Gas
-
Coal
Spain: A Renewable Kingdom
Spain has served as both exemplar and scapegoat when it comes to renewable energy policy. Though power policy must necessarily accommodate specific national resources and goals, Spain’s experience as an early and eager adopter of renewable energy technologies and subsidies is a cautionary tale of how the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
-
Gas
The T-Point Plant: The Ultimate Validation Test
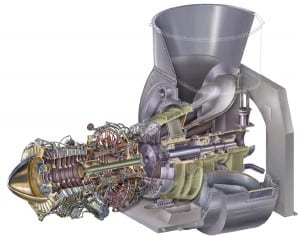
Fourteen years ago, the MHI T-Point demonstration combined-cycle plant in Takasago, Japan, changed the way modern gas turbines are validated under real operating conditions. In February, T-Point marked yet another milestone by starting to validate the world’s largest and highest efficiency gas turbine, which operates at the unprecedented turbine inlet temperature of 1,600C.
-
Gas
Selecting Your Next Combustion Turbine
With natural gas serving as the fuel de jour, many utilities and merchant generators will be considering the purchase of new combustion turbines in the near future. If you are in the market for a gas turbine, here are some key design features you should discuss with turbine vendors prior to your next purchase.
-
Gas
Sendai Plant Boosts Efficiency and Cuts Emissions
Located on the scenic Japanese coastline, Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc.’s new 446-MW Sendai Thermal Power Station Unit 4 is a combined-cycle plant that replaces three 175-MW coal-fired units that had been in operation for more than 50 years. The new plant features the first application of MHI’s 50-Hz M701F4 gas turbine, which provides a thermal efficiency boost from the old plant’s 43% to more than 58%. This change substantially reduces CO2 emissions.
-
Gas
E.ON Starts 417-MW Cogeneration Plant in Slovakia
At the beginning of 2011, German firm E.ON began operation of its new 417-MW Malzenice gas and steam turbine power station in Slovakia’s Trnava region, near the country’s capital, Bratislava (Figure 5). The facility, which is expected to generate more than 300 billion kWh annually, boasts an efficiency of 58%—which E.ON claims is among the “highest in Europe.”
-
Gas
Using Flue Gas to Mitigate Ocean Acidification
Lab-scale experiments have shown that seawater and calcium could effectively remove most of the carbon dioxide (CO2) from a natural gas power plant’s flue gas stream. A large fraction of the captured gas could then be converted into dissolved calcium bicarbonate—which, pumped into the sea, could be beneficial to the ocean’s marine life, says a researcher representing both the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) Carbon Management Program and the University of California, Santa Cruz.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Gas
RAM Process Optimizes IGCC Design
New methods of reliability, availability, and maintainability (RAM) evaluation help facilitate more-accurate plant output and revenue predictions, identify strengths and weaknesses of possible plant configurations, and determine potential improvements and enhancements for integrated gasification combined cycle plants.
-
Coal
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part I: Station-Level Metrics
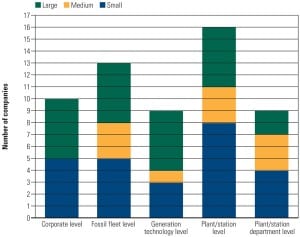
How does your company prepare and share fossil plant performance data? What data are important, and how much effort is required to collect and report the data? What are the most important statistics for reporting key fossil plant operations? The latest EUCG benchmarking survey reveals the favored fossil performance metrics at several of the largest utilities in eight key categories.
-
Gas
Automated Exhaust Temperature Control for Simple-Cycle Power Plants
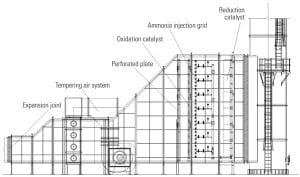
A common concern for gas turbine power plants is treating exhaust gases to comply with laws restricting pollutants present in the gases that are emitted into the ambient atmosphere. The challenge for designers is to control the exhaust gas operating temperature within a range that maximizes performance of the oxidation and reduction catalysts.
