Environmental
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (April 2008)
Tag-teamed seawater cleanup; New cooling towers to improve river’s health; Back to school
-
Water
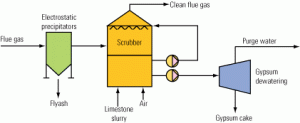
Benefits of evaporating FGD purge water
In the U.S. and the European Union, scrubbers are installed on all new coal-fired power plants because their technology is considered the best available for removing SO2. A zero-liquid-discharge system is the best technology for treating wet scrubber wastewater. With the future promising stricter limits on power plants’ water use, ZLD systems that concentrate scrubber purge streams are sure to become as common as ZLD cooling tower blowdown systems.
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: The True Costs of Going Green
Three of the best-kept secrets in the U.S. today have nothing to do with national security in the traditional sense. They all involve costs: the cost of fulfilling campaign promises, a valid estimate of the cost of carbon control legislation (S. 2191) expected to reach the Senate floor in a few months, and the real […]
-
Coal
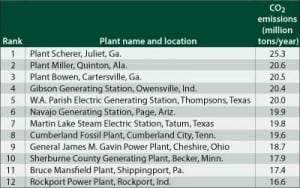
The Coal Patrol: Ranking the CO2 Emissions of the World’s Power Plants
The Environmental Integrity Project, a Washington-based advocacy group, announced in March that CO 2 emissions from U.S. power plants increased 2.9% last year over 2006 levels. The group used 2006 and 2007 CO 2 emissions data from the U.S. EPA and the DOE’s Energy Information Administration. It’s hard to normalize CO 2 numbers — and […]
-
Coal
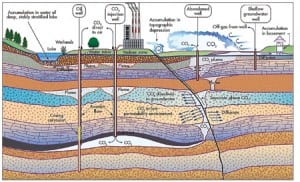
The Future of Coal Power: Modeling Geological Sequestration of CO2
Everyone in the power generation business knows that coal will continue to be a necessary fuel source for the foreseeable future. Many of those same people are beginning to understand that, politics aside, coal plant operations in the foreseeable future won’t look like the operations of yesterday or today. But what exactly will the future […]
-
Coal
The Future of Coal Power: Development and Siting Obstacles for New Coal Plants
In recent years, Sargent & Lundy has evaluated many potential sites for new coal-fueled generation. Some of the sites studied were lands adjacent to existing power plants (brownfield sites); others were undeveloped greenfield sites. The numerous technical, environmental, economic, and regulatory issues that bear on power plant siting generally apply to both brownfield and greenfield […]
-
Coal
Emissions: Unintended Consequences of Problem-Solving
Most folks probably don’t think that power plants burning coal and ethanol — the latter touted as a having a smaller carbon footprint — have much in common. But at least one ethanol plant — Blue Flint Ethanol in Underwood, N.D. — is co-located with a coal-fired power plant in order to use its excess […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (February 2008)
Survey captures industry’s carbon concerns; Sequestering coal plant emissions; Comparing mercury measurement methods
-
Coal
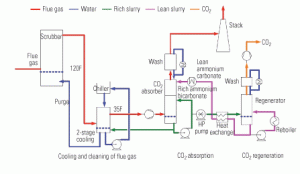
Alstom’s chilled ammonia CO2-capture process advances toward commercialization
Carbon dioxide emissions aren’t yet regulated by the EPA, but it’s likely they will be soon. There are many technically feasible, but as-yet-undemonstrated ways to reduce the considerable carbon footprint of any coal-fired plant, whether it uses conventional or unconventional technology. One promising approach to removing CO2 from a plant’s flue gas uses chilled ammonium bicarbonate to drive the separation process.
-
Commentary
What Congress can learn from Google
Chances are good that legislation to “cap and auction” greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions will become law as early as 2009. While many environmentalists, utilities, and energy companies agree that cap and auction is the right framework, huge differences remain. Environmentalists want an 80% reduction of GHG emissions by 2050, or sooner. Energy companies want more […]