Focus on O&M
-
Coal
Safety a Main Theme at Asian Coal Users’ Meeting
Power plant operators, managers, and other professionals from across Southeast Asia met in Hong Kong in early November for the second annual Asian Sub-Bituminous Coal Users’ Group meeting, created to share information and best practices related to safety, handling, combustion, characteristics, and risk management of the fuel.
-
O&M
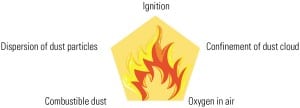
Controlling Fugitive Combustible Coal Dust
Regardless of how much prevention is employed to mitigate combustible dust in coal-fired power plants, fugitive coal dust is pervasive and can be dangerous. In coal-fired power plants, mechanical transfer points are leading sources for airborne fugitive dust. However, because coal dust travels quickly over large areas with minimal airflow, fugitive combustible dust settles in many areas.
-
Smart Grid
Conference Report: 12th ICS Cyber Security Conference
The 12th ICS Cyber Security Conference was held at Old Dominion University’s Virginia Modeling Analysis and Simulation Center (VMASC) October 22–25, 2012. There were approximately 150 attendees from multiple industries, universities, government, and vendors as well as consultants from the U.S., South America, Europe, and Asia.
-
O&M
Users Return to Fogging on Frame 7FAs
It has been a decade since an R0 compressor blade was liberated on one of the eight Frame 9FA combustion turbines at CLP Power Hong Kong’s Black Point Power Station. This catastrophic failure eventually led to GE’s recommendation that operators severely limit or cease using online water wash (OLWW), inlet fogging, wet compression, and evaporative coolers on F-Class turbines.
-
Nuclear
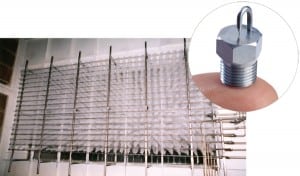
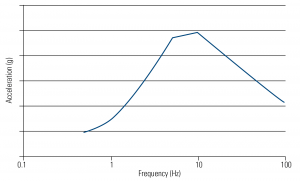
Seismic Instrumentation at Nuclear Power Plants
When a nuclear power plant experiences ground motion due to an earthquake, an evaluation may be needed before allowing the plant to continue operating or to resume operating if it has been shut down, as was the case after the seismic event that shut down both units at Dominion’s North Anna Power Station on August 23, 2011.
-
O&M
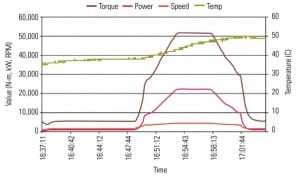
Maximizing Steam Turbine/Compressor Performance with Precise Torque Monitoring at the Coupling
All turbo machinery is subject to degradation that, over time, will affect the system’s efficiency and operational performance. Precise monitoring of turbo machinery performance with continuous torque-monitoring systems can be used to identify gradual efficiency loss. That, in turn, allows a more focused maintenance scope to be developed that can return the system to its optimum operation and efficiency.
-
Business
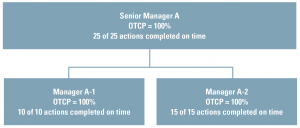
Measuring On-Time Completion to Improve Your EHS Audit Program
A number of factors promote effective and responsible completion of EHS audit action plans, with the most important being the proper alignment of responsibility and authority for developing and implementing the audit action plan.
-
O&M
Predictive Maintenance That Works
This is the sixth in a series of predictive maintenance (PdM) articles that began in the April 2011 “Focus on O&M” in which the essentials of PdM were introduced. In this occasional segment, we have explored specific PdM techniques, such as motor-current signature analysis, oil analysis and thermographic analysis and their routine use, and ultrasonic and vibration analysis. In this issue we look at lubricating oil wear-particle analysis.
-
O&M
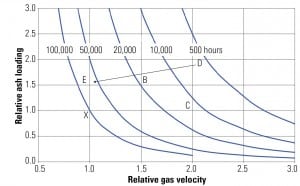
Fly Ash Erosion Control and Prevention
Boiler tube failures (BTFs) are responsible for the largest portion of availability loss (about 4%) in the fossil boiler industry, and approximately 25% of all tube failures are due to fly ash erosion (FAE). An Electric Power Research Institute report indicated that the problem was being managed in U.S. utilities by maintenance activities that were put into effect each time a boiler was taken off-line. The cost of an individual repair was a small fraction of the forced outage cost, and therefore has been considered justified in the past. However, many forced outages continue to be experienced each year due to FAE, and in many cases, these occur at identical locations, indicating that applied solutions relieve, but do not cure, the problem.
-
Solar
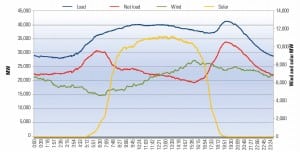
Maintaining Grid Reliability with a High Renewables Portfolio
The first problem with high renewable penetration is that wind and solar are not dispatchable.