Gas
-
Coal
Recession Reduces Demand for Electricity
When roving Contributing Editor Mark Axford attended several recent energy conferences, he found the same questions asked at each one about new U.S. generation sources and consumption patterns. Unfortunately, the experts had few good answers to those questions.
-
Gas
Hungary Building High-Efficiency Gas-Fired Plant
Germany’s E.ON laid the foundation stone in late March for a 433-MW combined-cycle power plant in Gönyü (Figure 6), a power-stricken region in northwestern Hungary. The power plant, expected to begin operation in 2011, will operate with a net efficiency of more than 58% — making it one of the most efficient power plants in […]
-
-
O&M
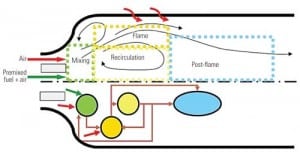
Advanced Modeling Tools Slash Combustor Analysis Chores
Combustor design simulation requires the resolution of complex geometry, turbulent flow patterns, heat transfer, and detailed chemistry. Although computational fluid dynamics (CFD) can simulate the reacting flow in realistic geometries, it requires the use of severely restricted chemistry models that are too simple to accurately simulate emissions and operational stability. A new simulation tool is now available that eliminates this CFD shortcoming while significantly reducing computing time.
-
Coal
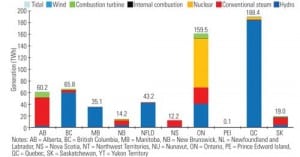
Canada Moves to Rebalance Its Energy Portfolio
Though Canada is rich in fossil fuels, nuclear power may fuel a significant portion of the nation’s future electrical generation needs, especially in provinces that have traditionally relied on hydropower and fossil fuels.
-
Coal
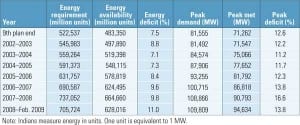
Powering the People: India’s Capacity Expansion Plans
India has become a global business power even though hundreds of millions of its citizens still live in poverty. To sustain economic growth and lift its people out of poverty, India needs more — and more reliable — power. Details of government plans for achieving those goals demonstrate that pragmatism may be in shorter supply than ambition and political will.
-
Gas
Gas Hydrates: Fuel of the Future?
Gas hydrates, a form of natural gas that forms when methane from the decomposition of organic material comes into contact with water at low temperatures and high pressures, could play a role — even if a small one — in future fuel supplies, researchers attending a March meeting organized by the American Chemical Society suggested.
-
Gas
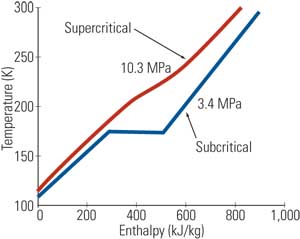
Consider CHP for LNG Vaporization
The conversion of liquefied natural gas (LNG) to pipeline-quality gas requires large quantities of low-grade thermal energy that may be available from industrial waste streams, steam power plants, or ocean water at the point of discharging LNG from the tanker. Alternatively, heat may be provided by the combustion of LNG or another fuel. In either case, the large temperature differences between these heat sources and the temperature of the LNG can be used to operate an engine that will offset or eliminate the pumping or fuel costs incurred.
-
Coal
CERAWeek 2009: Floundering Economy Eclipses Renewable, Carbon Plans
For the past 26 years, Cambridge Energy Research Associates (CERA) has hosted an annual conference in Houston that is world-renowned for its high-profile speakers and attendees’ willingness to exchange ideas and share industry forecasts. The consensus this year was that the power industry remains strong but market and political forces, often working at cross-purposes, make bringing any new power generation to market more problematic than ever.
-
Coal
Fossil Fuels + Solar Energy = The Future of Electricity Generation
Renewable energy, though still accounting for a comparatively small portion of overall supply, generates a larger portion of the world’s electricity each year. Combining many of the available solar energy conversion technologies with conventional fossil-fueled technologies could reduce fuel costs while simultaneously helping utilities that are struggling to meet their renewable portfolio goals.