-
Renewables
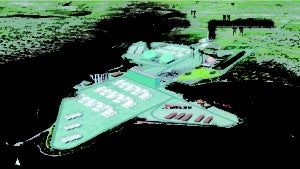
Redevelopment Project Converts Site from Coal to Renewables
The former Brayton Point coal plant’s transformation into an East Coast logistics and manufacturing center, renewable energy hub, and international seaport is a symbolic milestone representing the first of
-
Coal
Removing Asbestos and Regulated Materials Key to Power Plant Decommissioning
Retiring and decommissioning coal power plants is becoming a more-frequent occurrence around the world. The job comes with many challenges, but projects in the U.S. and UK have proven that remediation and
-
Safety
The Future Direction of Respiratory Protection
An estimated 5 million U.S. workers wear respirators. Employers are required to provide National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)-certified respirators using a written respiratory protection program enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Design and manufacturing focus on fit, comfort, and ease of use across product lines incorporating advanced technologies, such […]
-
Nuclear
A Thorium Molten Salt Reactor When and Where You Need It
ThorConIsle is an offshore 500-MWe thorium molten salt reactor constructed inside a ship’s hull, ready to provide power from navigable waterways. The ThorCon “pot” operates at a pressure of 3 bar gauge
-
O&M
A Semi-Automated Metal Decontamination and Recycling Process
A semi-automated and patented process for decontaminating and recycling radioactively contaminated heat exchanger tubes has been successfully demonstrated at the Ignalina nuclear power plant in Lithuania
-
Nuclear
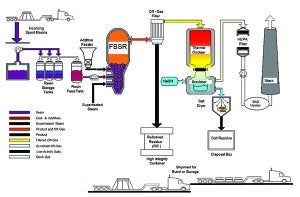
Fluidized Bed Steam Reforming Technology Reduces Volume of Radioactive Waste
A patented Fluidized Bed Steam Reforming (FBSR) technology uses superheated steam—instead of an open flame—and mineralizing additives to treat and immobilize radionuclides in a water-insoluble matrix
-
O&M
Maintaining Nuclear Plant Ice Condensers: A ‘Cool’ Responsibility
Although nuclear plant ice condensers are rare—only seven sites throughout the world have them—the theory behind these passive heat sinks is quite novel. In fact, some next-generation plant designers have built upon the concept and incorporated passive accident intervention schemes into their plans. A nuclear plant ice condenser is a passive, static heat sink that […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
ASME Operation and Maintenance lnservice Testing Program Ensures Nuclear Component Operational Readiness
Originally embedded in the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code , today the Operation and Maintenance of Nuclear Power Plants standard for inservice testing of pumps
-
Nuclear
No Longer an Afterthought, Nuclear Plant Decommissioning Industry Matures
The once seemingly insurmountable technical challenges of dismantling a commercial nuclear plant have been largely eliminated through experience. Decommissioning processes have been standardized and optimized
-
Nuclear
Safety Culture: A Common Construct Requiring Commitment from the Board Room to the Shop Floor
An intrinsically motivated safety culture does not usually emerge fully formed. Decisions and actions affecting behaviors are often linked to entrenched attitudes and beliefs within companies. Commitment and
-
O&M
New Renewable Projects Face Old Safety Hazards
Many of the dangers existing at conventional power plants also threaten personnel in the wind and solar energy sectors. All workers can benefit by reviewing lessons learned and implementing corrective actions to improve health and safety performance. The expanding wind and solar energy sectors are not immune to industrial hazards affecting all energy generation markets. […]
-
Nuclear
Watts Bar Unit 2: A “Deferred Nuclear Plant” Gets Back into the Game
