Nuclear
-
Nuclear
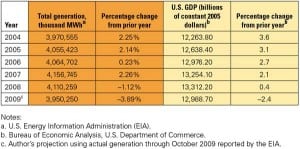
China Begins Operation of First CPR-1000
The first unit of Ling Ao phase II (Unit 3) in Guangdong Province, China, entered commercial operation in late September. The 1,080-MW reactor is the first CPR-1000—a Chinese design—to be built, and its start-up marks a major milestone in the country’s concerted nuclear power expansion.
-
Nuclear
NRC Confident in Long-Term Dry Cask Storage
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) approved an updated “waste confidence” rule in mid-September that reflects the agency’s confidence that spent nuclear fuel (SNF) can be safely stored for at least 60 years beyond the closing date of any U.S. nuclear plant. Approval of this rule was required before the NRC can license any new reactors that will be required to store SNF on site indefinitely.
-
Nuclear
EPRI Updates Spent Nuclear Fuel Storage Handbook
EPRI recently issued a handbook on nuclear spent fuel storage that examines regulatory trends affecting used fuel storage, describes available dry storage technologies, reviews planning considerations for spent fuel storage installations, and discusses technical issues affecting dry storage.
-
Nuclear
Collaborative Team Investigates Long-Term Nuclear Operations
The Atomic Energy Act originally established the length of a U.S. commercial nuclear reactor license as 40 years and made it renewable for another 20 years. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has stated that it bases the length of these licenses (and the 50+ renewed licenses granted to date) not on any particular technical limitation but on whether the plant meets current safety requirements. Does this mean there could be reactor life after 60?
-
Nuclear
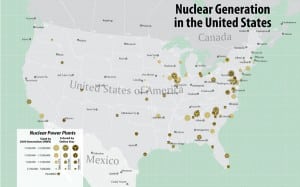
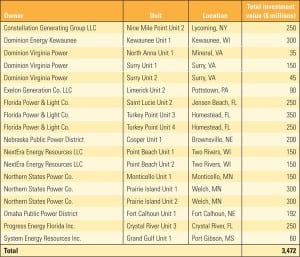
Map of Nuclear Generation in the United States
Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed. For full-sized maps, contact Platts.
-
Nuclear
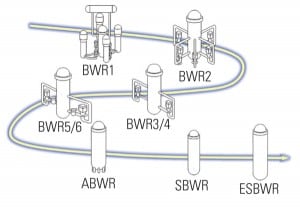
The Evolution of the ESBWR
The commercial nuclear industry is in the midst of developing multiple reactor technology options. Next in our series of articles exploring competing reactor technologies are GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) and Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR). The design improvements incorporated into these reactors include passive safety systems, design and construction simplification, and component standardization to reduce construction and operating costs.
-
Nuclear
Are Smaller Reactors Better?
Is a paradigm shift—an economic and engineering earthquake—in nuclear power plant design on the horizon? For most of the past 50 years, the mantra in planning new nuclear plants has been “bigger is better.” But a growing number of nuclear power engineers and designers are contemplating a world where small is beautiful.
-
Nuclear
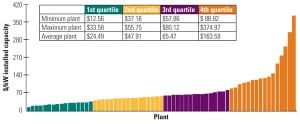
Benchmarking Nuclear Plant Capital Requirements
The EUCG Nuclear Committee’s primary goal is to optimize the costs and reliability performance of participating plants by publishing for its members a comprehensive database of performance metrics and best practices derived through surveys of its membership. Earlier reports examined staffing and performance data. In this exclusive EUCG report, we examine nuclear plant capital requirements.
-
Nuclear
The Best of U.S. Nuclear Developments 2010: Uprates and Loan Guarantees
Utilities are spending billions of dollars on nuclear plant uprate projects, and Southern Company has been offered $8.3 billion in federal loan guarantees to build Vogtle Units 3 and 4 (although the final deal has yet to be signed). Meanwhile, other nuclear developers have slashed preconstruction spending as the cost of the “nuclear renaissance” becomes evident.
