In This Issue
-
News
Fracking Problems
By most estimates, natural gas is likely to become the dominant power generation fuel in the U.S. within perhaps a decade. The rapid growth in natural gas supplies follows advanced drilling techniques that can economically tap large shale gas reserves located deep beneath Earth’s crust. Unfortunately, it only takes one outlaw drilling company to frack it up for the rest of us.
-
O&M
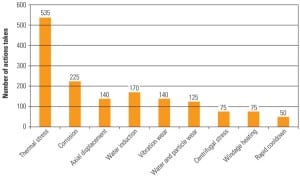
Make Your Plant Ready for Cycling Operations
Cycling your steam power plant is inevitable, so now is the time to learn how to minimize equipment damage and assess the true costs of cycling. Whether cycling is required by the grid operator because of renewable integration or other factors, you must be proactive about updating operating processes and upgrade equipment so the transition to cycling operation goes smoothly.
-
Nuclear
THE BIG PICTURE: Underground Nuclear Waste Disposal
According to the International Atomic Energy Commission, deep disposal in stable geological formations is the only sustainable way to safely manage spent fuel and high-level waste (HLW) from nuclear power reactors. No permanent geological repository has yet been built, but some countries have found a location for a future repository. Others are researching the option…
-
O&M
Mitigating the Effects of Flexible Operation on Coal-Fired Power Plants
As coal-fired power plants increasingly operate in cycling modes, many plants are confronting the potential for higher levels of component damage and degraded performance of environmental control equipment. Generators and EPRI are working together to find ways to mitigate the effects of cycling operation and to manage the transition of formerly baseload plants to flexible operation.
-
Smart Grid
Milestones for Flywheel, Lithium Battery Grid-Scale Projects
Energy storage developments got a boost as Beacon Power Corp. in June announced that its first flywheel energy storage plant in Stephentown, N.Y., achieved its full 20-MW capacity, and AES Energy Storage said its Los Andes battery storage system in Chile had performed continuously for more than 18 months as a critical reserve unit for the nation’s northern grid.
-
Nuclear
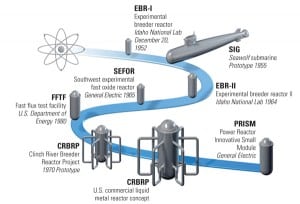
PRISM: A Promising Near-Term Reactor Option
PRISM is an advanced sodium-cooled reactor that simultaneously reduces proliferation concerns by consuming transuranics and weapons-grade plutonium and closes the nuclear fuel cycle. PRISM’s passive safety systems, successfully demonstrated in earlier liquid metal reactor programs, combined with modern design requirements, make PRISM invulnerable to most serious accidents that can affect light water reactors.
-
Gas
Alstom Launches Upgraded GT26
Just as GE Energy, Siemens, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) in May announced gas combustion technology developments—each seeking to push the 60% barrier with new gas turbine designs—Alstom has quietly been upgrading its KA26 combined cycle power plant. (See the July 2011 “Global Monitor” for more information on the GE, Siemens, and MHI turbines.) The firm says that the next generation of the 500-MW power plant, based on the advanced class GT26 gas turbine, features “achievable” efficiencies of over 61%, increased flexibility, and more than 350 MW, which can be delivered in less than 15 minutes to help integrate renewable energy sources (Figure 3).
-
Smart Grid
Accelerating the Pace of EV Deployment
A number of automotive manufacturers, electric utilities, electric power associations, and research groups are working to develop and evaluate technical approaches to integrating plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) into the U.S. electrical grid system. This is a key requirement of facilitating widespread, near-term adoption of PEVs by the American public.
-
Coal
Largest CCS Project in Operation
Companies continue to increase the size of carbon capture and sequestration test projects. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has launched operation of what it calls the world’s largest demonstration of carbon capture on a pulverized coal plant.
-
Marmaduke
Marmy’s One-Squirt Celebration
Steve Elonka began chronicling the exploits of Marmaduke Surfaceblow—a six-foot-four marine engineer with a steel brush mustache and a foghorn voice—in POWER in 1948, when Marmy raised the wooden mast of the SS Asia Sun with the help of two cobras and a case of Sandpaper Gin. Marmy’s simple solutions to seemingly intractable plant problems remain timeless. This Classic Marmaduke story, published more than 50 years ago, reminds us that an overhaul or startup may not go as planned, but it can still have a happy ending.
-
Hydro
Chile, Peru Put the Brakes on Mega-Hydro Projects
Weeks after Brazil’s environmental agency, IBAMA, granted final approval for construction of the mammoth 11.2-GW Belo Monte Dam in the Amazon region to proceed, an appeals court in Chile suspended plans for the 2.75-GW multi-dam HidroAysen project in the Patagonia region, and Peru’s government terminated a concession for the 1.5-GW Inambari in the Peruvian Amazon area after month-long mass protests (Figure 5).
-
News
Screened Tungsten Halogen Lights for Nuclear Plants
BIRNS Inc., designer and manufacturer of lights for the nuclear power industry, introduced enhancements to the popular BIRNS Kelvin—a 16,000-lumen tungsten halogen light that features a 120 volt/1,000 W lamp with instant on/off and hot-restrike capability. Designed for underwater use in areas with high levels of radiation and nuclear contamination, the new model 5813 now […]
-
Hydro
Osmotic Power Makes Headway
Statkraft began operating its 4-kW prototype osmotic power plant at Tofte, just outside Oslo, Norway, in 2009. Now the firm reports that it is close to developing a large-scale plant. In June, Statkraft and Japanese materials manufacturer Nitto Denko/Hydranautics signed an agreement for the development and supply of membranes specifically designed for use in large-scale osmotic power plants.