Construction was suspended on Watts Bar Nuclear Plant Unit 2 in the late 1980s, and the plant sat idle for more than 20 years. Now, through equipment refurbishment and replacement, Unit 2 is on track to become the first new commercial nuclear reactor to come online in the U.S. in the 21st century. Electricity consumption […]
-
Nuclear
Seismic Hazard Resiliency at U.S. Nuclear Power Plants
Since the beginning of the U.S. commercial reactor industry, regulatory agencies have required that nuclear power plant designs take into account the potential threats posed by natural hazards such as earthquakes and floods. The tsunami-caused disaster in Japan in 2011 prompted renewed attention worldwide on these hazards. Given the devastation caused at Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi […]
-
O&M
Prepare Your Nuclear Plant for Cold Weather Operations
During the Jan. 3–12, 2014, polar vortex that brought record-setting cold temperatures and severe winter weather to much of the U.S., nuclear plants not only survived, but thrived. According to the Nuclear
-
Nuclear
Evolved Strategy Accelerates Zion Nuclear Plant Decommissioning
The decommissioning of nuclear plants has developed into a mature industry in the U.S. It started in the 1960s with the dismantling of low-power prototype and test reactors originally built to demonstrate
-
Nuclear
UK Uses “Lead and Learn” Strategy for Magnox Reactor Fleet Decommissioning
Many American readers may not realize that, although the first major nuclear fission successes were achieved in the U.S., after World War II, when nations expanded their nuclear research to include power
-
Nuclear
Top Plant: Bruce Nuclear Generating Station, Kincardine, Ontario, Canada
Owner/operator: Bruce Power According to Duncan Hawthorne, president and CEO of Bruce Power, 2012 was one of the most successful years in the company’s history. The $7 billion investment to revitalize four
-
Nuclear
V.C. Summer Nuclear Station Construction Update
On Mar. 30, 2012, South Carolina Electric & Gas Co. (SCE&G), principal subsidiary of SCANA Corp., and Santee Cooper, South Carolina’s state-owned electric and water utility, received approval for
-
Nuclear
SILEX Process Promises Third-Generation Uranium Enrichment Technology for U.S.
On Sept. 25, 2012, the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) issued a construction and operating license (COL) to General Electric-Hitachi Global Laser Enrichment LLC (GLE) for its uranium enrichment plant
-
Nuclear
OPG Proposes New Nuclear Construction at Darlington
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission has issued a License to Prepare Site for Ontario Power Generation’s Darlington station expansion. This is the first of a series of licenses required to prepare, construct, and operate new nuclear reactors and the first of its kind issued in Canada in over a quarter-century.
-
Nuclear
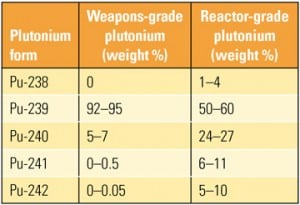
MOX Fuel Fabrication Facility: Turning Swords into Plowshares
The U.S. Department of Energy contracted Shaw AREVA MOX Services LLC to design, construct, and operate a Mixed Oxide (MOX) Fuel Fabrication Facility (MFFF) at its Savannah River Site in South Carolina. The MFFF will convert depleted uranium and excess weapons-grade plutonium stockpiles, equivalent to approximately 17,000 nuclear weapons, into MOX fuel assemblies that will be used in U.S. nuclear power plants by 2018.
-
Nuclear
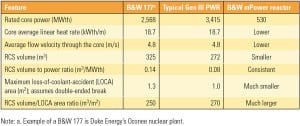
Small Is the New Big: The B&W Small Modular Reactor
Small reactors are big news, particularly the 180-MWe Generation III++ Babcock & Wilcox mPower small modular reactor (SMR). This SMR has all the features of its larger cousins, but the entire reactor and nuclear steam supply system are incorporated into one reactor vessel, all about the size of single full-size pressurized water reactor steam generator. Expect the first mPower—and probably the first SMR—to enter service before 2022.