-
Coal
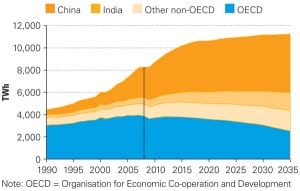
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.
-
Gas
MHI Prepares to Test J-Series in Japan
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has begun converting a combined-cycle plant in Japan to prepare for verification testing of its long-anticipated J-Series gas turbine in February 2011—a system that the company claims has the most power generation capacity and highest thermal efficiency in the 1,600C turbine inlet temperature class (Figure 3). The work being carried out at the Takasago Machinery Works facility in Hyogo Prefecture (where the company’s G-Series gas turbines were tested) includes installation of the J-Series turbine, and it marks another major milestone in the technology’s development.
-
Gas
TransCanada Opens 683-MW Halton Hills Combined-Cycle Plant
TransCanada Corp. on Oct. 28 officially opened its C$700 million Halton Hills Generating Station. The 683-MW 2 x 1 combined-cycle plant on a greenfield site in Ontario (Figure 5) will operate under a 20-year power purchase agreement with the Ontario Power Authority (OPA). Construction of the peaker plant started in December 2007 and was completed on time and on budget, TransCanada said.
-
Coal
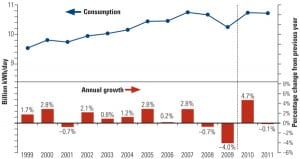
The U.S. Power Industry 2011: The Sequel
If Hollywood were scripting the power industry story for 2011, it would be a sequel to 2010—more of the same, but just not quite as good. Natural gas gets top billing and the accolades, wind power drops to a supporting role, and new nuclear answers the casting call but has yet to get a speaking part. Coal is like Mel Gibson—a talented Oscar winner unlikely to get another leading role. In this, our fifth annual industry forecast report, the story may be familiar, but the price of admission is going way up.
-
Coal
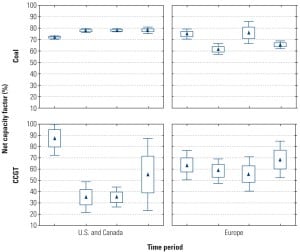
Coal Plants Challenged as Gas Plants Surge
European carbon trading is gradually pushing down coal-fired capacity factors, and operating costs are rising. The U.S. may not have a carbon market, but increasing regulatory requirements are having the same effect on coal-fired generation capacity factors and operating costs. In the meantime, gas-fired assets are enjoying increased usage and lower unit costs.
-
Gas
Turkey Opens Record-Breaking Combustion Gas Engine Plant
Turkey, a country that has seen rapid economic growth since the 1980s, largely spurred by a shift in governmental strategy to open up markets and increase private participation, has been actively overhauling its power infrastructure to meet soaring electricity consumption. According to grid operator Turkish Electricity Transmission Co., national consumption increased to 17 billion kWh this September—an 11% increase over the 15.3 billion kWh consumed in September 2009.
-
Gas
GE Launches 9.5-MW Engine for Distributed Generation
A 9.5-MW gas engine unveiled by GE this October for decentralized, independent power producers in remote, hot, or high-altitude regions features a 48.7% electrical efficiency and promises to reduce lifecycle costs by lowering fuel consumption.
-
Gas
Smart Power Generation at UCSD
The University of California, San Diego has been accumulating awards for its savvy use of a constellation of power generation and energy-saving technologies. The campus already controls a fully functioning microgrid—including a cogeneration plant—and, as befits a research institution, is constantly looking for new ways to make its energy system smarter. This “living laboratory,” as campus leaders like to call it, demonstrates what it takes to build a smarter grid and why the effort is worth it.
-
Gas
Microturbine Technology Matures
Microturbine technology has evolved from early systems of 30 kW to 70 kW to today’s systems, which can have individual ratings of 200 kW to 250 kW. Packages up to 1 MW are now available that can be assembled into multipac units for projects of 5 MW to 10 MW. These modern units are packaged with integrated digital protection, synchronization, and controls; they produce high combined heat and power efficiencies; and they are capable of using multiple fuels.