-
O&M
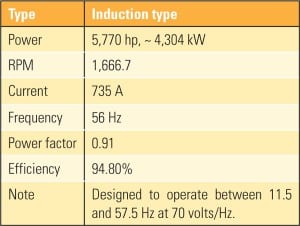
Retrofitting BWR Recirculation Pumps with Adjustable-Speed Drives
Exelon Nuclear recently replaced the original motor-generator sets for its boiling water reactor (BWR) recirculation pumps at its Quad Cities Generating Station Unit 1 with adjustable-speed drives. We examine the actual energy savings, motor-starting characteristics, control accuracy and stability, and motor and cable thermal behavior of this retrofit project.
-
Nuclear
TVA to Complete Bellefonte Unit 1
Thirty-six years after work first began at the 1,600-acre site housing the Bellefonte Nuclear Power Plant in Hollywood, Ala., the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) in August said it plans to invest $248 million to maintain the option to complete the 1,260-MW Unit 1 reactor. The announcement was made as the nation’s largest publically owned utility […]
-
Nuclear
India Kicks Off Construction of Indigenous Nuclear Fleet
India in August began building two 700-MW indigenous nuclear power reactors at Rawatbhatta, in the desert state of Rajasthan. The two pressurized heavy water reactors (PHWRs), which will use uranium as fuel and heavy water as both moderator and coolant, are the largest to be built by the central government–run Nuclear Power Corp. of India […]
-
Nuclear
Bruce A Proves There Are Second Acts in Nuclear Power
The refurbishment and restart of all four CANDU reactors at Bruce A may be Ontario’s most significant and complex power generation project since the first phase of the Bruce Nuclear Generating Station was built more than 30 years ago. Units 1 and 2 are expected to be synchronized in 2011 and return to commercial service by early 2012, joining Units 3 and 4, which restarted in 2004 and 2003 respectively. POWER visited Bruce A in April to witness the project’s progress.
-
Coal
Lean Construction Principles Eliminate Waste
Eliminate waste in coal, gas, or nuclear power plant construction through a holistic application of lean principles.
-
Nuclear
Russia’s Nuclear Mission
Nearly a quarter-century after the Chernobyl nuclear power station disaster in Soviet Ukraine, Russia has been making deals with energy-starved nations all over the globe to help them build new nuclear power plants using Russian second-generation reactor technology.
-
Nuclear
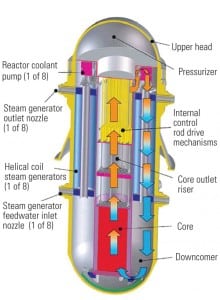
AREVA Installs Finnish EPR Reactor Vessel
This June, AREVA installed the reactor pressure vessel (Figure 6)—the core of the unit—at the world’s first EPR project, which is under construction in Finland. Now the company will engage in a flurry of installation activities for heavy nuclear components, including lifting into the reactor the first of the four steam generators. Most of the work is expected to be completed by the end of 2012, with power production beginning in 2013.
-
History
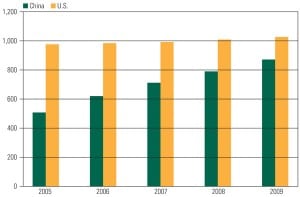
China: A World Powerhouse
It’s no surprise that China leads the world in recent power capacity additions. What may surprise you is the precise mix of options this vast country is relying upon to meet its ever-growing demand for electricity. As a result, this ancient civilization is fast becoming the test bed and factory for the newest generation and transmission technologies.
-
Nuclear
A Slow Slog Ahead for U.S. Nukes
There is a certain tentativeness about new nuclear power in the U.S. these days, a low-grade anxiety, as demonstrated by the comments made by electric utility representatives at May’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference in Baltimore.
-
Nuclear
Finnish Government OKs Two Nuclear Plant Proposals
Finland’s government in April approved two of three proposals for the construction of new nuclear reactors in an effort to rid the country of its dependency on electricity imports from other countries—especially Russia—as well as to decrease carbon emissions.
-
Nuclear
The U.S. Spent Nuclear Fuel Policy: Road to Nowhere
The Nuclear Waste Policy Act and Amendments of 1982 and 1987 established a national policy and schedule for developing geologic repositories for the disposal of spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes. Those deadlines have come and gone; the cancellation of Yucca Mountain was only the latest failure of this policy to become reality. The task of finding a new storage location is now a political committee’s homework assignment. History tells us that committee members have been given an impossible task.
