Environmental
-
Coal
From GHG to Useful Materials
Could the transformation of carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbonates and oxides solve the problem of greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) from fossil-fired power plants? Some companies are betting that such processes could make everyone happy and even create new profits. Buzz has been growing about this approach, though the concept has been around for many years.
-
Coal
New Coal Ash Rules May Focus on Conversion to Dry Storage
While the Environmental Protection Agency appears to have initially proposed to regulate power plant coal ash as hazardous waste, there are indications the Obama administration is preparing new federal rules that will at a minimum require utilities to convert coal ash impoundments from wet to dry storage to prevent leaks—a change that would cost tens of millions of dollars but also potentially increase regulated utilities’ rate base and earnings, a Wall Street firm says.
-
Coal
Congress, APPA Divided on EPA Greenhouse Finding
Highlighting a sharp division within the public power community, two senior House Democrats blasted the American Public Power Association for endorsing Sen. Lisa Murkowski’s effort to strip the Environmental Protection Agency of its Clean Air Act authority to regulate greenhouse gas emissions, with the lawmakers saying they have been informed that “numerous” APPA members oppose the endorsement.
-
Coal
New York Proposes Costly Retooling of Power Plant Cooling
In a move that could cost the state’s electricity generators an estimated $8.5 billion, New York regulators [have] issued a draft policy that would require the installment of closed-loop cooling systems at two dozen large power plants in the state, including oil, coal, nuclear and natural gas generators, to reduce fish kills and other harmful effects to wildlife in the water bodies that supply the plants’ cooling water.
-
O&M
The Unique Challenge of Controlling Biomass-Fired Boilers
Biomass has many advantages as a fuel for boilers: It’s inexpensive, readily available in many regions, CO2 neutral, and its use warrants government subsidies. The fuel also presents unique concerns to the designers, owners, and operators of biomass plants, especially in the design of the control system.
-
Coal
Big Bend’s Multi-Unit SCR Retrofit
Tampa Electric will soon complete a comprehensive selective catalytic reduction project on all four units at its Big Bend Power Station that will make Big Bend among the cleanest coal plants in the U.S. The project — the centerpiece of the company’s 10-year, $1.2 billion air quality improvement program — is on schedule to meet all of its air quality improvement goals by mid-2010.
-
Coal
Big Stone Remodels ESP into Pulse Jet Fabric Filter
Short of replacement, what are your options when your original electrostatic precipitator fails to meet your current emissions and opacity requirements? The management of Big Stone Plant chose the unconventional, yet economic approach of building a pulse jet fabric filter inside the casing of the old electrostatic precipitator. The upgrades restored plant availability and prepare the plant to meet the next regulated reductions in particulate matter emissions.
-
Water
Strategies to Reduce Sulfuric Acid Usage in Evaporative Cooling Water Systems
Concentrated sulfuric acid is often used to prevent calcium-based scale formation on condenser and heat exchanger tube surfaces in power plant evaporative cooling water systems. Unfortunately, the chemical’s price has jumped more than 300% over the past three years. If the rising cost of water treatment has you under the budget gun, here are some alternative strategies that can reduce or even eliminate your sulfuric acid usage.
-
Coal
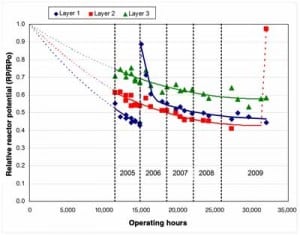
KnoxCheck Reports Reactor Potential and Catalyst Activity
Adding a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system to an operating coal-fired plant may be an expensive and time-consuming project, but the environmental benefits are without question. However, once construction is complete and operations staff assume control of the SCR, proper measurement tools are required to monitor the catalyst performance life cycle.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes To Tighten Ozone Standard
In one of the most far-reaching of numerous new air regulations expected from the Obama administration, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed to tighten the primary federal standard for ground-level ozone, the principal constituent of smog, to within a range of 60 to 70 parts per billion, saying the tougher standard is needed to protect human health.