-
O&M
NFPA Gas Purging Rules Updated
The CSB has made urgent recommendations to the NFPA and the International Code Council to prohibit indoor purging and require companies and installers to purge flammable fuel gases to safe locations outdoors, away from workers and ignition sources.
-
Gas
The World’s First Two-Stage Turbocharged Gas Engine
GE launched what it is calling the world’s first two-stage turbocharged gas engine this June.
-
O&M
Ten Years of Experience with FAC in HRSGs
We first reported on combined-cycle plant reliability concerns due to erosive wear and flow accelerated corrosion (FAC) in heat-recovery steam generator (HRSG) pressure parts at the 1999 EPRI Maintenance Conference. More than 10 years later, these damage mechanisms remain significant contributors to forced outages, pressure part repairs, and major component replacement.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Langage Combined Cycle Power Plant, Plymouth, Devon, UK
The UK grid, focused on adding valuable renewable generation, will rely on natural gas–fired generation for many years to come. One of the most recent additions is the Langage Power Plant, designed for quick response and low load “parking” at night while remaining below air emissions limits. With an extraordinary architectural design that blends into the natural surroundings, Langage is now a local landmark.
-
Gas
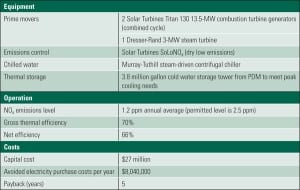
Top Plant: Panoche Energy Center, Firebaugh, California
The Panoche Energy Center is a 400-MW simple-cycle power plant using four of General Electric’s GE LMS100s with fast-start capability. Dispatched by Pacific Gas & Electric to meet regional power and grid stabilization needs, the project entered commercial service two months earlier than planned. Panoche is the largest LMS100 peaking facility in the U.S.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Ras Laffan Power and Water Plant, Ras Laffan Industrial City, Qatar
At the Ras Laffan Power Co. facility, the 756-MW net combined-cycle plant and the integrated 40 million gallons per day desalination plant are working in tandem to provide abundant, reliable electricity and desalinated water to residents of the State of Qatar, the most prosperous nation in the Middle East.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Sloe Centrale Power Plant, Vlissingen-Oost, Zeeland Province, Netherlands
There’s nothing slow about the fast-track operations at the new 870-MW Sloe Centrale Power Plant. The combined-cycle plant is designed for 250 starts per year and is capable of supplying power to the grid within a mere 30 to 40 minutes. In addition to its impressive rapid load response, the gas-fired plant produces low CO2 and NOx emissions by using the latest technology. It also attains an efficiency of 59%.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Timelkam Power Plant Vöcklabruck District, Upper Austria, Austria
Now that the 412-MW Timelkam Power Plant has replaced a 47-year-old coal-fired power plant located in the Vöcklabruck District, northern Austrians can bid auf wiedersehen (goodbye) to high levels of air pollution. Compared to its predecessor, the new gas-fired combined-cycle plant has dramatically cut CO2 and NOx emissions and produces seven times more energy.
-
Gas
Top Plant: West County Energy Center, Palm Beach County, Florida
The 3,600-MW West County Energy Center, with two recently commissioned power blocks and a third just entering start-up, is the first “greenfield” combined-cycle plant constructed by FPL since the 1970s. Thanks to FPL’s long history with repowering projects, the project team commissioned Unit 2 seven months early, with no operator errors during start-up. At just over $600/kW, the cost of the plant was a bargain.
-
Gas
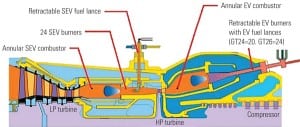
Flexible Turbine Operation Is Vital for a Robust Grid
Renewable electricity generation has many environmental advantages, but adding large amounts of far-flung renewable resources to a grid requires increased operating flexibility from dispatchable generators when the wind doesn’t blow or the sun doesn’t shine. One promising option: A combined-cycle plant based on Alstom’s GT24/GT26 combustion turbine can be “parked” at approximately 20% plant load while producing emissions comparable to those during baseload operation—with little loss in thermal efficiency. When demand returns, the combined cycle can return to baseload within minutes.