Features
-
O&M
"Blueprint" Your Pulverizer for Improved Performance
Pulverizer throughput is determined by the coal fineness desired for a given coal. However, compromising on coal fineness when your pulverizer isn’t up to snuff can increase NO x and cause many furnace problems. Your least costly option for increasing pulverizer capacity is to pay careful attention to key dimensions and critical tolerances during your next overhaul.
-
Environmental
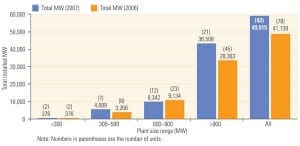
Update: What’s That Scrubber Going to Cost?
POWER published a summary of the flue gas desulfurization system scrubber cost survey conducted by the EUCG’s Fossil Productivity Committee in our July 2007 issue. Although the detailed results of the latest survey are proprietary to EUCG members that participated in it, we are privileged to present the newest summary data. The bottom line: Costs continue to rise but appear to be more predictable.
-
O&M
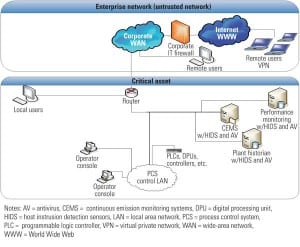
Helping Power Plant Control Systems Achieve NERC CIP Compliance
This guide offers suggestions from a control system engineering perspective for protecting power-generating units that are determined to be critical cyber assets
-
Water
Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment Primer
Purge water from a typical wet flue gas desulfurization system contains myriad chemical constituents and heavy metals whose mixture is determined by the fuel source and combustion products as well as the stack gas treatment process. A well-designed water treatment system can tolerate upstream fuel and sorbent variation over time and consists of multiple process treatment steps arranged in just the right order to produce wastewater acceptable for discharge.
-
Water
Oak Creek Power Plant Upgrades Cooling Water System
Formed suction intake designs have been used in many large vertical pump stations in flood control projects. Space limitations at the Oak Creek Power Plant Expansion Project near Milwaukee, Wisconsin, created a unique opportunity to apply this technology to an 800,000-gpm cooling water system upgrade for the entire Oak Creek Power Plant.
-
Coal
New Laser Technology Helps Reduce Coal-Slagging Headaches
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy is starting to light the way for power plant operators who want to reduce coal ash deposition in their boilers.
-
Business
HTS Cables Speed up the Electric Superhighway
High-temperature superconducting cables deliver up to 10 times as much power as conventional electric power transmission cables. They are poised to help to reduce grid congestion as well as installation and operating costs.
-
Business
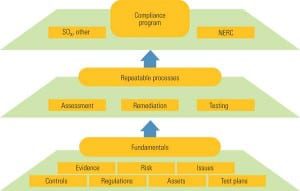
NERC Drives Development of Sustainable Compliance Programs
Compliance with reliability standards has moved beyond the "check the box" phase to one of regulations with real deliverables and fines for noncompliance. Utilities that aren’t vigorously evaluating and refining their compliance procedures today may find NERC’s 2009 audit cycle much more challenging.
-
Coal
A Fresh Look at Coal-Derived Liquid Fuels
Thirty-five percent of the world’s energy comes from oil, and 96% of that oil is used for transportation. The current number of vehicles globally is estimated to be 700 million; that number is expected to double overall by 2030, and to triple in developing countries. Now consider that the U.S. has 27% of the world’s supply of coal yet only 2% of the oil. Coal-to-liquids technologies could bridge the gap between U.S. fuel supply and demand.
-
Nuclear
Patchy Progress in Europe with Radioactive Waste Management
The future of high-level nuclear waste disposal at Yucca Mountain remains uncertain as a new U.S. administration considers its nuclear agenda. The European Union’s policies remain just as unsettled. With new projects under construction in several countries and a nuclear ban in effect in others, no unified long-term storage approach is in sight.