Cooling water
-
Water
How Advanced Monitoring and Early Warning Tools Are Revolutionizing Power Plant Cooling Water Intake Management
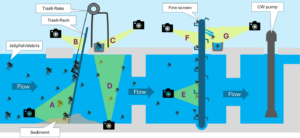
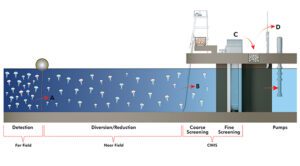
Thermal power plants, nuclear and fossil-fueled, rely on cooling water intake structures (CWIS) to withdraw water for rejecting waste heat. The CWIS serves as a critical interface between engineered systems and the natural environment, making it vulnerable to various external factors such as biological growth, water chemistry changes, hydraulic forces, drifting debris, and meteorologic events. […]
-
O&M
Improving the Efficiency of Power Plant Cooling Ponds
As electricity demand soars during summer heat waves, many power plants find themselves constrained by their ability to cool water efficiently for reuse. Innovative floating cooling technology is enabling
-
Full Coverage
Powering Performance with an Integrated Approach to Cooling Water
Power plant managers know that optimizing cooling water operations will improve efficiency. Using an integrated approach that combines advanced chemistry, digital technologies, such as deposit sensing, and
-
O&M
Preparing Steam and Water Analysis Equipment for Summer Heat
While the effects of extreme summer weather are one thing, even regular summer weather can wreak havoc on steam and water analysis systems (SWAS) without adequate preparation. Summer sunshine and increased temperatures can bring higher heat loads and increased cycling rates that put even more stress on steam and water sampling and related equipment, greatly […]
-
News
Water Intake Reliability in the Age of Environmental Uncertainty
Thermal power plants need a continuous supply of cooling water to operate, but as the natural environment changes, more and more screen blockages are occurring at cooling water intakes. Maintaining intake
-
Legal & Regulatory
B&W to Restructure Power Business, Cites Dismal Coal Projections
Projections that coal utilization will decline faster than previously forecast have spurred Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises (B&W) to shed 200 jobs and restructure its traditional power business that serves coal-fired power generation in a bid to reduce overhead and improve efficiency. The Charlotte, N.C.–based energy and environmental technology and service company said on June 28 […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Federal Judge Thwarts Implementation of “Expansive” EPA Final Waters of U.S. Rule
A federal judge on Thursday halted implementation of the Clean Water Rule that is controversial for its broad definition of “Waters of the U.S.” one day before it was to go into effect, saying it was likely that the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) overstepped its authority when it promulgated the “exceptionally expansive” rule. Judge Ralph […]
-
Press Releases
Video: A Novel Phosphorus-Free Cooling Water Treatment Solution
POWER Associate Editor Aaron Larson recently interviewed LaMarr Barnes, vice president of marketing and business development for U.S. Water Services Inc. U.S. Water is a Minnesota-based integrated water treatment solutions provider that has developed a phosphorus-free cooling water treatment solution, which may be beneficial for power generation companies. Many power plants add phosphate-based treatments to […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
A U.S. Power Industry Regulatory Update
The U.S. power sector has seen a number of developments on the regulatory front in recent months. Here’s where major federal rules stand today. (For a more dynamic and graphic version of this article, see http://powermag.com/long-form-stories/bw-power/ .) GHG Rules New Power Plants. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in September 2013 revised a 2012 proposal to […]
-
Power
Nuclear Plant Deals with Water Shortage Emergency
On Aug. 28, the South Florida Water Management District (SFWMD) approved an emergency order allowing Florida Power & Light (FPL) to divert water from the district’s L-31E Canal system to help moderate unusually high temperatures and salinity that are occurring in the Turkey Point cooling canal system (CCS). The CCS—an approximately 5,900-acre network of unlined […]
-
Coal
EPA Issues Final Cooling Water Intake 316(b) Rule
A final rule released by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) today will affect cooling water intake structures at 544 U.S. power plants and provide those plants with lower-cost compliance options than previously proposed to reduce fish impingement and entrainment. The final rule issued under Section 316(b) of the Clean Water Act applies to facilities that […]