Latest
-
Wind
Finding Fault: Improving Wind Farm Availability
Survey wind turbine manufacturers about how to calculate wind farm availability and you will get countless different definitions and exceptions to the rule.
-
O&M
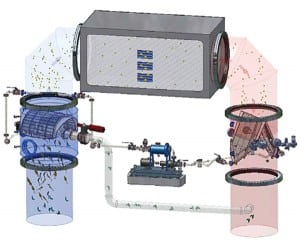
Keeping Condensers Clean
The quality of the cooling water intake and the amount of debris in that water affects the operation and performance of the condenser and therefore the thermal performance of the typical steam plant.
-
O&M
Expanding the Use of Predictive Maintenance as a Business Strategy
The Linde Group is a world-leading gases and engineering company operating in more than 100 countries. It’s no surprise that the company uses a variety of advanced monitoring techniques and equipment to keep its plants operating reliably. In the U.S. and UK particularly, Linde plants have used online machine condition monitoring for a number of years. At its Shanghai headquarters, Linde has formed a large and impressive remote operations center where it monitors and tracks the process operations of all its major gas plants in China 24 hours a day.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Regulatory Options for Feed-in Tariffs
Feed-in tariffs (FITs) have been used by European countries to foster the growth of renewable generation resources, notably solar. These tariffs generally require electric distribution companies to purchase power produced by a specified class of generators at above-market rates. The object of the tariffs is to encourage development of the favored generation resources by ensuring the existence of a profitable market for their power production.
-
Geothermal
Top Plant: Blue Mountain Faulkner 1 Geothermal Power Plant, Humboldt County, Nevada
Completed in 2009 and partially funded under the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act, the 50-MW Blue Mountain Faulkner 1 Geothermal Power Plant is harnessing large amounts of renewable energy by tapping into an underground geothermal reservoir in northern Nevada. This subterranean source of heat allows the binary plant to generate pollution-free baseload electricity.
-
Waste to Energy
Top Plant: Colmac Energy Inc.’s Biomass- Fueled Power Plant, Mecca, California
The 47-MW Colmac Energy facility is the largest biomass-fueled power plant in California. Colmac operates with a capacity factor consistently in the 92% to 95% range and at a net plant heat rate comparable to waste coal facilities. Colmac Energy has demonstrated that biomass plants using urban wood wastes as fuel can generate significant environmental benefits, including reduced air pollutants from open-air burning and lowered demand for landfill space.
-
Solar
Top Plant: DeSoto Next Generation Solar Energy Center, DeSoto County, Florida
The forecast is looking sunny for the 25-MW DeSoto Next Generation Solar Energy Center, which has more than 90,000 photovoltaic (PV) panels and is the largest solar PV plant in the U.S. Completed in October 2009, it is a sustainable energy solution with minimal maintenance costs. The site uses no fuel, consumes no cooling water, has no air emissions, and creates no waste products.
-
Waste to Energy
Top Plant: Kajang Waste-to-Energy Plant, Semenyih, Malaysia
At Malaysia’s first waste-to-energy plant, municipal solid waste (MSW) is converted into refuse-derived fuel for use in an integrated steam power plant. This facility was designed to achieve the twin objectives of environmentally friendly MSW disposal and generating renewable power.
-
Waste to Energy
Top Plant: Kaukaan Voima Oy Biomass-Fired Power Plant, Lappeenranta, Finland
Located in the heavily forested country of Finland, the Kaukaan Voima biomass-fueled power plant produces process steam and electricity for UPM’s Kaukas pulp and paper mill as well as electricity and district heating for Lappeenrannan Energia, a city-owned power company. Launched in 2009, the plant can provide 125 MW of electricity, 110 MWth of district heat, and 150 MWth of process steam thanks to one of the world’s largest wood-fired fluidized bed boilers.
-
Wind
Top Plant: Thanet Offshore Wind Farm, Isle of Thanet, UK
In September, the 300-MW Thanet Offshore Wind Farm, the world’s largest offshore wind energy facility, began operation off the southeastern coast of England. The wind farm has 100 3-MW turbines manufactured by Vestas. The facility will generate electricity equivalent to the annual consumption of more than 200,000 British households.