Environmental
-
Environmental
EIA Releases State-by-State Report on Energy-Related CO2 Emissions
In a report released on Monday, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) presents data on energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions for each state by year, fuel, sector, and other breakouts for the years 2000 through 2010.
-
Environmental
Power Plant Global Warming Suit Dismissed by Federal Court
A three-judge panel at the 5th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in New Orleans on Tuesday dismissed a lawsuit that alleges carbon dioxide emissions by several power companies contributed to global warming that intensified Hurricane Katrina.
-
Coal
AES Corp. to Retire 990 MW of Coal Capacity on Environmental Rule Concerns
AES Corp.’s subsidiary Dayton Power & Light (DP&L) plans to retire six coal-fired units representing about 390 MW at its 414-MW Hutchings coal-, gas-, and oil-fired plant in Miamisburg, Ohio, by June 2015 as a result of existing and expected environmental regulations, including the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). The news comes on the heels of Indianapolis Power & Light Co.’s (IPL’s) announcement that it plans to retire 600 MW of coal-fired capacity to comply with environmental rules.
-
Environmental
Carbon Capture, Use, and Storage Project Reaches Industrial Scale
Air Products and Chemicals hydrogen production facilities in Port Arthur, Texas, have successfully begun capturing carbon dioxide from industrial operations and are now using that carbon for enhanced oil recovery (EOR). The $431 million project, supported by $284 million from the Department of Energy (DOE), is being touted as a milestone in carbon capture, use, and storage (CCUS) for progressing beyond demonstration to industrial scale.
-
Environmental
Methanation of CO2: Storage of Renewable Energy in a Gas Distribution System
Energy storage has been the achilles heel of the renewable boom, but new technology may offer a way to join gas and renewables even more closely—by using excess renewable generation to manufacture synthetic natural gas from carbon dioxide.
-
Coal
Power Sector Is Critically Vulnerable to Drought, Hearing Panel Testifies
Drought is a serious vulnerability for the power sector, witnesses testified at a full committee hearing held last week in the Senate to assess the impacts of drought on the power and water sectors. Members of the panel invited by the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources offered a number of possible solutions for federal agencies and power companies that could mitigate adverse effects from drought.
-
Coal
Ontario Goes Coal-Free in a Decade
By the end of 2013, one year ahead of its goal, the province of Ontario will be virtually coal-free—a first for a North American jurisdiction. How did the most populous part of Canada go from 25% to 0% coal-fired generation in just a decade, and what does this phaseout mean for the rest of the world?
-
Coal
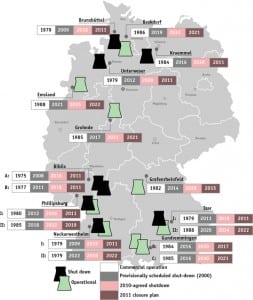
Germany’s Energy Transition Experiment
Germany has chosen to transform its energy system within a few decades—an ambition that has evoked equal admiration and confusion. Has Europe’s largest economy embarked on a rational path to an energy future that will make it the bellwether for global acceptance of renewables, or will the complex array of current challenges encumber its grand transformation?
-
Coal
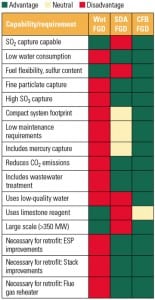
CFB Scrubbing: A Flexible Multipollutant Technology
The number of regulated air emission constituents is increasing while the acceptable amounts for release are decreasing. In the long run, picking the most flexible multipollutant technology is surely the least cost option.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes Revisions to Steam Electric Power Plant Effluent Guidelines
Revisions proposed on Friday by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to technology-based effluent limitations guidelines and standards could set the first federal limits on the levels of toxic metals in wastewater discharges from steam electric power plants. The proposed rule would help reduce pollutants in U.S. waterways from coal ash, air pollution control waste, and other power plant waste, but they could come at a cost of between $185.2 million to nearly $1 billion a year, the agency said.
-
Environmental
Budget Proposal to Sell TVA Blasted by Republicans, Clean Energy Groups
Reform—and the possible partial or total sale—of Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), the federally owned and operated but self-financed 80-year-old corporation, as proposed by the White House in its fiscal year 2014 budget, was reportedly unexpected and has been criticized by varied entities.
-
Coal
IEA: Carbon Mitigation Efforts Have Stalled Despite Rapid Renewables Expansion
The carbon intensity of the global energy supply has barely budged in more than two decades despite otherwise successful efforts in deploying renewable energy, the International Energy Agency (IEA) warns in an annual report submitted to the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) on Wednesday.
-
Coal
EPA Nominee Says Environmental Protection Is a Nonpartisan Issue
Gina McCarthy, who has served for the past four years as assistant administrator for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Office of Air and Radiation, responded to questions from a Senate committee on April 11 in a hearing on her nomination to become the next administrator of the EPA.
-
Coal
EPA Delays GHG Emissions Decision and Adds to FutureGen Challenges
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) deadline for placing greenhouse gas (GHG) emission limits on new fossil-fueled power plants has come and gone. Comments from EPA staff indicate little urgency in setting a new deadline. Meanwhile, prospects for FutureGen 2.0, originally developed with GHG limits in mind, are looking bleaker.
-
Coal
EPA, DOJ Settle with Dominion Energy on CAA Violations
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced on Monday that Dominion Energy has agreed to pay a $3.4 million civil penalty and spend approximately $9.8 million on environmental mitigation projects to resolve Clean Air Act (CAA) violations.
