so is even harder when a new […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: Illinois Coal Poised for Comeback
Sylvester Stallone, as Rocky Balboa, staged another magical comeback earlier this year — in the ring and at the box office. Just when you think Rocky is down and out for good, the sixth release of the Rocky franchise just may be the best of the lot. "Down but not out" is also an apt […]
-
O&M
Pollution Control: Low-NOx Combustion Retrofit Options
Reducing NOx emissions from large utility coal-fired boilers has been a primary focus of the U.S. power generation industry since passage of the 1970 Clean Air Act and subsequent legislation. By the early 1990s, nearly all such boilers had installed some form of low-NOx burner (LNB) technology and/or overfire air (OFA) — the least expensive […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (April 2007)
Control pollution and slagging on a shoestring / Keeping HRSGs young, cool, and clean / Natural air conditioning
-
Coal
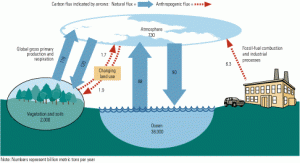
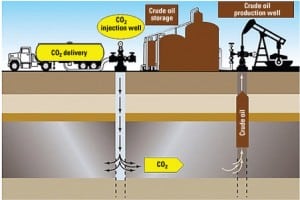
Exploring the many carbon capture options
Carbon capture and sequestration have many technical hurdles to leap in coming years. The capture and reuse of CO2 to enhance oil recovery preceded the current clamor over climate change, and that experience is often used as an example that the process is a viable way to handle this greenhouse gas. This article explores options for the first part of the process: CO2 separation and capture.
-
O&M
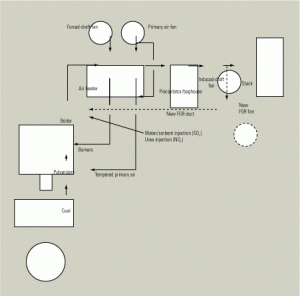
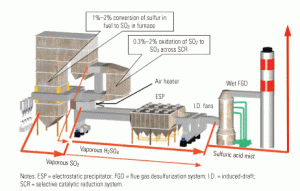
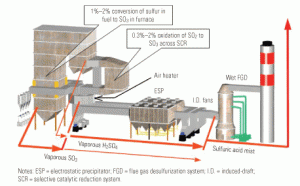
SO3’s impacts on plant O&M: Part III
Part I of this three-part series (POWER, October 2006) explored the negative impacts of sulfur trioxide (SO3) on the operations and maintenance of back-end plant equipment. Part II (February 2007) listed and quantified the likely and potential benefits of limiting the concentration of SO3 in flue gas to 3 ppm at the entrance to the air heater. This final part describes the characteristics of an optimal SO3 removal technology and details the operating experience of a patented process that has worked successfully at a half-dozen plants for up to three years.
-
O&M
Speaking of Coal Power: Coal in a Carbon-Constrained World
Carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) have elbowed their way into the nation’s lexicon with the rise in concern over climate change. But few of the journalists who are hyping global warming have taken the trouble to learn the ins and outs of producing affordable electricity from coal. Citizens of the industrialized world now wring their […]
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Glaciers and New Coal Plants
The big buzz still echoing through world of coal-fired generation is the move by two big-bucks private equity investors to take TXU Corp. off the public market, including scuttling announced plans for eight new pulverized coal – fired plants. That leaves alive plans for three new units at TXU’s existing Sandow and Oak Grove sites. […]
-
Environmental
Birds in the hand for CO2
The January call for a national policy on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by a coalition that includes some of America’s largest companies and electric utilities—GE, Alcoa, Dupont, Duke, FPL, and PG&E—makes clear that carbon management is now as much of a raison d’être for CEOs as it has been for environmentalists. The momentum to reduce […]
-
Gas
Global Monitor (February 2007)
China to buy four AP1000 reactors / Midwest Gen, Blagojevich reach pollution deal / Behold, the carpet gasifier / AREVA casks green-lighted by NRC / Brookfield Power upgrades Oswego Falls / Korea fires up 50-MW landfill gas project / Alstom lands big Russian deal / POWER digest / Correction
-
O&M
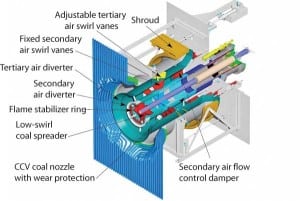
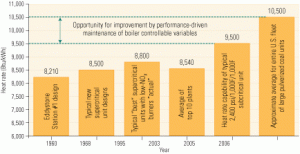
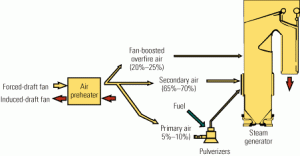
To optimize performance, begin at the pulverizers
A systematic, performance-driven maintenance program for optimizing combustion can achieve great results. The challenge for an O&M staff is deciding which proven strategy and tactics for reducing NOx and improving plant reliability to adapt and implement. The structured approach presented here has proven its worth at several plants that have wrestled with problems similar to yours.
