-
Nuclear
Global Monitor (July 2007)
Pistachio plant gives new meaning to green/Slightly sun-powered grill/Will lithium revolutionize hydrogen storage?/Calpine’s major Geysers geothermal upgrade/Rhone-Alps is French PV hot spot/Fuel cell–powered ice-resurfacing machine/Westinghouse proposes revised AP100 design/Sandia perfects solar alignment/SCE wants comprehensive coal study/POWER digest
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (July 2007)
Hydro-demolition speeds reactor dome entry;
Tips for keeping your unit stable;
Air makes heavy move a breeze -
Legal & Regulatory
Cogeneration qualifying facilities warrant extended contracts
Congress’s enactment of the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 (PURPA) triggered a revolution in the development and construction of power plants. PURPA’s creation of an independent class of generators—qualifying facilities (QFs)—exposed a century-old economic myth that had justified restricting ownership of generating facilities to governmental and investor-owned utilities (IOUs). The success of QFs […]
-
Coal
Westar’s Lawrence Energy Center wins for not blinking on safety
It took Westar Energy eight years to upgrade the Lawrence Energy Center to burn Powder River Basin coal. Its zero lost-time accident record during the million-man-hour project is a testament to Westar’s commitment to workplace safety. Here’s your backstage pass to meet the PRB Coal Users’ Group 2006 Plant of the Year.
-
Coal
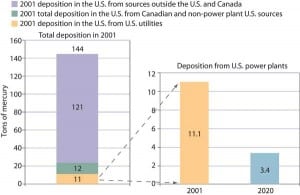
Mercury Control: Capturing Mercury in Wet Scrubbers: Part I
Are you using your flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system to its highest potential? You might not be if you’re not making it do double duty. It seems that million-dollar wet scrubber you installed to rid your flue gases of sulfur dioxide also can do a decent job of capturing mercury — under the right conditions. […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: IGCC Sticker Shock
Former Illinois Senator Everett Dirksen once observed, "A billion here and a billion there, and pretty soon you’re talking real money." The same can be said about skyrocketing estimated costs of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants as their designs are fleshed out. The higher price tags shouldn’t be a surprise — the more you learn […]
-
O&M
PRB Tech Notes: Lawrence Energy Center Showcases Winning Plant
Lawrence Energy Center (LEC) proudly hosted about 60 representatives of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) at its July 24th open house, luncheon, and plant tour. LEC was named the PRBCUG’s 2007 Plant of the Year at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference and Exhibition in Chicago, May 1 – 3. Traditionally, the winning […]
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: Smart Sootblower Tailors Cleaning to Need for It / Blending’s Impact on Coal Quality
The 1990 amendments to the Clean Air Act require coal-fired power plants to reduce their emissions of the pollutant SO2. To do so, many have switched to, or are considering switching to, Powder River Basin (PRB) coal. Unfortunately, PRB coal has a tendency to leave excessive and tenacious deposits on boiler heat-exchange surfaces. Complicating the problem, the distribution of the deposits is far from uniform.
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Coal to Synfuels: Deal or No Deal?
Synfuels’ political bubble has burst in Washington, but the market may step in where Congress fears to tread. When coal industry interests, in the form of the CTL Coalition, got a bill with strong federal support for coal-to-liquids technology before the Senate this spring, it appeared that the political skids were greased for some kind […]
-
O&M
Lignite Drying: New Coal-Drying Technology Promises Higher Efficiency Plus Lower Costs and Emissions
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Great River Energy are testing a new coal-drying technology that could dramatically reduce the emissions of lignite-burning power plants. The project was selected for funding during Round I of the DOE’s Clean Coal Power Initiative (CCPI), a series of competitions to demonstrate a range of promising clean-coal technologies. […]
Search