News
-
News
Sumitomo Introduces Battery System
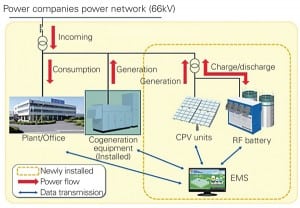
Japan’s Sumitomo Electric Industries in July began operation of a new power generation and megawatt-class storage system at its Yokohama Works site.
-
News
Compact Pump Series
Thompson Pump’s new Compact pump series has all the benefits of the popular Thompson Pump JSC series but is lighter, has fewer parts, needs less maintenance, and has a lower price. The Thompson Compact pump is 35% smaller and 20% lighter but offers the same performance as a standard size pump with 24-hour run time […]
-
News
Federal Court Strikes CSAPR, Reactions Swift
In a landmark ruling that has been seen as a major victory for thermal generators, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit on Tuesday vacated the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR), finding that it violated federal law. The EPA must now continue implementation of the Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR) until it can promulgate a replacement, which likely will not happen until at least 2014, industry analysts said.
-
News
DHS Warns of Potential Control System Vulnerability
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) on Tuesday issued an alert warning that industrial Ethernet switches and other devices made by network equipment manufacturer RuggedCom and widely used by power companies could be vulnerable to compromise.
-
News
OPT Gets FERC’s First Wave Power License
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) on Tuesday approved a full build-out of a 1.5-MW gird-connected wave power station that is planned by Ocean Power Technologies’ (OPT’s) Oregon subsidiary Reedsport OPT Wave Park. The license is the first issued for a wave power station in the nation.
-
News
Canadian Nuclear Regulator Awards License to Proposed Darlington Reactors
Canada’s nuclear regulator on Friday issued a 10-year nuclear power reactor site preparation license to Ontario Power Generation’s (OPG’s) proposed reactor at its Darlington nuclear site in Ontario. The license, described as "an important milestone in Canada’s nuclear history," is the first of its kind in nearly 25 years.
-
News
GAO: EPA Rules Could Spur Retirements, Increased Power Prices
Four rules recently proposed or finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) could prompt power companies to retrofit most coal-fired generating units and retire 2% to 12% of coal-fired capacity. The rules would also likely increase power prices in some regions, though they may not cause widespread reliability concerns, a new report by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) suggests.
-
News
Next Generation of Gas-Fired Power Starts to Take Shape
Incremental advances in gas turbine technology have made these industry workhorses bigger, more efficient, and more powerful. But some developments on the horizon suggest the industry is now poised to make some major leaps forward.
-
News
Agricultural Producers Get $8.7M in Federal Funding to Spur Renewables, Energy Efficiency
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) on Tuesday announced that 106 projects in 29 states, Guam, and Puerto Rico would receive $8.7 million in loans and grants to produce renewable energy and make energy efficiency improvements under the federal agency’s Rural Development’s Rural Energy for America Program (REAP).
-
News
Congressional Briefs: Action on Distributed Generation, Nuclear Waste Storage, Loan Guarantees
Congress kicked up action on several measures last week before it adjourned for a five-week recess. Two new bills were introduced: One calls for communities to generate at least 20% of their own power needs in preparation for grid emergencies, and the other seeks to put into legislative language recommendations regarding the nation’s nuclear waste storage policy that was finalized this January by the Blue Ribbon Commission. The House, meanwhile, advanced its “No More Solyndras Act.”
-
News
Seven Nuclear Stations Partner to Leverage Operational, Regulatory, Financial Performance
The owners of 13 reactors at seven nuclear power plants located Texas, California, Arizona, and Kansas last week formalized an alliance that they say would “leverage the strengths” of their plants and collaboratively focus on improving their operational, regulatory, and financial performances. Chief nuclear officers of the seven plants formally signed and agreed to the formation of a limited liability company, the STARS Alliance LLC.
-
News
Senate Cybersecurity Bill Defeated
Senate Republicans last week voted down the Cybersecurity Act of 2012 offered by Sens. Joe Lieberman (I-Conn.) and Susan Collins (R-Maine), citing concerns that the bill would burden businesses with unnecessary regulations.
-
News
Delays, Funding Hurdles, and Cancellations for Three Major U.S. Transmission Lines
Review of the TransWest Express, a 725-mile transmission line running from Cheyenne, Wyo., to Las Vegas, Nev., has been delayed at least six months, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) said last week. Developers of the Tres Amigas Superstation in New Mexico are meanwhile, reportedly tackling funding troubles, while U.S. grid operator PJM Interconnection formally announced it would axe the $1.8 billion PATH transmission line.
-
News
White House Expedites Seven Solar and Wind Energy Projects
Seven solar and wind energy projects with a total nameplate capacity of 5 GW in Nevada, California, Arizona, and Wyoming will be expedited under President Obama’s “We Can’t Wait” initiative, the White House announced on Tuesday.
-
News
Black Hills to Suspend, Retire Coal-Fired Units
Black Hills Corp. (BHC) is the latest power company to announce slated closures at fossil fuel–fired power plants. The company’s subsidiary Black Hills Energy/Colorado Electric will suspend operations at its 42-MW W.N. Clark coal-fired power plant in Cañon City, Colo., and natural gas–fired steam units 5 and 6 in Pueblo, Colo., by the end of 2012. Another subsidiary will shut down the 25-MW Ben French power plant in Rapid City, S.D., by Aug. 31, 2012, as well as the 34.5-MW Osage and 22-MW Neil Simpson 1 coal-fired power plants on Mar. 21, 2014. The company cited “environmental regulations” and changing energy demands as reasons for the measures.
