Latest
-
Nuclear
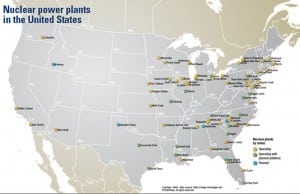
Comanche Peak Steam Electric Station, Glen Rose, Texas
A Luminant-Bechtel team completed replacement of four steam generators and the reactor vessel head—plus almost 200 other work packages—in a short, 55-day outage at Comanche Peak Unit 1. Matching or exceeding this schedule will become the goal for those who follow.
-
Nuclear
Fermi 2 Power Plant, Newport, Michigan
Detroit Edison teamed with Washington Group International to complete a first-of-its-kind nuclear retrofit project: replacing two moisture separator reheaters during a single 35-day outage with a perfect safety record. POWER recognizes this significant accomplishment by naming Fermi 2 Power Plant a 2007 Top Plant.
-
Nuclear
Fort Calhoun Nuclear Generating Station, Omaha, Nebraska
Just under a year ago, Omaha Public Power District completed perhaps the most complex nuclear power plant renovation in the history of the industry in a scant 85 days—five fewer days than the original plan called for. POWER recognizes Fort Calhoun Nuclear Generating Station as a Top Plant for packing more work into one outage than was thought possible, and then executing the plan ahead of schedule and below budget.
-
O&M
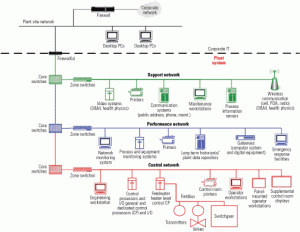
Plantwide data networks leverage digital technology to the max
To make the most of their digital devices and enable the sharing of data by different departments, new and old plants alike need a reliable digital data infrastructure.
-
O&M
Upgrade your BWR recirc pumps with adjustable-speed drives
The U.S. is home to more than 30 boiling water reactors of BWR-3 through -6 vintage. At one time or another, all have experienced obsolescence, reliability, or control problems with their reactor recirculation flow control systems and components. Temporary down-powers are often required for corrective maintenance. Exelon Nuclear plans to begin upgrading the recirculation pump motor drives at its BWRs in the spring of 2009. The upgrade project’s technical design and business case were developed in great detail before the project was approved. This article presents the results of all key internal analyses.
-
Nuclear
Defined scope, experienced team essential to nuclear I&C upgrade projects
Over the past few years, U.S. nuclear power plants have begun replacing their obsolete analog control systems with digital control systems. Many of these projects have been completed successfully, yielding a tidy return on investment in the form of increased generation. However, some have encountered difficulties, which resulted in cost overruns and schedule delays. This minority of projects may have eroded the industry’s confidence in digital upgrade projects, but a well-run project is still one of your best options for squeezing the last drop of performance out of your plant.
-
Nuclear
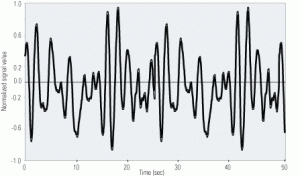
Accurately measure the dynamic response of pressure instruments
How do you know if a pressure transmitter is giving poor results? Unless the transmitter actually fails, most operators won’t notice a very slow loss in accuracy or response time. Fortunately, the noise analysis technique can identify such changes before they cause a problem. The technique has been used to effectively measure the dynamic response of nuclear power plant pressure sensors and their associated sensing lines. It also can be applied to any plant that relies on accurate instrumentation for control and monitoring plant performance.
-
Business
Milestones on the road to commercial operation
The electric power industry is capital-intensive, and it takes several years to build and commission a baseload plant for commercial operation. Owners seek contractors who are willing—given proper incentives—to build a plant for a lump-sum price with a guaranteed schedule and performance. Matching an owner’s wants with contractors’ needs is an exercise in allocating risk. Avoid the contract traps that can stall a project and cost millions to resolve.
-
Business
This month in POWER . . .
POWER began its life in October 1882 as a tabloid-size publication originally entitled Steam. About the same time, two young Boston advertising salesmen decided to launch a new magazine about textile mill steam plants, called POWER. They bought Steam prior to publishing POWER’s first issue, so early issues of this magazine carried the flag “POWER, […]