O&M
-
O&M
CSB Releases Hot Work Safety Notice
The Chemical Safety Board (CSB)—an independent federal agency charged with investigating serious chemical accidents such as equipment failure, as well as inadequacies in regulations, industry standards, and safety management systems—recently released multiple reports that should be made part of every power plant’s safety training program.
-
O&M
NFPA Gas Purging Rules Updated
The CSB has made urgent recommendations to the NFPA and the International Code Council to prohibit indoor purging and require companies and installers to purge flammable fuel gases to safe locations outdoors, away from workers and ignition sources.
-
O&M
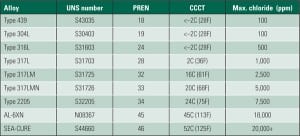
Abrasion-Resistant Pipe Handles Ash Slurry
Steel piping systems are widely used at coal-fired power plants for a variety of purposes, including the conveying of coal ash slurry to nearby settling ponds, the transfer of limestone slurry to absorber spray towers for removal of SO2 and dilute hydrochloric acid from flue gases, and for transporting away the calcium sulfate by-product of the flue gas desulfurization process.
-
O&M
Air Casters Speed Equipment Moves
When it comes to moving megaton items like feedwater heaters or recirculating pumps, conventional moving tools such as wheel rollers, cranes, hoists, and come-alongs may be virtually useless. In some cases, moving large components is dangerous in a space-constrained location surrounded by delicate process control equipment. Feedwater heater and recirculating pump removal and replacement are […]
-
O&M
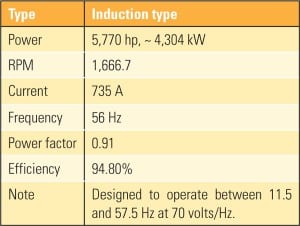
Retrofitting BWR Recirculation Pumps with Adjustable-Speed Drives
Exelon Nuclear recently replaced the original motor-generator sets for its boiling water reactor (BWR) recirculation pumps at its Quad Cities Generating Station Unit 1 with adjustable-speed drives. We examine the actual energy savings, motor-starting characteristics, control accuracy and stability, and motor and cable thermal behavior of this retrofit project.
-
O&M
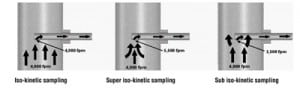
Pulverized Coal Pipe Testing and Balancing
If you want the most accurate test results, it’s worth the extra effort to take isokinetic coal samples from coal pipes when collecting fuel and air measurements. Together, the data collected will allow more accurate balancing of coal pipes, measure fuel fineness, and improve the combustion efficiency of your steam generator.
-
O&M
Air Preheater Seal Upgrades Renew Plant Efficiency
The air preheater is a critical, yet often overlooked, component of the boiler combustion air system. Evaluating and optimizing a heater’s performance is difficult given how entwined it is with the entire combustion system and the lack of standardized calculation tools. Reducing leakage by using modern seal technology will improve combustion efficiency, maintain fan performance, and keep your downstream air quality control equipment operating within spec.
-
O&M
Taming Condenser Tube Leaks, Part II
In Part I of this two-part report we examined the various chemical forces at work in condenser tube leaks, the steam plant components placed at risk, and the suite of instrumentation most capable of providing early warning of a leak. Assuming you were able to repair the leak and quickly resume operation, the next step is to identify the damage mechanisms that caused the problem so you can minimize future leaks.
-
O&M
FBC Control Strategies for Burning Biomass
As a boiler fuel, biomass has shown great promise while suffering from a slow development history. One factor limiting its use has been the combustion system. For the most part, conventional grate-fired boilers have been the only option. Today, the most efficient approach to burning biomass to produce electricity and steam is fluidized bed combustion (FBC). Whether you choose FBC or grate, biomass presents unique challenges to control system designers.
-
O&M
Innovative Cleaning of Air Preheater Coils with Pressurized Liquid Nitrogen
Cleaning air heaters in power plants or recovery boilers has traditionally involved using high-pressure water, chemicals, or steam. These techniques, though effective on moderate airside fouling of heat exchange surfaces, are usually ineffective on the more tenacious deposits that can develop in coal-fired plants. If these deposits are not removed by periodic cleaning, heat transfer in the heaters is reduced, which in turn reduces boiler efficiency and increases a unit’s heat rate. Severe fouling on air preheaters (APHs) can even reduce a unit’s power output.