Coal
-
Coal
Re-Industrializing America with Clean Coal Technologies
Balancing the rising energy needs of a globally expanding population (most of which lives in poverty) against the need to reduce increases in atmospheric emissions is a monumental problem. What role can clean coal technologies play?
-
Coal
Predicting U.S. Coal Plant Retirements
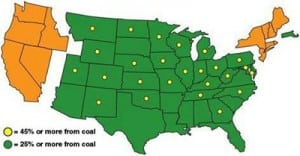
The question concerning coal plant retirements forced by looming regulatory rules, low gas prices, and moribund load growth has changed from “Why?” to “How many plants?” Many highly detailed analyses and reports have been written on the subject by superbly qualified analysts. This approach to estimating potential plant closures is much more qualitative, and much easier to understand. However, the results closely align: About 50 GW are threatened.
-
Coal
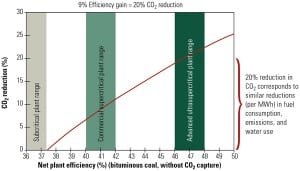
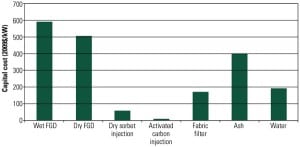
Coal-Fired Generation Cost and Performance Trends
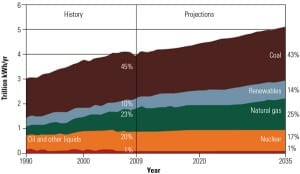
Increasing regulatory requirements and a focus on reducing carbon emissions in the U.S. have significantly reduced the number of new coal-fired plants under development compared with past years. In addition, projected capital costs for new coal-fired plants have risen sharply in the past year, while those for natural gas combined-cycle and combustion turbines have stayed relatively flat. In order to keep coal a viable energy source, many countries, including the U.S., are seeking ways to improve plant efficiency while reducing carbon emissions.
-
Coal
Proactive Strategies for Dealing with Combustible Dust
The challenges of using Powder River Basin (PRB) coal are as significant as the rewards. The subbituminous coal contains lower amounts of sulfur dioxide than bituminous coal but can be prone to combustible dust explosions if it is not properly managed. To eliminate such hazards, plant personnel need to establish best practices for the safe operation and maintenance of PRB coal-handling and -storage systems based on best available technologies.
-
Coal
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part III: Metrics Used for Compensation
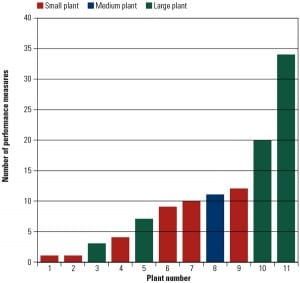
In Part III of this three-part report, we look at plant- and fleet-level metrics used to determine compensation. As expected from this EUCG-sponsored benchmarking survey, there is broad use of quantifiable metrics to set portions of compensation, but the metrics selected vary substantially across the surveyed utilities. More surprising was the number of utilities that used no performance metrics as part of their employee compensation packages.
-
Coal
China’s Five-Year Plan Is Heavy on Non-Fossil Generation
The People’s Republic of China’s Congress approved a much-anticipated draft of the country’s 12th Five-Year Plan (2011–2015) on March 14. Along with key objectives that included boosting its gross domestic product (GDP) by 7% annually on average, the country for the first time in a five-year plan established targets to tackle climate change. It plans to reduce carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by 17% from 2010 levels by 2015 and to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 16% from 2010 levels by 2015.
-
Coal
Large-Scale Tests Begin to Convert Flue Gas to Usable Water
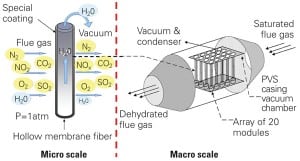
Subsidized by the Dutch government, a number of Dutch utilities, the European Membrane Institute at the University of Twente, and Dutch consulting firm KEMA have, for over a decade, been testing membrane technology that promises to directly convert water vapor from power and other industrial plants’ flue gases into drinking water. The technology could provide a new source of large volumes of potable water.
-
Coal
Research and Development for Future Coal Generation
If coal is to be a viable long-term fuel for a significant percentage of electricity generation, research and development is needed to increase thermal efficiency, demonstrate cost-effective and secure carbon dioxide capture and storage, further improve emission controls, and reduce water demands.
-
Coal
Added Regulatory Hurdles Will Accelerate Coal Plant Retirements
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is developing a number of new regulations for the power sector governing air emissions, cooling water intake structures, and coal combustion waste disposal methods. Combined, these regulations have the potential to drive as much as 40% of existing coal-fired generating units to retire in the next 10 years, representing about 51 GW.
-
O&M
Condenser Performance Improvement Through Innovative Cleaning and Leak Detection Technologies
One of the largest returns on investment a plant can achieve is the improved condenser performance that results from an effective condenser tube cleaning. Perhaps it is time to reevaluate your choice of cleaning technologies, establish an optimal cleaning schedule, and add routine air and water in-leakage surveys to your plant’s maintenance schedule.