Water
-
Water
Fish and cooling water intakes: Debunking the myths
Thermal power plants are required to use fish protection technologies or make changes in plant operation to protect aquatic organisms. We intuitively understand that some organisms in the water drawn in to cool a power plant can be injured or killed when they hit a screen or enter the circulating water system. You have options for compliance with EPA rules; some are extremely expensive and burdensome, whereas others are brilliant in their simplicity. This article debunks several fish impingement myths and gives practical advice for successful compliance.
-
O&M
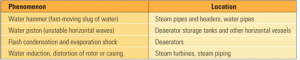
Water hammer and other hydraulic phenomena
The term "water hammer" encompasses a handful of hydraulic and thermohydraulic mechanisms. They include water hammer in steam and water piping, water piston, water induction, flash condensation and evaporation, and shock waves generated by transonic flow. All can lead to failures of steam and water cycle components and put plant operators and workers at risk. Proper design and O&M practices can keep water hammer and similar phenomena under control.
-
O&M
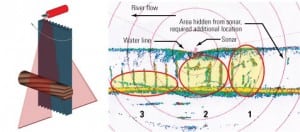
Advanced sonar revolutionizes underwater structure inspections
Ongoing maintenance is critical to the performance and longevity of underwater structures such as cooling water intake tunnels. Commercial divers or robotic vehicles can do the needed inspections, but such manual methods require a costly plant shutdown and provide only qualitative results. ASI Group Ltd. has designed and built an advanced, dual-axis sonar system that works in fast-moving water and can deliver quantitative data about the extent and location of debris buildup on submerged assets.
-
Water
Organics in the boiler and steam: Good or bad?
Among utility chemists, opinions differ on the effect that organic compounds—both naturally occurring types and those added as treatment chemicals—have on the steam cycle. Some chemists raise the specter of corrosion of low-pressure turbines caused by organic acids created as the compounds degrade. Others defend and encourage the use of organic treatment chemicals, particularly neutralizing amines, by pointing to a long and positive history of their use in boiler and feedwater systems.
-
Water
Focus on O&M (May 2006)
Desalination, Italian style; How to minimize DI operating costs; Advanced flow meter works with shorter pipe runs; Why tubing beats piping.
-
Water
Recycling, reuse define future plant designs
The Valley of the Sun went off the water wagon on March 4, ending a record 136 consecutive days without measurable rainfall. That first 0.05-inch sip, followed by a 0.18-inch gulp the next day, only left residents yearning for more. But Mother Nature was only teasing, because the rest of March remained dry. On March […]
-
Water
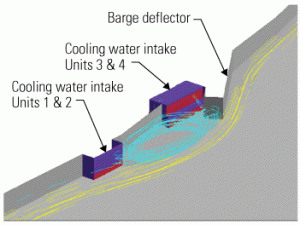
Alternative cooling water intake analysis under CWA Section 316(b)
New rulemaking by the EPA has highlighted the importance of fish protection technologies and/or operational changes to improve fish survival at circulating water intake structures. In this first of three reports from Alden Laboratories, the focus is on step one of the design process: analyzing the intake system to inform development of cost-effective solutions for meeting Section 316(b) performance standards. The other two reports, to be published later this year, will explore fish protection technologies through laboratory and field evaluations, and alternative cooling water intake technologies.