Features
-
Gas
Cheng Cycle flirts with 2 ppm NOx— and CO
Three years ago, an article in POWER described how Cheng Power Systems, by modifying the combustors of several popular gas turbines, had used steam injection to lower the units’ NOx output to about 5 ppm—but some models had substantial CO levels without combustor modifications. Since then, the company has developed new combustor nozzles that recently […]
-
Coal
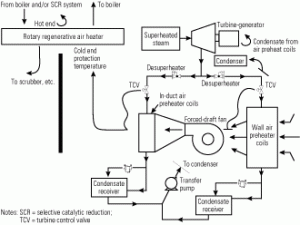
Designing and maintaining steam coil air preheaters for reliability and effectiveness
If engineered well and drained properly, a simple finned-tube heat exchanger can help maximize a fossil-fueled power plant’s combustion efficiency, capacity, and air pollution reduction. Use the guidelines in this article either to return a disabled steam coil air preheater to service or to improve the performance of a unit that may have been wasting […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
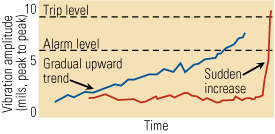
Solving plant vibration problems
Solving insidious vibration problems in rotating equipment may sometimes seem like a black art that requires the right incantation. But identifying the root cause of the vibration is actually a science. By using cutting-edge vibration measurement tools in concert with computer simulations, plant operators can arrive at a permanent, cost-effective solution to virtually any vibration […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
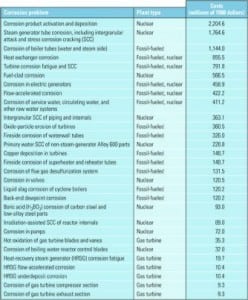
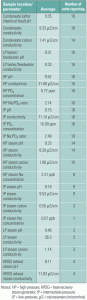
Designing steam cycles to avoid corrosion
U.S. power producers and owners of industrial steam systems each spend about $15.4 billion annually to combat corrosion in their plants. Scale and deposits are thought to be responsible for another $20 billion a year in reduced plant efficiency and lost generation capacity. Corrosion is the primary cause of every other forced outage, and the […]
-
Coal
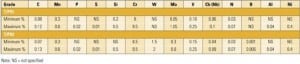
Why new U.S. supercritical units should consider T/P92 piping
T/P92 is being heralded as a superior and lower-cost alternative to T/P91 for new power plants with pressures above 3,600 psi and temperatures above 1,100F—such as the supercritical and ultra-supercritical units proposed to be built in the U.S. over the next few years. The switch from T/P91 to T/P92 would represent the next step in […]
-
Marmaduke
Marmy stops dreaming
Steve Elonka began chronicling the exploits of Marmaduke Surfaceblow—a six-foot-four, steel brush-mustached marine engineer with a foghorn voice—in the pages of POWER in 1948. That was the year that Marmy raised the wooden mast of the SS Asia Sun with the aid of two cobras and a case of Sandpaper Gin. This classic episode, written in the late 1960s, shows that even minor consequences of a steam turbine overhaul can cause problems. And as Marmaduke shows, solving any problem requires equal parts judgment, logic, and experience. Enjoy.
-
Coal
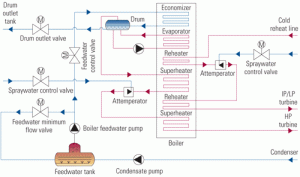
Designing HRSG desuperheaters for performance and reliability
Increased cycling of combined-cycle plants has made precise control of attemperator spray water within heat-recovery steam generators more important if damage to their hardware and piping is to be avoided. Complicating the issue is the industry’s still-limited experience with cycling and the fact that demands on the attemperator and turbine bypass of cycled plants are more stringent than those on baseloaded units.
-
Gas
Fleetwide standardization of steam cycle chemistry
Nearly five years ago, a major IPP began standardizing steam cycle chemistry feed, control, and monitoring across its combined-cycle fleet. This article discusses the steps taken, the costs incurred, and the technical and financial benefits achieved. Although the project focused on non-cogeneration plants, the findings detailed below are broadly applicable to other kinds of plants. However, the specific implementations (especially of the chemistry standards) described may have to be modified slightly for application to cogen plants.
-
Gas
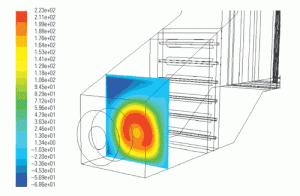
Fluid dynamics of the HRSG gas side
Designers of heat-recovery steam generators are using computational fluid dynamics software as one tool to reveal the invisible forces affecting the flow over, under, around, and through structures such as inlet ducts, distribution grids, and guide vanes.
-
Coal
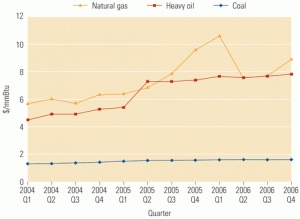
Gas turbine "refueling" via IGCC
The jury is still out on the economic and technical feasibility of burning gasified coal to generate electricity. Gasification technology has yet to be proven on a utility scale, especially with Powder River Basin coal as the feedstock. And on the generation side, there are more questions than answers about the capital cost and availability of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants. But with natural gas prices high and rising, it’s definitely worth examining whether it would be economically and technically feasible to convert the existing U.S. fleet of gas-fired combined-cycle plants to burn gasified coal.