Nuclear
-
Nuclear
New South Korean and Russian Reactors Go Online
Three nuclear reactors under construction in the Eastern Hemisphere reached major milestones over the past few months. South Korea’s Korea Hydro and Nuclear Power Co. connected its 960-MW Shin-Wolsong 1 reactor near Nae-ri to the grid on Jan. 27 and, a day later, its sister plant, the 960-MW Shin Kori 2 (Figure 5) in the southwest city of Gori. Both units are expected to become commercially operational this summer. And last December, Russia began commercial operation of its 950-MW Kalinin 4 plant, a V-320 model VVER 1000.
-
Nuclear
Happy Days for Nuclear Power?
The first license to construct a new nuclear power plant in the U.S. in 34 years was granted by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission on Feb. 9. Has the elusive nuclear renaissance finally begun?
-
Coal
Vietnam Works Hard to Power Economic Growth
For the past 15 years, Vietnam has enjoyed enviable gross domestic product increases, averaging 7% annually. That kind of economic growth increases power demand, but financing new capacity remains a challenge. Reaching its ambitious capacity growth goals will require Vietnam to expand its financing and vendor base, attract foreign investment, and ensure future fuel supplies in a region thick with competition for those resources.
-
Nuclear
The Big Picture: DOE Loan Guarantees
Of the $35.9 billion in loan guarantees awarded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) since 2009, roughly $26.5 billion have financed nuclear and renewable power projects across the nation through the Section 1703 and 1705 loan guarantee programs.
-
Nuclear
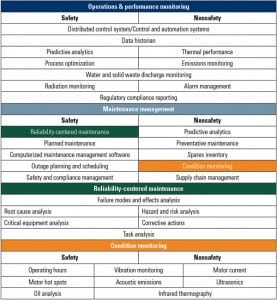
Comprehensive Asset Management for Nuclear Plant
Asset management means different things to different people. But it boils down to converting raw data and observations about equipment and components into information and knowledge that is then used, propagated, and shared by workers and digital components to manage performance. Nuclear plants have special asset management needs, given the level of their safety, reliability, and regulatory requirements.
-
Nuclear
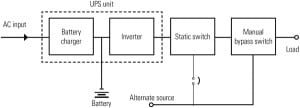
Specifying Nuclear DCS Power Supplies
The consideration of power supplies has become critical to the success of converting analog instrumentation and control systems to digital control systems (DCSs). Careful planning is particularly necessary for nuclear power plants, where instrumentation systems are required for safely shutting down a reactor, mitigating the consequences of an accident, and performing post-accident analysis.
-
Coal
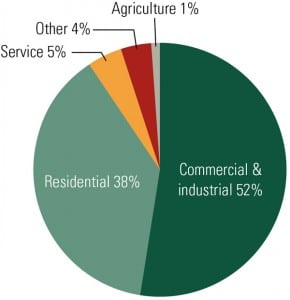
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Coal
Editors Select Top Five Stories of 2011
The POWER editorial staff’s picks for the most significant stories of 2011.
-
Coal
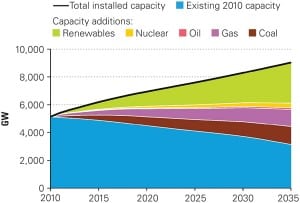
World Energy Outlook Forecasts Great Renewables Growth
Driven by policies to limit carbon emissions, as well as government subsidies, the share of worldwide nonhydro renewable power is set to grow from just 3% in 2009 to 15% in 2035, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its recently released World Energy Outlook 2011. Under the same scenario—which assumes that carbon pricing, explicit […]
-
Nuclear
NRC to Implement Lessons Learned from Fukushima
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) in October directed staff to begin implementing seven safety recommendations put forth by the federal body’s Near-Term Task Force on lessons learned from the nuclear accident at Tokyo Electric Power Co.’s Daiichi power plant in Japan’s Fukushima prefecture last March. The recommendations affecting all 104 nuclear reactors (Figure 1) […]
-
Coal
U.S. Confronts Pipeline Gaps While Europe Juggles Renewables and Debt
U.S. optimism has been restored by reports of abundant, reasonably priced natural gas to fuel most new generation; however, huge gaps in the fuel delivery system (thousands of miles of pipelines are needed) will soon challenge gas plant development. Meanwhile, the cloud of sovereign debt hangs over all major capital projects in Europe, where the UK moves ahead with new nuclear projects while many of its neighbors shut the door on nuclear and struggle to finance their commitment to renewables.