-
Nuclear
Resurrecting Nuclear: "We Have to Get It Right"
Offers of nuclear loan guarantees are pending, construction permit applications are at an industry high, and the political stars seem to be properly aligned. However, there remains one obstacle in the development path of the next-generation of nuclear plants: How will these plants be financed?
-
Nuclear
Benchmarking Nuclear Plant Staffing
The EUCG Nuclear Committee has collected benchmarking data of U.S. nuclear plant staffing for many years. A summary of this highly desirable data was gleaned from EUCG databases and is now, for the first time, made public through an exclusive agreement with POWER.
-
Nuclear
U.S. Spins Nuclear Wheels as Other Nations Roll Out New Plants
President Barack Obama’s January State of the Union speech called for incentives to make clean energy profitable — mainly through the construction of a new generation of nuclear power plants. That comment, an apparent effort to reach out to Republican members of Congress, drew furious applause. Within three weeks, the president’s backing of nuclear power had already made a significant impact on the U.S. nuclear sector.
-
Nuclear
Initial Experiments Meet Requirements for Fusion Ignition
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) in California speculate that a prototype nuclear fusion power plant could be operational within a decade, thanks to a test of the world’s largest laser array that confirmed a technique called inertial fusion ignition is feasible. Their first experiments have demonstrated a unique physics effect that bodes well for NIF’s success in generating a self-sustaining nuclear fusion reaction. Fusion energy is what powers the sun and stars.
-
Nuclear
China Nuclear Plant Construction Gets Boost—With Technology Transfer
China’s nuclear power plant building spree got a little more frenzied this January, as the country kicked off its 21st project at Ningde 3.
-
Nuclear
Concerns About Electromagnetic Interference in Nuclear Plants Related to Digital Upgrades
In order to operate aging nuclear power plant instrumentation and control systems for up to 60 more years or longer, there must be a smooth transition from existing analog technologies to advanced digital platforms. For this to occur, electromagnetic compatibility concerns related to both qualification testing and the electromagnetic environment must be addressed to ensure safe and reliable operation of these systems within the plant’s electromagnetic and radio frequency interference environment. By understanding the regulatory requirements and sharing implementation experience, digital system upgrades can be installed successfully.
-
Nuclear
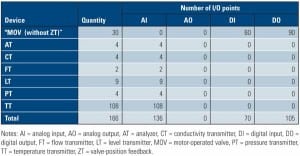
The Advanced Digital Fieldbus Option for Nuclear Plants
Digital fieldbus technologies, including Foundation fieldbus and Profibus, are increasingly being used with success in the nuclear and fossil fuel power industries. This article compares a conventional control system with a Foundation fieldbus – based digital control system used in a typical circulating water system in a nuclear power plant. As shown in this example, using digital fieldbus technologies can result in significant savings in terms of installation and hardware costs.
-
Nuclear
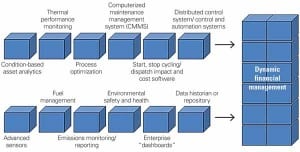
The Value of a Knowledge-Based Culture Grows in Lean Times
Given delays and cancellations of new generating capacity, pushing the existing power generation fleet is more important than ever. At ELECTRIC POWER 2009, multiple presentations explored the premise that an active knowledge management strategy — requiring a blend of digital and human elements unique to each power plant — will help you extract the most productivity from your assets.
-
Nuclear
Nontechnical Issues Affecting Digital Upgrades at Nuclear Power Plants
Existing nuclear power plants are increasingly facing the conversion to digital instrumentation and controls technology. Meanwhile, new nuclear designs have digital technology integrated throughout the plant. Digital controls will soon be inevitable, so how do we make the transition as smooth as possible? Without losing focus on the technical solutions, organizations have to pay attention to the nontechnical issues as well.
-
Coal
Digital Plant Controls Provide an Essential Edge
It’s a digital world, and even aging power plants are experiencing the benefits of digital controls technologies. The following cover stories provide insight into the latest options and inspiration for your own plant controls projects.