Coal
-
Coal
CO2 Injection Begins at Fully Integrated Coal-Fired CCS Project
Injection of carbon dioxide has begun at one of the world’s first fully integrated coal-fired carbon capture, transportation, and geologic storage projects.
-
Coal
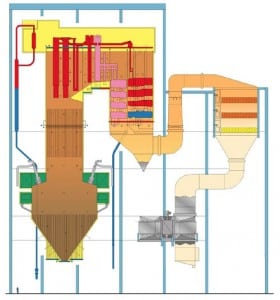
Jinzhushan 3: The World’s First PC-Fired Low Mass Flux Vertical Tube Supercritical Boiler, Part 1
The world’s first supercritical pulverized coal–fired low mass flux vertical tube Benson boiler is Jinzhushan 3, located in the Hunan Province of the People’s Republic of China. The 600-MW Babcock & Wilcox Power Generation Group Inc. once-through boiler burns Chinese anthracite using downshot pulverized coal (PC) technology. Part 1 of this three-part article provides a project summary and overview. The other two parts will look at technology features of the unique boiler design and plant performance test results.
-
O&M
Cycle Chemistry Commissioning Deserves Its Own Strategy
After years of development, design, and construction, your plant is finally nearly ready for startup. But don’t light that cigar yet—at least not until you’ve developed a strategy for commissioning your water cycle chemistry. Root causes of corrosion can be predicted and avoided. The best way to avoid corrosion is to develop and implement plant-specific cycle chemistry commissioning guidelines.
-
O&M
Give Your Plant a Dust Control Tune-Up
Because Powder River Basin (PRB) coal is smaller, more friable, and contains more fine particulates than bituminous coal, controlling the fugitive dust generated as PRB coal moves from bunker to burner tip is problematic. The challenge for material-handling systems at power plants that have switched coals is to minimize this dust and capture it cost-effectively and without compromising safety.
-
Coal
Reactions to Federal Court Striking Down CSAPR
In a landmark ruling that has been seen as a major victory for thermal generators, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit vacated the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) in August, finding that it violated federal law. The EPA must now continue implementation of the Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR) until it can promulgate a replacement, which likely will not happen until at least 2014.
-
Coal
Coal to Gas Once More for Dominion
Dominion Virginia Power plans to convert its oldest coal-fired power plant, the 227-MW Bremo Power Station near Bremo Bluff, Va., to natural gas, the company announced earlier this month. The two-unit plant would be the ninth in its fleet to be closed or converted to alternative fuels.
-
Coal
PPL Montana to Mothball Corette Coal Plant, Cites Environmental Rules, Economic Factors
PPL Montana plans to mothball its 154-MW coal-fired J.E. Corette power plant in Billings, Mont., starting in April 2015. The company cited "effects of pending Environmental Protection Agency [EPA] regulations combined with economic factors," as reasons for its decision.
-
Coal
RWE Sets Closure Dates for 2-GW Didcot and 1-GW Fawley Plants
RWE npower, the German energy company’s UK arm, on Tuesday said it would shutter its coal-fired 2,000-MW Didcot A Power Station in Oxfordshire and the 1,000-MW oil-fired Fawley Power Station in Hampshire at the end of March 2013 under the European Union’s (EU’s) Large Combustion Plant Directive (LCPD).
-
Coal
Progress Shutters 382-MW H.F. Lee Coal Plant
Progress Energy last week shuttered its 382-MW coal-fired H.F. Lee power plant near Goldsboro, N.C. The 1951-built station is the second to be retired under the Duke Energy subsidiary’s fleet modernization program.
