Water
-
Coal
EPA Issues Final Cooling Water Intake 316(b) Rule
A final rule released by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) today will affect cooling water intake structures at 544 U.S. power plants and provide those plants with lower-cost compliance options than previously proposed to reduce fish impingement and entrainment. The final rule issued under Section 316(b) of the Clean Water Act applies to facilities that […]
-
Water
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Not Our Only Problem
Marilu Hastings With all the recent scientific studies, media coverage, and policy decisions about reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, one might think that the emissions issue is the only challenge that
-
Coal
Water Shortages Threaten Global Coal Power
Water stresses in developing countries threaten to derail a massive build-out of coal capacity, according to a new analysis from the World Resources Institute (WRI). The WRI estimates that about 1,400 GW of new coal capacity is being proposed worldwide, and of that, three-quarters of it are in China and India. Unfortunately, much of this […]
-
Coal
EPA Breaches Legal Commitment to Issue Final 316(b) Cooling Water Rule
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) failed to issue a final rule governing power plant cooling water by April 17 as agreed with environmental groups. In court papers, the agency instead stated its intention to complete the rulemaking by May 16, 2014. The agency secured more time under a modified settlement agreement with a coalition of […]
-
Coal
Advanced Cooling and Water Treatment Technology Concepts for Power Plants
Technology development to reduce freshwater withdrawals and consumption for all types of thermoelectric power plants is emerging as a top research and development (R&D) priority. Thermoelectric plants in
-
Legal & Regulatory
GE Executive Markhoff Talks About the Water/Energy Nexus
Source: POWER During IHS CERAWeek in Houston in early March, POWER Editor Gail Reitenbach sat down with Heiner Markhoff, president and CEO of GE Power & Water’s Water & Process Technologies, to ask him about several issues of concern to power plants. Though the “water/energy nexus” theme has gained prominence recently, Heiner Markhoff’s comments underscored […]
-
Renewables
GAO Report: Power Sector Is Clearly Exposed to Climate Change Risks
U.S. energy infrastructure is increasingly vulnerable to acute weather events and long-term changes in the climate, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) says in a new report. Options to help reduce those risks include measures to improve its durability and resiliency. The Mar. 4–released report titled “Energy Infrastructure Risks and Adaption Efforts,” cites data from the National Research […]
-
Renewables
Statkraft Shelves Osmotic Power Project
Norwegian power company Statkraft has shelved its much-watched effort to harness energy from pressure-retarded osmosis (PRO). It said in a rare industry admission that the technology could not be sufficiently
-
Coal
EPA to Miss Legal Deadline to Finalize 316(b) Cooling Water Rule
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) will today miss a legally set deadline to issue finalized standards for cooling water intake structures for all existing power generating facilities under Section 316(b) of the Clean Water Act. The EPA’s 2004 Phase II Cooling Water Intake Structure rules were suspended in July 2007 in response to the Second […]
-
Renewables
Redefining Priorities for Quebec’s Hydro Power Cluster
A land of lakes and rivers, Quebec benefits today from an abundance of clean and green energy, vastly generated by means of hydro power, which is increasingly complemented by the province’s eastern wind energy farms. Download a pdf of this report.
-
Commentary
How U.S. Power Generators Are Preparing for 2014
The business environment for generating companies worldwide continues to become increasingly complex, and not just as a result of regulations. Even in the U.S., the concerns and constraints faced by generators
-
Water
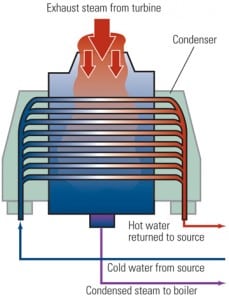
Why Your Power Plant Needs a Water Management Plan
Recent articles in POWER and elsewhere have noted that all types of generating technologies are more frequently feeling the pain of constrained water supplies. The limitations can come from increased
-
Coal
North Carolina Sues for Coal Ash Water Contamination at 12 Duke Energy Sites
North Carolina on Friday sought a state Superior Court order to force Duke Energy to address groundwater and wastewater violations at 12 power plant sites that the utility uses to store coal ash residuals. The state’s Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) filed two lawsuits for injunctive relief against Duke Energy Progress Inc. and […]
-
Water
DOE Releases Report on Energy Sector Vulnerabilities to Climate Change
The Department of Energy has released a report on current and potential impacts of climate change on the energy sector, including power plants.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: Parched
Water scarcity as it relates to energy use is becoming a major concern.
-
Water
Energy Storage Developments and Demand Ramp Up
Despite technical and financial hurdles, annual global demand for grid-scale energy storage is expected to soar to 185.4 GWh by 2017, which means a possible 231% average year-on-year demand growth between 2012 and 2015, according to Lux Research.
-
Coal
Water Issues Challenge Power Generators
Drought and competing uses for water continue to challenge power plant operators worldwide. In response, innovative approaches for reducing water use are being explored from South Africa to China.
