In This Issue
-
News
Follow the Leader
Another year has passed and the promised U.S. nuclear renaissance is still in the Dark Ages. Blame for slow progress is usually cast on the pedestrian pace of finalizing loan guarantees, the economy and slow load growth, or the rising cost of construction. The excuses end when competition increases. Two years have elapsed since the […]
-
Nuclear
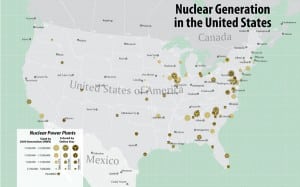
Map of Nuclear Generation in the United States
Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed. For full-sized maps, contact Platts.
-
Nuclear
Russia Powers On, Boosting Nuclear Reactor Sales
Atomstroyexport, the Russian Federation’s nuclear power equipment and services export monopoly, in September signed a US$1.8 billion contract with the Chinese government for development of the second stage of the Tianwan nuclear power plant in Lianyungang City. Under the agreement, Units 3 and 4 are to be built in a way similar to construction of the first stage of Tianwan—two Russian-designed VVER-1000 reactors that came online in 2007, each with a rated capacity of 1,060 MW.
-
Nuclear
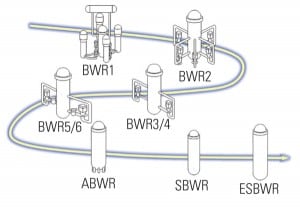
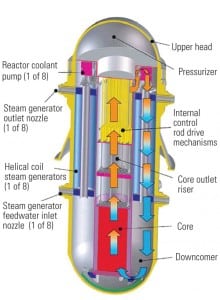
The Evolution of the ESBWR
The commercial nuclear industry is in the midst of developing multiple reactor technology options. Next in our series of articles exploring competing reactor technologies are GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) and Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR). The design improvements incorporated into these reactors include passive safety systems, design and construction simplification, and component standardization to reduce construction and operating costs.
-
Nuclear
China Begins Operation of First CPR-1000
The first unit of Ling Ao phase II (Unit 3) in Guangdong Province, China, entered commercial operation in late September. The 1,080-MW reactor is the first CPR-1000—a Chinese design—to be built, and its start-up marks a major milestone in the country’s concerted nuclear power expansion.
-
Gas
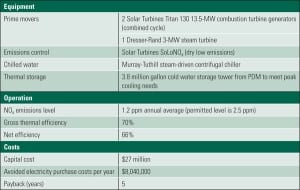
Smart Power Generation at UCSD
The University of California, San Diego has been accumulating awards for its savvy use of a constellation of power generation and energy-saving technologies. The campus already controls a fully functioning microgrid—including a cogeneration plant—and, as befits a research institution, is constantly looking for new ways to make its energy system smarter. This “living laboratory,” as campus leaders like to call it, demonstrates what it takes to build a smarter grid and why the effort is worth it.
-
Wind
World’s Largest Offshore Wind Farm Opens in the UK
Swedish company Vattenfall in late September officially opened the 300-MW Thanet Offshore Wind Farm in southeast England. Covering an area of 35 square kilometers, the installation comprising 100 Vestas V90 turbines, each 115 meters (m) high, is the largest offshore wind farm in the world to date.
-
Gas
Microturbine Technology Matures
Microturbine technology has evolved from early systems of 30 kW to 70 kW to today’s systems, which can have individual ratings of 200 kW to 250 kW. Packages up to 1 MW are now available that can be assembled into multipac units for projects of 5 MW to 10 MW. These modern units are packaged with integrated digital protection, synchronization, and controls; they produce high combined heat and power efficiencies; and they are capable of using multiple fuels.
-
Coal
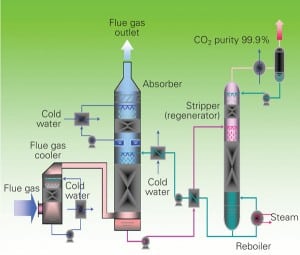
Southern Co. Captures Carbon Dioxide at Plant Yates Pilot
The pilot-scale project at Georgia Power’s Plant Yates near Newnan, Ga.—the first step in one of the industry’s largest demonstrations of a start-to-finish coal-fired power plant carbon capture and storage system—reached a significant milestone this September, capturing the greenhouse gas for the first time.
-
Nuclear
Are Smaller Reactors Better?
