Environmental
-
Coal
DOE Official Floats NSR ‘Carve-Out’ for Some Coal Plants
The Energy Department’s top fossil energy official said [in December that] he might seek exemption or relaxation of “new source review” requirements for certain U.S. coal-fired power plants that are boosting efficiency through retrofits if the plants are also good candidates for subsequent installation of carbon capture and storage systems.
-
O&M
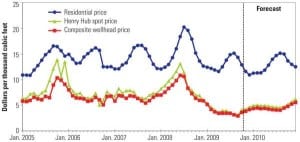
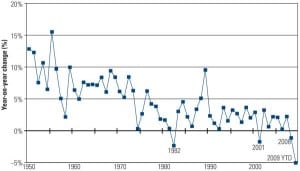
The U.S. Gas Rebound
"It’s déjà vu all over again," said Yogi Berra. The Hall of Fame catcher could easily have been predicting the coming resurgence of natural gas – fired generation. Yes, a few more coal plants will be completed this year, but don’t expect any new plant announcements. A couple of nuclear plants may actually break ground, but don’t hold your breath. Many more wind turbines will dot the landscape as renewable portfolio standards dictate resource planning, but their peak generation contribution will be small. The dash for gas in the U.S. has begun, again.
-
Environmental
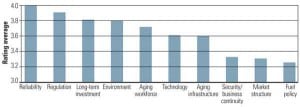
A New Regulatory and Environmental Milieu
There will be no shortage of important issues to keep utility executives and their staffs busy throughout 2010. Few of these will be surprises, although a number will emerge quickly and assume larger-than-life significance. The confluence of the great recession and the sturm und drang of environmental legislation will create the liveliest of the debates, but more subtle trends will drive additional stressors. The results of Black & Veatch’s 2009 fourth annual industry strategic directions survey can offer guidance as to how these issues will affect the industry in the coming year.
-
Coal
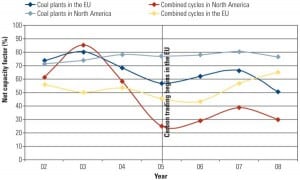
The Impact of Carbon Trading on Performance: What Europe’s Experience Can Teach North American Generators
The European carbon trading system experience suggests that North American generators should expect severely altered coal-fired power plant operating profiles if cap-and-trade legislation becomes law. In a groundbreaking study, Solomon Associates predicts the reduction in mean run time that North American generators should expect. The trends outlined in this study provide an overview of some of the broad challenges facing generators in moving to a carbon-constrained market environment.
-
Solar
A New Foundation for Future Growth
As the economy begins to grow again, the banking industry continues to stabilize, and lawmakers work on finalizing climate change legislation, the decisions made in 2010 will lay the foundation for the power industry for decades to come.
-
Coal
Brazil: Latin America’s Beacon
With the eighth-largest economy in the world, Brazil has a clear need for power, but balancing supply and demand has proven tricky in recent decades. Even in a country where over 80% of generation capacity comes from renewables, planning for future capacity additions isn’t straightforward or easy.
-
Coal
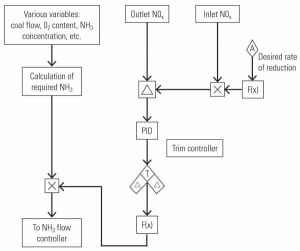
Tuning Ammonia Flow to Optimize SCR Performance
The selective catalytic reduction system has become ubiquitous throughout the world of power plants. Emission control requirements are ever-more stringent, and the cost of excursions is becoming increasingly high. The key to staying under the regulators’ radar is precisely controlling the ammonia injected into the boiler. A new control strategy does precisely that.
-
Commentary
Carbon-Cutting Solution: Dynamic Demand Technology
Once upon a time, climate change felt like a distant threat on the horizon. Now it is happening in front of our very eyes. Across the world, global warming is sparking more intense heat waves, more flooding, and more droughts. If climate change continues at its current pace, the social, environmental, and economic costs don’t […]
-
Solar
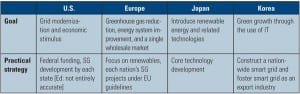
Which Country’s Grid Is the Smartest?
The U.S. isn’t the only country evaluating and implementing elements of smart grid technology. In fact, it could be argued that other nations are much farther along the path to a comprehensive, technically advanced system for integrating renewables, managing load, and creating a more flexible power grid.
-
Legal & Regulatory
GHG Emissions Reporting Begins Jan. 1
Last fall, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a rule creating a mandatory national system for reporting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The agency requires regulated entities to begin monitoring GHG emissions January 1, 2010, and to submit their first annual emissions reports March 31, 2011. This is a key step toward federal regulation of GHG emissions (a step that may have major implications regarding "major sources" and permitting requirements for new sources). It’s also an opportunity for power producers to implement their inventory management plans.