-
O&M
SO3’s impacts on plant O&M: Part II
Part I of this three-part series (POWER, October 2006) explored the negative impacts of sulfur trioxide (SO3) on the operation and maintenance of back-end plant equipment. In this issue, we list and quantify the likely and potential benefits of limiting the concentration of SO3 in flue gas to 3 ppm at the entrance to the air heater. Part III—to appear in the April 2007 issue—will describe the characteristics of an optimal SO3 removal technology and present the technical details and operating experience of one patented process that has worked successfully at a half-dozen plants for up to three years.
-
Coal
Sealing abandoned mines with treated flyash kills two birds with one stone
Environmentally benign disposal of coal combustion products/by-products (CCPs) such as flyash and bottom ash has been a problem since the first coal-fired power plant went on-line. In recent years, ways have been developed to recycle CCPs into useful commercial products like bricks and roadbase. This article describes an innovative State of Maryland program that is putting CCPs to yet another use: stabilizing abandoned mines to permanently sequester acids and harmful metals.
-
Coal
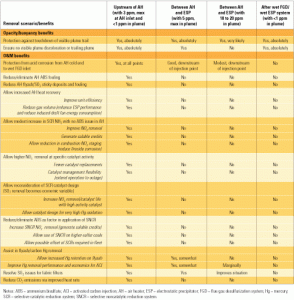
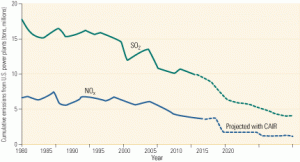
NOx, SO3 in the spotlight at NETL’s 2006 Environmental Controls Conference
As emissions caps drop, technological solutions must become increasingly effective and efficient. Researchers, equipment vendors, and plant operators are exploring alternatives to SCR and SNCR, with a view to reducing the overall costs of NOx reduction. They’ve also achieved 95% to 99% removal of SO3, with no visible plume opacity.
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: Shedding More Heat Than Light
When Charles Dickens began A Tale of Two Cities with, "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times," he was referring to the French Revolution of the late 18th century. But Dickens’ words apply equally well to the American generation industry of the late 20th century. A decade of overbuilding U.S. […]
-
Gas
Global Monitor (Nov/Dec 2006)
Renewables require rethinking just about everything/Torque-splitting drive train improves wind turbine reliability/Waste gas–burning engines reach milestone/Hybrid power plant targets pipeline losses/Power from paint/Gulf Coast Power Association conference report/Pat Wood talks about the challenges facing ERCOT
-
Legal & Regulatory
Renewable power: Environmental or political product?
What’s in a name? Plenty, if the word is "renewable." Intuitively, most people outside the energy industry consider hydroelectric power "renewable." The dictionary defines the word as follows: "capable of being replaced by natural ecological cycles." Accordingly, rainwater should indisputably qualify as renewable. Yet since the early days of renewable portfolio objectives, most hydro […]
-
O&M
SO3’s impacts on plant O&M: Part I
The visible consequences of sulfuric acid aerosol emissions—opaque stack emissions called “blue plumes”—are merely the tip of an iceberg. In sufficient concentration, SO3 also can increase corrosion and fouling of equipment and components downstream of the furnace while decreasing their efficiency and penalizing overall plant heat rate.
-
O&M
Apply the fundamentals to improve emissions performance
The O&M staff of AES Westover Station wisely took a holistic approach to optimizing combustion within Unit 8’s boiler in order to reduce its NOx emissions while maintaining acceptable levels of carbon-in-ash content. The results of major modifications—centered on the addition of a fan-boosted overfire air system—were a 60% reduction in NOx levels, improved unit reliability, and a project payback period measured in months rather than years. As this project proved, the whole is more than the sum of its parts.