-
Nuclear
Vogtle Gets Green Light
In February 2012, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission approved two combined construction and operating licenses for Southern Nuclear’s Plant Vogtle Units 3 and 4 in Georgia. They were the first licenses ever approved for a U.S. nuclear plant using the one-step licensing process and the first allowing construction in more than three decades. Now the real work begins.
-
Nuclear
The U.S. Spent Nuclear Fuel Policy, Part 2: Playing Hardball
Ongoing investigations into cancellation of the Yucca Mountain project have revealed an astonishing number of irregularities by agencies responsible for the project. Those investigations have exposed a broken system that failed to properly manage the project and that surrendered to political pressure. Worse still, the draft report of President Obama’s Blue Ribbon Commission on America’s Nuclear Future gave the industry little reason to hope that there would ever be a long-term nuclear waste fuel repository.
-
Nuclear
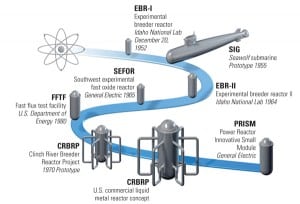
PRISM: A Promising Near-Term Reactor Option
PRISM is an advanced sodium-cooled reactor that simultaneously reduces proliferation concerns by consuming transuranics and weapons-grade plutonium and closes the nuclear fuel cycle. PRISM’s passive safety systems, successfully demonstrated in earlier liquid metal reactor programs, combined with modern design requirements, make PRISM invulnerable to most serious accidents that can affect light water reactors.
-
Business
HAZCOM Is Essential for Avoiding Explosive Situations
In 1983, OSHA published its Hazard Communication (HAZCOM) Standard, which requires that the hazards of all chemicals used in the workplace be communicated to employees so that responsible protective measures can be taken. Today, HAZCOM remains near the top of the list of most frequently violated OSHA standards that result in a citation. The 1917 Halifax Explosion, one of the world’s largest nonnuclear explosions, testifies to what can happen when you don’t have—or don’t follow—an effective HAZCOM program.
-
Nuclear
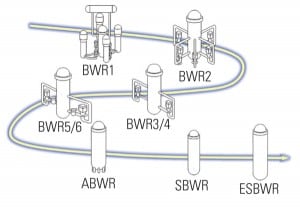
The Evolution of the ESBWR
The commercial nuclear industry is in the midst of developing multiple reactor technology options. Next in our series of articles exploring competing reactor technologies are GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) and Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR). The design improvements incorporated into these reactors include passive safety systems, design and construction simplification, and component standardization to reduce construction and operating costs.
-
Nuclear
Bruce A Proves There Are Second Acts in Nuclear Power
The refurbishment and restart of all four CANDU reactors at Bruce A may be Ontario’s most significant and complex power generation project since the first phase of the Bruce Nuclear Generating Station was built more than 30 years ago. Units 1 and 2 are expected to be synchronized in 2011 and return to commercial service by early 2012, joining Units 3 and 4, which restarted in 2004 and 2003 respectively. POWER visited Bruce A in April to witness the project’s progress.
-
Nuclear
The U.S. Spent Nuclear Fuel Policy: Road to Nowhere
The Nuclear Waste Policy Act and Amendments of 1982 and 1987 established a national policy and schedule for developing geologic repositories for the disposal of spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes. Those deadlines have come and gone; the cancellation of Yucca Mountain was only the latest failure of this policy to become reality. The task of finding a new storage location is now a political committee’s homework assignment. History tells us that committee members have been given an impossible task.
-
Nuclear
Plant Vogtle Leads the Next Nuclear Generation
In August 2009, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) issued its fourth Early Site Permit for two new units at Southern Nuclear’s Vogtle site and its first for the Westinghouse AP1000 pressurized water reactor design. The two new units planned for Vogtle also became the reference plant for the AP1000 under NuStart in June 2009. This means Vogtle Units 3 and 4 will be the first licensed installations of the new AP1000 reactor design in the U.S. Plant Vogtle is expected to get the NRC’s approval to begin construction in 2011.
Search