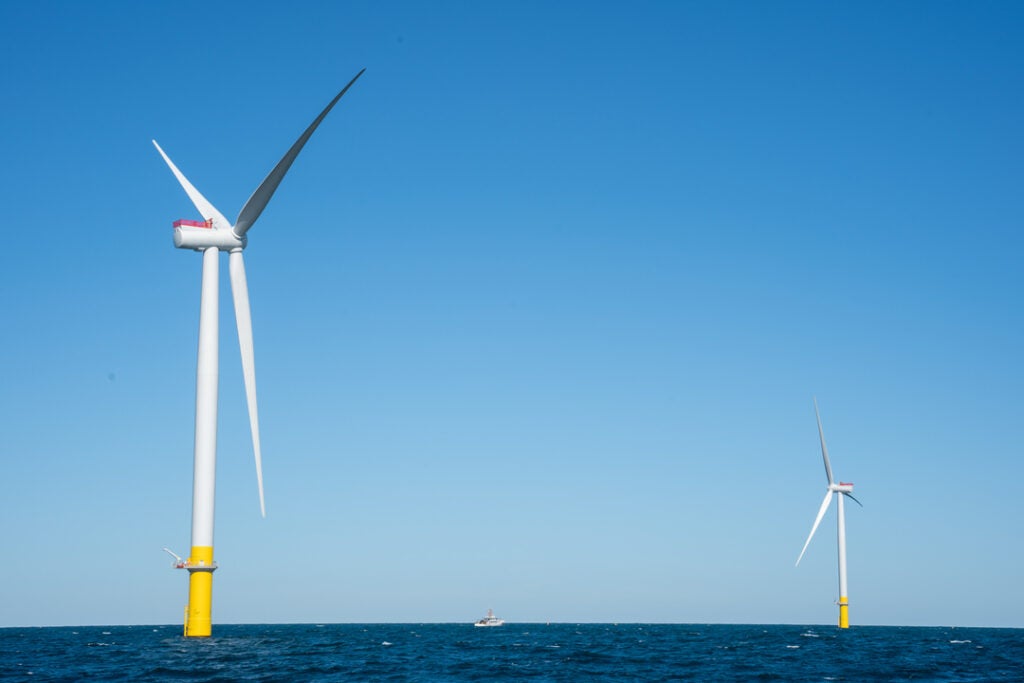
Analysis of the levelized cost of energy shows how renewables have become more cost-efficient every year. Today, the least-expensive way to meet energy needs is with renewable resources. For industries at risk of power outages or those requiring always-on power, clean energy projects can offer a lifeline.
Fundamentally, distributed energy resources (DERs) can give organizations a hedge against increasing energy costs, helping meet decarbonization goals and enabling cost-effective and sustainable electrification. Further, microgrid systems that balance how, when, and where electricity is used enable greater control over energy infrastructure. These systems often integrate existing onsite energy sources with DERs and storage—providing affordable power when energy prices are high, bolstering resilience when the grid is down, powering increasing electrical loads and reducing carbon footprint.
Want to learn more about DERs and the decentralization of power generation. Read “Central Theme for Energy’s Future: Decentralizing Power Generation” in the January 2025 issue of POWER.
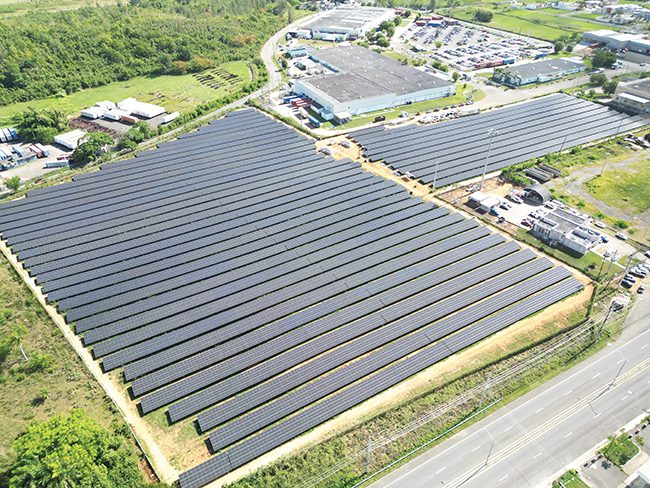
A prime example of this approach is the clean energy microgrid project completed last year at Eaton’s Arecibo, Puerto Rico, manufacturing facility, where the company produces circuit breakers for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. This microgrid is a first-of-its-kind in Puerto Rico, and it significantly reduces the facility’s carbon footprint while enhancing energy resilience and supporting local infrastructure.

Eaton in September 2024 received the “International Energy Project of the Year” award from the Association of Energy Engineers (AEE) for the Arecibo project.
An important first step of this project was simply reducing how much energy was consumed at the site. By implementing comprehensive energy efficiency measures, Eaton achieved a remarkable 45% reduction in energy usage at the plant. The addition of a solar-plus-storage microgrid improved the company’s control over energy supply and costs. Collectively, these initiatives are significantly boosting Eaton’s energy resilience, cutting carbon emissions and lowering energy expenditures by nearly 20%.

The microgrid currently meets more than half of the facility’s energy needs. It incorporates 5 MW (MWac) of solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity and about 1.1 MW of battery storage, tying directly into existing onsite generators. This architecture can generate nearly 10 GWh of renewable energy annually, and prevents the release of about 7,100 metric tons of carbon dioxide each year.
A key feature of this microgrid is its ability to balance electricity consumption based on real-time demand, providing greater control over onsite energy resources. This includes the ability to operate independently from the grid, ensuring continuous power supply during outages.

The microgrid is also engineered to withstand Category 5 hurricane-force winds, which was an integral design consideration for the island location. Further, in normal grid-connected conditions, the system can generate renewable energy that not only serves Eaton’s facility but also feeds back into the local grid, reducing the burden on Puerto Rico’s utility infrastructure. Following the success of the Arecibo project, Eaton is moving forward with a second microgrid at the company’s Las Piedras manufacturing facility to further enhance energy resilience across the island.
The need for sustainable, resilient, and cost-effective energy solutions is more pressing than ever. Projects like the Arecibo microgrid serve as a blueprint for integrating clean energy into industrial operations, benefiting both businesses and the communities they serve. As organizations increasingly electrify their operations and expand electric vehicle charging infrastructure, microgrids can often provide the necessary onsite capacity additions quickly and cost-effectively, especially when government funding and tax incentive programs are available.
Successful clean energy initiatives require meticulous planning and stakeholder collaboration, including technology providers, financing partners and local utilities. There is no universal solution or “one-size-fits-all” approach for modernizing and decarbonizing energy systems. Tailored strategies that align with specific organizational goals are essential. Establishing clear operational goals and maintenance responsibilities from the outset is also critical for long-term success.
Eaton focuses on clean energy projects that maximize impact, especially in regions where energy sources remain heavily reliant on fossil fuels. These initiatives not only help manage energy costs but also support the company’s operational and regulatory objectives.
Deployment of clean energy resources is not just a forward-thinking strategy, it is part of doing business right, providing organizations a competitive advantage. As organizations navigate an evolving energy landscape, it’s important to consider how the functionality of DERs and microgrids can help maximize the capabilities of energy systems to build the foundation for a stronger, more resilient, and more sustainable future across a company’s operations.
—Rich Gorze is senior global energy manager for Eaton.