-
Coal
Congressional Briefs: Back from Recess
Congress has returned from its summer break. As the House prepares to vote on its Upton-Stearns "No More Solyndras Act," lawmakers also expect to focus on a bill that could prohibit finalization of any Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) power plant rules that curb greenhouse gas emissions while carbon capture and storage technology is commercially unavailable. House Democrats, meanwhile, called for hearings to examine the impacts of climate change on the nation’s generators.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: A Big Switch
The widespread transition from coal to natural gas for new generation is exemplified by the morphing fleets of some of the biggest U.S. generators. Figures show the amount of power generated by each company using coal (top) and natural gas (bottom). Sources: POWER, NextEra, Duke Energy, Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), Southern Co., American Electric Power […]
-
Coal
EU Ruling Slackens Poland’s Coal Power Expansion Ambitions
Poland, a country that currently depends on coal power for nearly 85% of its electricity and plans to build another 11,300 MW of new coal-fired capacity by 2020, suffered a critical planning setback in mid-July as the European Union (EU) effectively blocked the country from using free carbon emission permits to build new coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
Major Projects Commissioned in the U.S., Kuwait, and India
Several major power plants around the world began operations over the past months.
-
Coal
Chile’s Power Challenge: Reliable Energy Supplies
Droughts, unreliable gas imports, and protests against proposed projects have hampered the Chilean power sector and its largest economic driver, the copper-mining industry. Recent policies designed to foster more reliable supplies are a move in the right direction, but remaining obstacles are formidable.
-
Coal
Federal Court Holds TVA Liable for Kingston Coal Ash Spill
A federal district court on Thursday ruled in favor of more than 800 plaintiffs when it held the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) liable for the December 2008 failure of coal ash containment dikes at its Kingston Fossil plant in Roane County, Tenn., that resulted in the spill of more than a billion gallons of coal ash sludge.
-
Coal
Carbon Dioxide Injection Begins at Fully Integrated Coal-Fired CCS Project
Injection of carbon dioxide began last week at one of the world’s first fully integrated coal-fired carbon capture, transportation, and geologic storage projects. The "Anthropogenic Test" conducted by the Southeast Regional Carbon Sequestration Partnership (SECARB) transports carbon dioxide via a 12-mile pipeline from a 25-MW post-combustion carbon capture facility at Southern Co.’s 2,657-MW Plant Barry in Bucks, Ala., and sequesters it within a saline Paluxy Formation at the nearby Citronelle Oil Field operated by Denbury Resources.
-
Coal
Four Workers Dead, Others Severely Injured in Indian Conveyor Belt Fire
A fire sparked by a conveyor belt at a coal-fired power plant in India’s southern state of Tamil Nadu has killed four workers and seriously injured four others, news media reported on Tuesday.
-
O&M
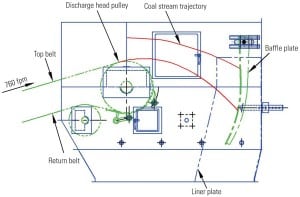
Flow Control Chutes Reduce Fugitive Coal Dust
Moving thousands of tons of coal per hour at high speeds through a complex handling system is a main cause of airborne coal dust in a coal-fired plant. Depending upon the coal’s characteristics, that dust can become explosive when its concentration reaches 80 g/m3 and, hence, a threat to life and property. The best option is to stop the dust from becoming airborne in the first place.
-
Coal
New Environmental Rules Keep Pressure on Coal-Fired Generation
New U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulations affecting the nation’s coal power plants are routinely in the national news. The latest proposed rule focuses on the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. With a substantial amount of coal generation expected to be shut down (up to 40 GW to 50 GW in the coming years by some accounts), the new regulations are increasing the likelihood that this lost capacity will not be replaced by new coal generation.
-
Coal
Tactical Advantage
A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit on June 26 unanimously rejected all pending legal challenges against the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) interpretation of the Clean Air Act (CAA) that allows the agency to regulate greenhouse gases (GHGs). What is the EPA’s future strategy in its war on coal?
