Coal
-
O&M
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part II
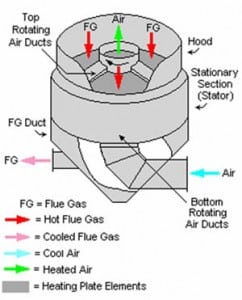
Efficient boiler operation requires boiler auxiliary equipment to operate in harmony. The air preheater, for example, though it has few moving parts, is vital to maintaining efficient boiler performance. In this second installment of our Power 101 series, we examine performance degradation caused by corrosion and fouling of the air preheater that results from the combustion of coal plus the effects of ammonia and sodium bisulfite injection for SO3 mitigation.
-
Commentary
Pre-Combustion Technologies: A Key Environmental Compliance Tool
Arizona Public Service’s (APS) plan to close three older coal-fueled units at the Four Corners Power Plant in New Mexico and buy out Southern California Edison’s 48% share of the two remaining units is a creative means of surviving the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) committed action against coal-fueled generation.
-
O&M
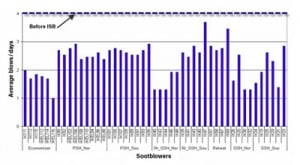
Clinker Minimization at San Miguel Electric Co-Op
San Miguel Electric Cooperative selected and installed an automatic sootblowing system for its Unit 1 to minimize clinkers in the boiler that caused semi-annual unscheduled outages. New boiler surface-cleaning equipment and intelligent cleaning software eliminated these expensive outages.
-
Coal
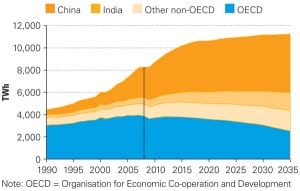
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.
-
Coal
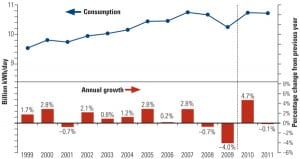
The U.S. Power Industry 2011: The Sequel
If Hollywood were scripting the power industry story for 2011, it would be a sequel to 2010—more of the same, but just not quite as good. Natural gas gets top billing and the accolades, wind power drops to a supporting role, and new nuclear answers the casting call but has yet to get a speaking part. Coal is like Mel Gibson—a talented Oscar winner unlikely to get another leading role. In this, our fifth annual industry forecast report, the story may be familiar, but the price of admission is going way up.
-
Coal
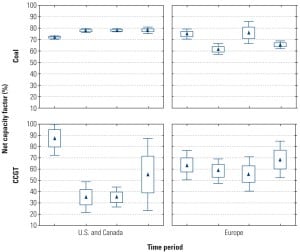
Coal Plants Challenged as Gas Plants Surge
European carbon trading is gradually pushing down coal-fired capacity factors, and operating costs are rising. The U.S. may not have a carbon market, but increasing regulatory requirements are having the same effect on coal-fired generation capacity factors and operating costs. In the meantime, gas-fired assets are enjoying increased usage and lower unit costs.
-
Coal
Oxy-Combustion: A Promising Technology for Coal-Fired Plants
For more than a decade Babcock & Wilcox Power Generation Group Inc. and Air Liquide have been developing oxyfuel technology with the goal of using it to concentrate CO2 from pulverized coal-fired power plants and achieve up to 90% CO2 capture and storage. This technology was recently selected for demonstration as part of FutureGen 2.0.
-
Coal
Spain Makes Headway in CCS Efforts
A 14-MW pilot plant built by energy firm ELCOGAS at its 335-MW integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) facility at Puertollano in Spain in September captured its first metric ton of carbon dioxide. Now the company plans to begin tests to procure more technical and economic information about carbon capture and storage (CCS), including how efficient it is to co-produce hydrogen and power with carbon capture processes.
-
O&M
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part I
Boiler auxiliary equipment often receives no respect for the role it plays in maintaining efficient boiler performance. In this second installment of our Power 101 series, we examine the design and performance of the air preheater.
-
Coal
Efficiency Favored in EPA Greenhouse Guidance To States
A long-awaited Clean Air Act regulatory guidance document released by the Environmental Protection Agency recommends that state air regulators strongly emphasize energy efficiency in determining the most cost-effective and technically feasible greenhouse gas control technologies that must be used by utilities and other major industrial emitters when expanding existing facilities or building new ones.