-
News
Explosion Briefly Evacuates Kansas Coal Power Plant Workers
An explosion in the B coal bunker at Kansas City Power and Light’s (KCP&L’s) 651-MW Iatan Power Plant Unit 1 near Weston, Mo., on Wednesday morning required the brief evacuation of 250 personnel onsite at the facility. No employees or contractors were injured, and the fire was quickly contained, the company said.
-
News
GAO: Complexity of NSR Permitting Process, Lack of EPA Data, Hinders Compliance
A new report by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) finds that the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) lacks centralized information on New Source Review (NSR) permits typically issued to fossil fuel-fired power plants by states, though the agency has spearheaded enforcement efforts for noncompliance. The report, which concedes that the NSR permitting process is “complex and controversial,” also suggests that a "substantial number" of existing generating units may not have complied with requirements to obtain NSR permits.
-
News
NRC Warns of Design Vulnerability in Reactor Electric Systems, Requests Information
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) last week issued a bulletin to all holders of nuclear plant operating licenses in the U.S., alerting them to a potential design vulnerability discovered at Exelon’s Byron Nuclear Generating Station in January that it says "could have damaged the plant’s emergency core cooling system."
-
News
Progress Energy Carolinas to Accelerate Retirement of Coal Plants
Progress Energy Carolinas, which recently became a Duke Energy subsidiary, on Friday said it would accelerate the retirement of its 316-MW Cape Fear coal-fired plant, located near Moncure, N.C., and the 177-MW H.B. Robinson Unit 1 coal-fired plant, located near Hartsville, S.C., due to “pending changes in the environmental regulations and other rising costs for smaller, older technology plants.”
-
News
Unprecedented Grid Failures Underscore India’s Infrastructure Woes
Back-to-back transmission grid failures in India plunged nearly 670 million people—roughly 10% of the world’s population—into darkness on Monday and Tuesday, paralyzing transport networks and crippling the country’s economic ambitions. Larger than both the August 2003 North American blackout and the March 1999 southern Brazil blackout, the unprecedented Indian grid failures are among the world’s worst.
-
News
Non-Discharging Synthetic Media for Pulse Systems
Camfil Farr Power Systems added two new products for dusty environments to its Campulse product line: Campulse GTC and GTD. Both have new, non-discharging fiber media, which are sturdy, durable, and offer high dust-holding capacity. The Campulse GTC’s smooth synthetic fibers offer low resistance to airflow and maintain a low pressure drop throughout the filter […]
-
News
Tray Cable Connectors
Appleton, a manufacturer of products for hazardous location electrical systems, now offers a versatile line of tray cable connectors engineered for use with TC, ITC, PLTC, and other commonly used types of tray cable. Key to the success of the new connectors is a compensating displacement seal that provides ingress protection to NEMA 4X and […]
-
News
Sensors for Detecting Corrosion Under Insulation
Rohrback Cosasco released three types of Cosasco corrosion under insulation (CUI) corrosion sensors for detecting corrosion under insulation: continuous insulated braid “corrosion fuse” wire (Type 1), inserted “corrosion fuse” probe array (Type 2), and the CUI Corrosometer Probe (Type 3). The three techniques offer direct corrosion detection and a much lower cost per monitoring point […]
-
News
Rotary Screw Air Compressor
Ingersoll Rand is offering a newly improved single-phase control scheme for its 5 and 7.5 versions of the small UP6 5-15c line of air compressors. It has added a run-on timer and load/unload and blowdown solenoids to improve the reliability and performance of single-phase units in general industrial applications up to 28 cfm. The company […]
-
News
Compact Electric Pump
A new compact electric pump designed for bolt tensioning applications in the wind turbine industry is now available from specialist bolt tensioner manufacturer Boltight Ltd. The standalone power pack is lightweight (19.5 kg) and portable, as the pump, reservoir, and motor are combined into one easily handled package. The 0.75-kW rated pump is driven by a 220-240 V single-phase electric […]
-
News
Flowmeter for Utility Gases
Endress+Hauser released the Proline t-mass 150 thermal mass flowmeter for measuring gases such as compressed air, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and argon. The flowmeter measures mass flow, gas temperature, free air delivery, and corrected volume—all without the need for pressure or temperature compensation. The t-mass 150, with its high turndown of 100:1, can reliably measure small […]
-
News
Comprehensive Spectrophotometer
Hach Co.’s new DR 6000UV-Vis spectrophotometer was designed to fulfill any water testing needs using one spectrophotometer. It is equipped with RFID technology, integrated QA software, and more than 250 testing methods and guided procedures. The instrument is programmed to take absorbance readings of a single sample at different wavelengths or over a specific period […]
-
News
Point Lepreau Reactor Gets Federal OK to Restart After Four-Year Refurbishment
Canada’s Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) on Tuesday approved restart activities at New Brunswick Power Nuclear’s (NBPN’s) Point Lepreau Generating Station, a 680-MW Candu 6 on the northern shore of the Bay of Fundy that has been offline for more than four years for a major refurbishment.
-
News
DOI, DOE Blueprint Foresees 23.7 GW of Solar Energy Development on Federal Lands
A Final Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement (PEIS) released by the Department of the Interior (DOI) and Department of Energy (DOE) on Tuesday identifies 17 Solar Energy Zones (SEZs) in six southwestern states—Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, and Utah—totaling about 285,000 acres of public lands, as priority areas for utility-scale solar development.
-
News
NRG and GenOn to Merge in $1.7 B Deal
Princeton, N.J.-based NRG Energy and Houston, Texas-based GenOn on Monday signed a definitive agreement to combine the two companies in a $1.7 billion stock-for-stock tax-free transaction. The merger will create "the largest competitive generator" in the U.S. with a fleet of about 47 GW and assets in the East, Gulf Coast, and West, and a combined enterprise value of $18 billion, the companies said.