-
O&M
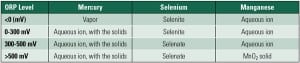
ORP as a Predictor of WFGD Chemistry and Wastewater Treatment
Recent studies have shown that system oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) is not only an important factor for predicting wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGD) absorber chemistry but also may be a predictor of process equipment corrosion and wastewater treatment requirements.
-
Coal
Your Guide to the White House Climate Action Plan
President Obama’s highly anticipated Climate Action Plan (CAP) released today outlines a wide variety of executive actions founded on three pillars: slashing U.S. carbon pollution through stringent rules for new and existing power plants while doubling renewables deployment and promoting fuel switching from coal to natural gas; preparing the U.S. for impacts of climate change; and leading international efforts to combat global climate change.
-
O&M
LADWP Harnesses LMS100 to Solve Once-Through Cooling Dilemma
Los Angeles sits alongside the world’s largest body of water, and naturally the city’s Department of Water & Power (LADWP) placed its generating stations along the shoreline to take advantage of that abundant resource for cooling. The LADWP built three coastal generating stations that provide the city with 2,162 MW, about 35% of the peak annual demand.
-
O&M
Microbial Control in Cooling Water Improves Plant Performance
Microbial inhibition, as part of a robust cooling water treatment program, presents a special challenge because of the variability in makeup water sources, plant processes, and discharge permits. Failure to maintain a proper microbial inhibition program will affect your bottom line as a result of heat rate degradation.
-
Water
A Moderating Tone from the EPA on 316(b)?
Final water intake structure rules from the EPA expected this June suggest the agency may be listening to industry and even moderating its tone. Stretch goals as part of the Section 316(b) rule are likely, but overall the rule may prove more reasonable than many expected.
-
Solar
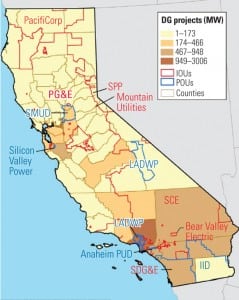
Distributed Generation: California’s Future
Once you synthesize all the elements of the Golden State’s clean energy strategy and extrapolate current trends, it’s easy to see that an impending break with the traditional power generation paradigm is coming, intended or not.
-
Water
Research Center Dedicated to Power Plant Water Use Opens
The Electric Power Research Institute and several partners—including the Southern Research Institute, Southern Co. subsidiary Georgia Power, and Southern Research—are testing a new technology that could reduce the amount of water needed for power plant cooling.
-
Coal
Potential Impacts of Closed-Cycle Cooling Retrofits at U.S. Power Plants
The Clean Water Act Section 316(b) rule changes regarding cooling water intake structures that are expected next year could affect up to 428 power plants, representing 1,156 individual units, according to the Electric Power Research Institute. Depending on plant size and the complexity of the retrofit project, retrofit capital costs could range from very low to over $500 million for large nuclear plants. The power industry total cost is projected to be over $100 billion.
-
Water
Evaluating Technologies to Address Proposed Effluent Guidelines
Upcoming revisions to U.S. federal effluent guidelines are anticipated to include new discharge limits for mercury and selenium in flue gas desulfurization wastewater, in addition to other potential revisions. Collaborative R&D is helping inform the rulemaking and is evaluating the cost and performance of technology options that might be used to meet the new targets.
-
Water
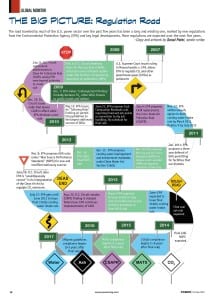
THE BIG PICTURE: Regulation Road
To view a larger version of this graphic, download the file here.
-
Water
Water Conservation Options for Power Generation Facilities
The electric power industry is a large water user and is dependent upon reliable water supplies. Adopting new water-conserving technologies for power production can help alleviate the impact of future water shortages. Several water use reduction technologies are available, each with different benefits and costs.
-
Water
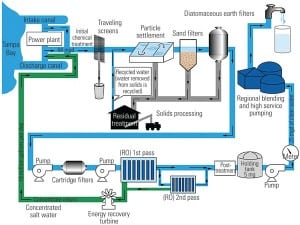
Water and Power: Will Your Next Power Plant Make Both?
In much of the developing world, two essentials are often in short supply: potable water and reliable electricity. Some countries have invested heavily in desalination and combined cycle technologies to simultaneously solve both problems.
-
Water
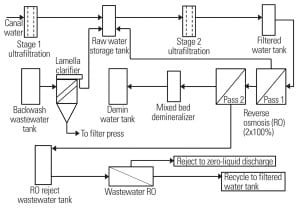
Design and Testing of a Water Treatment and ZLD System
In the following case study, Aquatech International Corp. discusses a water treatment system designed to minimize water usage and waste discharges, both liquid and solid, at a gas-fired combined cycle plant in California.