-
Coal
EPA Updates MATS for Power Plants
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on March 28 finalized updates to emission limits for new power plants under the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). The rule includes emission limits for mercury, particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), acid gases, and certain individual metals.
-
Environmental
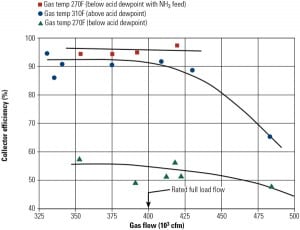
Electrostatic Precipitator Upgrade Opportunities
The results of stack emissions testing conducted at several coal-fired power plants during the past three years have provided useful guidance for plant operators who are required to meet new federal guidelines regarding the release of particulate matter. The data and guidelines presented here will assist those who operate plants with electrostatic precipitators to develop a strategy for filterable particulate emissions control.
-
Environmental
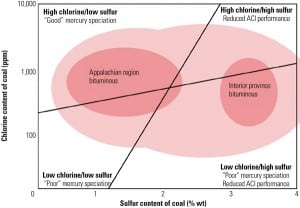
Enhancing Mercury Capture: An Asset-Based Approach
The Mercury and Air Toxics Standards will soon force many coal-fired plants to install mercury-specific emission control equipment. Planners can use particular characteristics of a plant to quickly screen for the best mercury removal technology.
-
Coal
EPA Directs 36 States to Revise SIPs for Emissions During Plant Startup, Shutdown, Malfunction
A rule proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) directs 36 states to revise their Clean Air Act State Implementation Plans (SIPs) to eliminate exemptions for excess emissions of air pollutants at power plants during startup, shutdown, or when the plant malfunctions.
-
Environmental
When Dinosaurs Roamed California: The Coming Extinction of Fossil Fuel Use
California’s push to boost its renewable capacity may be doing more than spurring the development of wind and solar. A review of recent data suggests the state’s regulatory schemes have the potential to spell the end of fossil-fuel generation altogether.
-
Coal
EIA: U.S. Power Sector SO2, NOx Emissions Lowest Since 1990
Power plant emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the U.S. declined to their lowest level since 1990, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) said in early March.
-
Environmental
Carbon Capture for Gas Power Appears on the Horizon
You may think of carbon capture and sequestration as a coal industry issue, but two forward-thinking companies are joining forces to make it work for gas.
-
Coal
Four Major EPA Air and Water Rules Forthcoming Through May, Agency Schedule Shows
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates final regulations curbing greenhouse gas (GHG), mercury, and air toxics emissions from new sources could appear in the Federal Register by the end of April. Also forthcoming are final cooling water intake rules and proposed effluent guidelines. The coal ash rule, which has no target date for a final rule, may not be issued this year, the agency said.
-
Coal
Kemper County IGCC Project Update
The integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) plant located in Kemper County, Mississippi, is a 2 x 1 plant that will produce 582 MW at peak and 524 MW fired on syngas, with ammonia, sulfuric acid, and carbon dioxide as by-products. The carbon dioxide will be used for enhanced oil recovery (EOR). Engineering was completed in Q3 2012, and the facility’s commercial operation date is planned for May 2014.
-
Coal
Project Planning Key to Smooth J.T. Deely 2 SCR Retrofit
Recent experience on the Deely 2 SCR retrofit project reminds us that the time spent in thoroughly planning a project prior to the start of construction is usually repaid with avoided construction delays.
-
Coal
Senate Democrats Urge Obama to Amend EPA’s GHG Rules for New Coal Plants
In a letter to President Obama last week, four Senate Democrats expressed "continued concern" about the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) plans to issue greenhouse gas (GHG) new source performance standard (NSPS) rules for new fossil fuel-fired power plants. The proposed rules could ban "new state-of-the-art" plants from being built and hamper advancements that could benefit the nation’s coal power sector, the senators argued.
-
Solar
Environmental Groups Remonstrate Against U.S. Challenge of India’s Solar Domestic Content Rules
A dozen environmental groups on Wednesday called on the U.S. Trade Representative to reconsider a World Trade Organization (WTO) challenge to domestic content rules and subsidies in India’s national solar program, urging it instead to agree to a solution that allows India to support and build its domestic solar industry.
-
Environmental
Democrats Seek Feedback on Newly Proposed Carbon Fee for Emission Sources
A new draft carbon-pricing bill that solicits feedback on how much industrial sources burning fossil fuels should pay per ton of carbon dioxide emitted was released by a bicameral group of Democrats on Tuesday. The bill diverges from a previously introduced measure to levy carbon taxes at the point of production or sale of a fossil fuel and applies instead at the “point of emissions”—which includes coal, oil, and natural gas generators.
-
Coal
Four Major EPA Air and Water Rules Forthcoming Through May, Agency Schedule Shows
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates final regulations curbing greenhouse gas (GHG), mercury, and air toxics emissions from new sources could appear in the Federal Register over the next six weeks. Also forthcoming are final cooling water intake rules and proposed effluent guidelines. The coal ash rule, which has no target date for a final rule, may not be issued this year, the agency said.
-
Coal
Gates Calls for Increased Spending on Energy Research, Renewed Focus on Nuclear
Bill Gates didn’t mince words last night when sharing with the IHS CERAWeek crowd his thoughts about public support for basic scientific research in the United States.