-
-
O&M
Plant of the Year: AES Gener’s Angamos Power Plant Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
AES Gener recently completed construction of twin coal-fired, 260-MW units in the electricity-starved desert of northern Chile that may serve as models for future hybrid-fossil plant designs. For meeting an aggressive construction schedule, integrating a 20-MW battery energy storage system, embracing desalination, using the first-of-its-kind seawater cooling tower in South America, and employing innovative financing methods, the AES Gener Angamos plant has earned POWER’s 2012 Plant of the Year Award.
-
Coal
WPL to Retire Three Coal Units, Tamp Down Pollution Emissions with New Controls
Wisconsin Power and Light (WPL) Co. plans to retire three of its oldest and smallest coal-fired generating units and invest $1.4 billion into the company’s generating fleet over the next five years to ensure it will be able to manage "current and emerging environmental regulations," the Alliant Energy Corp. subsidiary announced on Friday.
-
Coal
Consent Decree Could Force Closure of FirstEnergy Coal Ash Impoundment Facility in Penn.
A lawsuit filed in federal court on Friday by Pennsylvania’s Department of Environment Protection (PDEP) alleges that FirstEnergy’s Little Blue Run Dam coal ash impoundment pond in Beaver County, a facility that stores coal ash from the generator’s 2,470-MW Bruce Mansfield coal-fired power plant in Shippingport, Pa., has leached heavy metals in drinking water supplies and surface water. A proposed consent decree could force the generator to shut down the impoundment facility.
-
Coal
Eight Oxy-Combustion Projects Get DOE Awards to Advance CCUS
The Department of Energy (DOE) on Thursday announced it would award $7 million to eight projects to advance the development of transformational oxy-combustion technologies capable of high-efficiency, low-cost carbon dioxide capture from coal-fired power plants. Leveraged with recipient cost-sharing to support about $9.4 million in total projects, the awards are expected to support the development and deployment of “carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS)” by focusing on further improving the efficiency and reducing the costs associated with carbon capture.
-
O&M
Why Coal Plants Retire: Power Market Fundamentals as of 2012
Announcements about coal plant retirements have become commonplace. Are new EPA rules completely to blame, or are there other power market pressures at play?
-
Coal
Design Features of Advanced Ultrasupercritical Plants, Part III
Advanced ultrasupercritical (A-USC) is a term used to designate a coal-fired power plant design with the inlet steam temperature to the turbine at 700C to 760C. In the first two parts of this three-part report, we introduced the A-USC boiler and the metallurgical advancements required for the A-USC boiler to operate at such high temperatures. This final report explores the A-USC boiler’s unique design challenges.
-
O&M
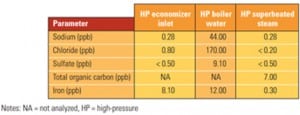
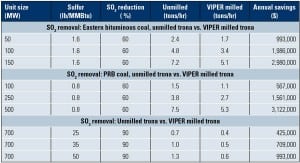
In-Line Sorbent Milling Improves Dry Sorbent Injection Performance
Complying with air emissions rules doesn’t always require construction of a scrubber or SCR. Finely ground trona has proven to be very successful at economically removing SO3, SO2, and HCl from stack gases.
-
Coal
Federal Court Rejects Challenges to EPA Industrial, Automotive GHG Rules
A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit on June 26 ruled that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was "unambiguously correct" in its interpretation of the Clean Air Act (CAA) to regulate carbon dioxide emissions. The federal agency’s endangerment finding that greenhouse gases (GHG), including carbon dioxide, are a threat to public health and welfare, and its decision to set limits for industrial and automotive emissions of GHGs, was "neither arbitrary nor capricious," the court ruled. The court, however, found that it lacked jurisdiction to review the timing and scope of the GHG rules that affect larger stationary sources, including new coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes Clean Air Standards for PM2.5
In response to a court order, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed updates on June 15 to its national air quality standards for harmful fine particle pollution, including soot (known as PM2.5). The agency says that 99% of U.S. counties are projected to meet proposed standards without any additional actions.