-
News
Clean-Up Kit for Large Outdoor Oil Spills
New Pig Corp. launched the “PIG UV-Resistant Spill Kit in a 95-Gallon Container” as an easy oil-spill clean-up solution to large outdoor spills. Suitable for outdoor use and storage, the PIG UV-Resistant Spill Kit is nontransparent, providing superior protection of absorbent contents from UV degradation during long-term storage outdoors. The container includes enough PIG oil-absorbent […]
-
Gas
E.ON Commissions 433-MW Hungary CCGT
Two years after it laid the foundation stone, Germany’s E.ON on June 27 opened Hungary’s most efficient combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) power plant (Figure 7). The €400 million ($573 million) plant in Gönyü has a capacity of 433 MW and an efficiency of over 59%, E.ON claims. Siemens supplied the main components: an SGT5-4000F gas turbine, an SST5-5000 steam turbine, an SGEN 5-3000W generator, and the entire electrical and instrument and control equipment. The natural gas–fired power plant is of single-shaft design with the main components arranged in a single driveline.
-
News
Heavy-Duty Lathe Carriage Shields
Danray Products introduced a line of heavy-duty lathe carriage (saddle) shields that are designed for manual lathes or similar machines. The shield attaches directly to the backside of the carriage, so it moves with the carriage as the work piece is being machined. This provides a barrier between individuals and the point-of-operation hazard. The shield […]
-
Business
POWER Digest (August 2011)
The Tide Turns for Marine Energy Devices. Siemens Energy recently secured a 10% stake in Marine Current Turbines, the UK company that owns SeaGen, a 1.2-MW tidal power plant, which was commissioned in 2008 on the Irish Sea. Marine Current Turbines is planning to build a larger, 8-MW plant off the coast of Scotland by […]
-
Commentary
Coal: A Key Part of Our Clean Energy Future
With the U.S. economy still struggling, few things are as important as having an abundant, reliable supply of energy to help drive our recovery. Many American families are hurting and our businesses are being challenged to create new jobs. That’s why federal, state, and local public policies must balance the need for broader economic prosperity, […]
-
O&M
Systems Integration, Flexible Control Reduce Makeup Water Cost
Longview Power, a 695-MW coal-fired power plant now under construction in Maidsville, W.Va., is scheduled to begin commercial operation later this year. The $2 billion project reached 580 MW in early June, just a month after completing the “first fire on coal” schedule milestone. Testing and tuning of the controls and various systems continue.
-
O&M
Improving the Efficiency of Toronto’s District Heating Plant
Enwave Energy Corp.’s district heating plants in downtown Toronto will be operating cleaner and more efficiently before the fall 2011 heating season begins when boiler upgrades now under way are completed. Enwave hired Benz Air Engineering (BAE) to design and install upgrades to all eight boilers inside Enwave’s Pearl Street Station. When the $20 million project is completed, the retrofits will produce energy savings exceeding $5 million per year. In addition, the company will receive incentives of $100,000 per boiler from Enbridge, its natural gas provider.
-
O&M
Fighting Pipe Abrasion
Steel piping systems used to convey coarse materials, often over long distances, are under constant attack from abrasion. In power plants, the materials are usually coal and limestone slurry. The common industry solution has been to install abrasion resistant (AR) pipe that is much harder on the Brinnell Scale than standard steel pipe. The harder the inner wall, studies have shown, the better it resists the gouging or plowing action of abrasive sliding particle flow.
-
Legal & Regulatory
New Approach Needed for Renewable Integration
It is time for the renewable integration discussion to move beyond simply identifying the challenges of ensuring reliability in a nation increasingly served by intermittent renewable resources and toward developing real-world solutions to these challenges.
-
Coal
Plant of the Year: KCP&L’s Iatan 2 Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
Kansas City Power & Light (KCP&L) began engaging stakeholders in 2003 to develop consensus on a regional energy plan designed to balance customers’ desire for low electricity costs with system reliability needs and environmental requirements. The culmination of that plan was the completion of Iatan 2, which entered service in August 2010. For executing an innovative energy plan that reduced overall fleet emissions, ensuring the region’s future electricity supply, and completing an approximately $2 billion project in time for the summer 2010 peak load by using innovative contracting and project controls, KCP&L’s Iatan 2 is awarded POWER’s 2011 Plant of the Year Award.
-
O&M
Marmaduke Award: CFE Extends CTG Universidad Unit 2’s Life with Conversion to Synchronous Condenser
CTG Universidad is a two-unit combustion turbine plant commissioned in late 1970 by the Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) on the north side of Monterrey, Mexico’s third-largest city and an important industrial center. By the 1990s, the two 14-MW turbines were obsolete, used sparingly, and slated for demolition in 2010. However, by 2002, portions of Monterrey began experiencing power restrictions caused by a lack of sufficient reactive power production, and that situation presented an opportunity for the plant. By repurposing an old combustion turbine for use as a synchronous condenser to provide local reactive power, CFE significantly reduced local power supply limitations. For that savvy plant repurposing, CFE’s CTG Universidad Unit 2 is the winner of POWER’s 2011 Marmaduke Award for excellence in power plant problem-solving. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence.
-
Smart Grid
Smart Grid Award: Vermont Electric Cooperative Takes Wise Approach to Smart Grid Projects
A cooperative in northern Vermont serving a largely rural area has proven that even small utilities can achieve great smart grid results by planning wisely. For improving service to its members by developing a grid modernization strategy before “smart grid” was a buzz phrase, Vermont Electric Cooperative is the winner of the first POWER Smart Grid Award.