Is a paradigm shift—an economic and engineering earthquake—in nuclear power plant design on the horizon? For most of the past 50 years, the mantra in planning new nuclear plants has been “bigger is better.” But a growing number of nuclear power engineers and designers are contemplating a world where small is beautiful.
-
Business
Turkey Joins European Grid
Turkey, a country that has long vied to become part of the European Union, is finally part of its grid, at least. The nation’s power system was synchronized with Continental Europe’s interconnected grid this September, marking the beginning of a year-long trial period in which security and performance will be monitored.
-
Nuclear
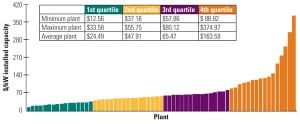
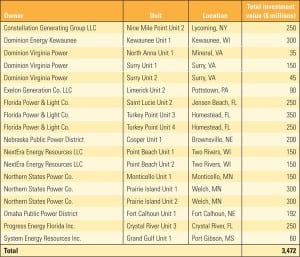
Benchmarking Nuclear Plant Capital Requirements
The EUCG Nuclear Committee’s primary goal is to optimize the costs and reliability performance of participating plants by publishing for its members a comprehensive database of performance metrics and best practices derived through surveys of its membership. Earlier reports examined staffing and performance data. In this exclusive EUCG report, we examine nuclear plant capital requirements.
-
Coal
Frog-Inspired Artificial Foam Could Help Trap CO2
In August, researchers from the University of Cincinnati who are working on creating an artificial foam that could absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the flue gas at power plants and convert it into biofuel won the grand prize at the 2010 Earth Awards in London.
-
Nuclear
The Best of U.S. Nuclear Developments 2010: Uprates and Loan Guarantees
Utilities are spending billions of dollars on nuclear plant uprate projects, and Southern Company has been offered $8.3 billion in federal loan guarantees to build Vogtle Units 3 and 4 (although the final deal has yet to be signed). Meanwhile, other nuclear developers have slashed preconstruction spending as the cost of the “nuclear renaissance” becomes evident.
-
Business
POWER Digest (November 2010)
TVA’s 550-MW Combined-Cycle Plant Starts Operations. The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) on Sept. 30 officially began operating the Lagoon Creek Combined Cycle Plant, a 550-MW natural gas–fired plant, near Brownsville, Tenn. The federal utility said that the new plant, the first new power generation source built by TVA since 2002, would provide power during days […]
-
O&M
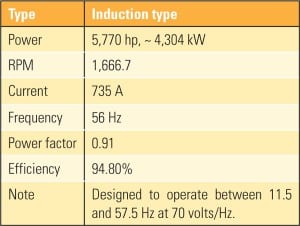
Retrofitting BWR Recirculation Pumps with Adjustable-Speed Drives
Exelon Nuclear recently replaced the original motor-generator sets for its boiling water reactor (BWR) recirculation pumps at its Quad Cities Generating Station Unit 1 with adjustable-speed drives. We examine the actual energy savings, motor-starting characteristics, control accuracy and stability, and motor and cable thermal behavior of this retrofit project.
-
Nuclear
NRC Confident in Long-Term Dry Cask Storage
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) approved an updated “waste confidence” rule in mid-September that reflects the agency’s confidence that spent nuclear fuel (SNF) can be safely stored for at least 60 years beyond the closing date of any U.S. nuclear plant. Approval of this rule was required before the NRC can license any new reactors that will be required to store SNF on site indefinitely.
-
Commentary
Biomass Power Under Attack
Biomass energy has been an up-and-down industry for decades. As public awareness grows, it inevitably influences new tax legislation and environmental regulations. Two recent events have made the climate for development of this renewable resource even more volatile.
-
Nuclear
EPRI Updates Spent Nuclear Fuel Storage Handbook
EPRI recently issued a handbook on nuclear spent fuel storage that examines regulatory trends affecting used fuel storage, describes available dry storage technologies, reviews planning considerations for spent fuel storage installations, and discusses technical issues affecting dry storage.
-
News
Semi-Automated Tube Bundle Cleaner
Part of a family of automated and semi-automated tube-cleaning accessories, the new Saflex 2000 makes tube bundle cleaning more productive because it can clean four times as many tubes in a given period as manual water jetting, says NLB Corp. Operating at pressures up to 40,000 psi, the semi-automated accessory cleans two tubes (ranging from […]
-
O&M
CSB Releases Hot Work Safety Notice
The Chemical Safety Board (CSB)—an independent federal agency charged with investigating serious chemical accidents such as equipment failure, as well as inadequacies in regulations, industry standards, and safety management systems—recently released multiple reports that should be made part of every power plant’s safety training program.
