Environmental
-
Coal
Pleasant Prairie Power Plant Air Quality Control Upgrade Project, Pleasant Prairie, Wisconsin
We Energies’ Pleasant Prairie Power Plant is a good example of how existing plants retrofitted with NOx and SO2 removal systems benefit from early planning and action. P4, as everyone calls it, recently completed a multiyear project to add a selective catalytic reduction system to one of its two units and a scrubber to both. The unique design and contracting aspects of the project make Pleasant Prairie one of POWER’s top coal-fired plants of 2007.
-
Coal
Polk Power Station Unit 1, Mulberry, Florida
Ten years ago, POWER selected Tampa Electric’s 250-MW Polk Power Station and its revolutionary integrated gasification combined-cycle demonstration project as the magazine’s 1997 Plant of the Year. Although no new commercial IGCC projects have been built since then, interest in deploying the coal-gasification technology is getting traction in some parts of the U.S. In 2007, POWER recognizes Polk Unit 1 as a Top Plant for developing trailblazing O&M practices and technical improvements that enable it to operate today as reliably as a modern pulverized coal plant, with lower pollutant emissions.
-
Coal
R.E. Burger Plant, Shadyside, Ohio
FirstEnergy’s R.E. Burger Plant has hosted a number of R&D projects over the years, but none as large as the demonstration of Powerspan’s 50-MW Electro-Catalytic Oxidation (ECO) multipollutant removal process a few years ago. Credit Powerspan for scaling up the demo unit and for adding CO2 as a target of a new pilot process called ECO2. And don’t forget the behind-the-scenes support of Burger’s plant staff and their willingness to incubate R&D projects while producing power. That’s what makes R.E. Burger a Top Plant in our book.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (October 2007)
Siemens ships first blade from U.S. plant; GE’s frames hit 1,000; Battery problems hit hybrid EV programs; Solar thermal rebounds in California;Peabody’s Illinois coal plant gets green light;EPA could sink 278-MW CFB unit; Longest-serving NRC commissioner dies at 58; POWER digest; Readers talk back; corrections
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: BACT to the Future
This August, Peabody Energy’s 1,600-MW Prairie State Energy Campus project in Illinois won a major federal appeals court decision, removing the last obstacle to groundbreaking. The six-year regulatory review process ended with an unsuccessful Sierra Club challenge to the $2.9 billion project’s air permit. The decision is sure to reverberate across the nation, and I […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: AmerenUE Teams with Charah and Home Depot to Market Ash for Concrete Mix
Burning Powder River Basin (PRB) coal can be a curse or a blessing, depending on your attention to the details of plant design and operations. One disadvantage of PRB coal combustion is the abundance of bottom ash and flyash generated as a by-product. Handling and properly disposing of the ash can be challenging and costly. […]
-
Coal
Coal Plant O&M: How Switching to PRB Lowered O&M Costs
Lansing Board of Water & Light (LBW&L), which has generated electricity since 1892 and steam since 1919 in mid-Michigan, primarily serves the city of Lansing’s business district and all state government buildings in the downtown area. But one of the municipal utility’s plants, Moores Park, has an additional and very important steam customer: General Motors’ […]
-
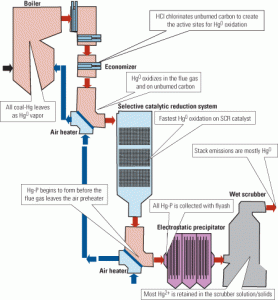
O&M
Mercury Control: Capturing Mercury in Wet Scrubbers: Part II
In Part I of this two-part report ( COAL POWER, July/August 2007, p. 22), we introduced the integrated R&D effort by the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Energy Technology Laboratory (DOE/NETL) to improve understanding of the mechanisms of mercury (Hg) capture and retention in flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems and the fate of Hg in […]
-
Environmental
Field experience with mercury monitors
With U.S. mercury regulations pending and control technologies in the full-scale demonstration stage, accurate and reliable measurement of mercury in flue gas is becoming more important than ever. This article compares the results of field measurements of commercially available mercury monitors to approved reference methods. A key but not-so-surprising finding: Not all mercury monitors are created equal.
-
O&M
Use predictive techniques to guide your mercury compliance strategy
Several states have mandated faster and/or deeper reductions in plant mercury emissions than those called for by the Clean Air Mercury Rule. Unfortunately, differences between plants make accurate evaluation of control options difficult. In most cases, even statistically based Hg emission models don’t pass muster because they don’t account for the dynamic chemical behavior of Hg species in gas cleaning systems. This article describes one system evaluation tool that has been validated using Hg field test data from 50 full-scale flue gas cleaning systems. It is already being used by TVA and other utilities.