-
News
No-Glass ORP Sensors
Engineers and technicians searching for a high-performance oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) sensing solution will find that the S10 and S17 ORP Sensors from Electro-Chemical Devices (ECD) feature a no-glass design with platinum or gold sensor tips to operate safely in a wide range of applications. ECD’s ORP S10 and S17 Sensors come with easily replaceable ORP […]
-
O&M
NFPA Gas Purging Rules Updated
The CSB has made urgent recommendations to the NFPA and the International Code Council to prohibit indoor purging and require companies and installers to purge flammable fuel gases to safe locations outdoors, away from workers and ignition sources.
-
News
Pre-Cleaner for Vulcanized Conveyor Belts
The new QC#1 MT Pre-Cleaner from Martin Engineering is a high-quality cleaning blade for use on vulcanized conveyor belts. It features a special polyurethane blend and tungsten carbide tip to deliver service life two to three times longer than conventional urethane blades, the company claims. Designed to provide excellent cleaning performance without any break-in period, […]
-
O&M
Abrasion-Resistant Pipe Handles Ash Slurry
Steel piping systems are widely used at coal-fired power plants for a variety of purposes, including the conveying of coal ash slurry to nearby settling ponds, the transfer of limestone slurry to absorber spray towers for removal of SO2 and dilute hydrochloric acid from flue gases, and for transporting away the calcium sulfate by-product of the flue gas desulfurization process.
-
News
Correction (November 2010)
Correction In the September issue’s “Taming Condenser Tube Leaks, Part I,” the first full paragraph in the main text on page 57 should say, “If chloride and sulfate in the steam cannot be maintained below 8 ppb….” POWER regrets the error.
-
O&M
Air Casters Speed Equipment Moves
When it comes to moving megaton items like feedwater heaters or recirculating pumps, conventional moving tools such as wheel rollers, cranes, hoists, and come-alongs may be virtually useless. In some cases, moving large components is dangerous in a space-constrained location surrounded by delicate process control equipment. Feedwater heater and recirculating pump removal and replacement are […]
-
Solar
The Global Smart Grid Scene
Presenters at the inaugural GridWise Global Forum in Washington, D.C., September 21 to 23 had a lot to say about the prospects for smarter grids. This synopsis of facts and opinions shared at the event, which attracted several smart grid A-listers, looks at the major challenges ahead, especially for the U.S.
-
Legal & Regulatory
EPA’s Mercury Rule: Another Incarnation Coming
Much like the shape-shifting substance it regulates, the mercurial enforcement rule that governs mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants has changed unpredictably several times in recent years.
-
Distributed Energy
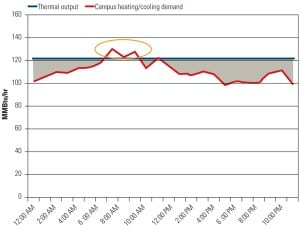
Matching Load and Generation at UCSD
“Smart Power Generation at UCSD” explains how the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) is maximizing the value of combined heat and power. However, like any other grid-controlling entity large or small, the campus has to match generation and load. Its two Solar Turbines gas turbines operate in baseload mode 24/7 while the cogeneration side of the plant maximizes the value of “waste” heat and electricity that isn’t needed to serve immediate load by generating steam and chilled water for campus heating and cooling.
-
Nuclear
Collaborative Team Investigates Long-Term Nuclear Operations
The Atomic Energy Act originally established the length of a U.S. commercial nuclear reactor license as 40 years and made it renewable for another 20 years. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has stated that it bases the length of these licenses (and the 50+ renewed licenses granted to date) not on any particular technical limitation but on whether the plant meets current safety requirements. Does this mean there could be reactor life after 60?
-
Smart Grid
Combined Heat and Power Across the U.S.
The University of California, San Diego (see “Smart Power Generation at UCSD”) is just one of many combined heat and power (CHP), or cogeneration, systems in the U.S. A 2008 report by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), “Combined Heat and Power: Effective Energy Solutions for a Sustainable Future,” notes that Texas has the most CHP capacity—much of it used by the petrochemical and petroleum refining industries. California ranks second, largely a result of “industrial demands, stringent air quality requirements, and effective policies that encourage adoption of CHP.”