-
O&M
EPRI Bridges Industry R&D Gaps
The technologies used to generate and distribute electricity will be radically transformed during the coming decade. Amid that change, the power industry must continue to meet customer reliability, safety, and cost-of-service expectations. Achieving the right balance among these often-conflicting goals is the primary focus of every utility. The Electric Power Research Institute is helping utilities achieve that balance with R&D programs for many new and emerging technologies.
-
Coal
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan Pushes Power Industry in New Directions
The Five-Year Plan is the expression of the centralized planning goals for China’s economy. The 12th Five-Year Plan, approved by the Chinese Government on March 14, 2011, established many social and economic goals, including significant expansion of the country’s power generation industry in many new directions.
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.
-
Nuclear
Airtight Cover Completed for Daiichi 1
Tokyo Electric Power Co.’s (TEPCO’s) Fukushima Daiichi 1 reactor—a unit that suffered a core melt and hydrogen gas explosion after the March 11 earthquake in Japan and subsequent tsunami devastated the six-reactor facility—was fully encased in an “airtight” cover in October.
-
Nuclear
Siemens Joins Trend to Quit Nuclear
The number of companies pulling out of the nuclear business continues to grow. Just weeks after Louisiana-based engineering firm The Shaw Group announced it would sell its 20% stake in the nuclear company Westinghouse back to partner Toshiba, German engineering conglomerate Siemens said that, prompted by the German government’s decision to phase out nuclear power by 2022, it would quit the nuclear business.
-
Nuclear
German Court Questions Legality of Nuclear Tax
A German finance court in September questioned the constitutionality of a controversial tax on fuel used in nuclear power plants, a decision that could influence rulings in various finance courts around the country that are reviewing complaints by nuclear operators regarding the levy.
-
Nuclear
ITER Gets New Life
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) in southern France, the world’s biggest nuclear fusion research project, is seeing a revival. After a budget shortfall last year and cost projections that continue to escalate, in September, the project got the European Parliament’s (EP’s) backing for an autonomous budget that seeks to guarantee transparent and reliable financing while limiting cost overruns. Japan also announced that it would increase its budget for ITER by 50% (the current ITER director-general is Japanese). Also in September, scientists announced that after an 18-month shutdown to upgrade the Joint European Torus (JET)—the world’s largest magnetic fusion device—the machine is ready to test materials to be used inside ITER (Figure 5).
-
Nuclear
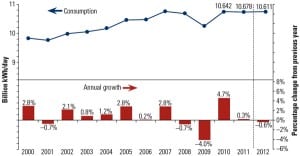
THE BIG PICTURE: Reactors Under Construction
For seven years in a row, the number of new nuclear construction starts increased markedly. Then the accident at Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi plant occurred, prompting shutdowns of existing plants and a rethinking of future plans in many countries. Nevertheless, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) expects “continuous and significant growth” in the use of nuclear […]
-
Nuclear
Top Plants: Four Plants Demonstrate Global Growth of Nuclear Industry
The global nuclear industry is moving forward at a brisk pace, only slightly slowed by the Fukushima Daiichi accident. The International Atomic Energy Agency’s most realistic estimate is that 90 new nuclear plants will enter service by 2030. Ten new nuclear plants went online over the past two years. We profile four of them as POWER’s nuclear Top Plants for 2011.
-
Nuclear
The U.S. Spent Nuclear Fuel Policy, Part 2: Playing Hardball
Ongoing investigations into cancellation of the Yucca Mountain project have revealed an astonishing number of irregularities by agencies responsible for the project. Those investigations have exposed a broken system that failed to properly manage the project and that surrendered to political pressure. Worse still, the draft report of President Obama’s Blue Ribbon Commission on America’s Nuclear Future gave the industry little reason to hope that there would ever be a long-term nuclear waste fuel repository.
-
Nuclear
Crossing the Digital Divide
One of the great successes of the power generation industry over the past two decades has been the significant increase in nuclear plant reliability and other performance standards. However, there is reason to be concerned that the design, operation, and maintenance practices used by the current fleet of plants do not leverage all the possible advantages from a digital controls upgrade. Perhaps past success is the biggest barrier to future success.
-
Nuclear
Browns Ferry Unit 1 Restart: World-Class ALARA Performance
TVA completed the $1.9 billion restart of the 1,100-MW Browns Ferry Unit 1 in 2007. That restart project provided the opportunity to incorporate state-of-the-art materials and radiation-reduction techniques to ensure that Unit 1 would be an industry-leading low-ALARA-exposure plant when it returned to service. The reductions achieved were significant.
-
Nuclear
Combustion Gas Analyzer
Building on the success of the Fluegas 2700 combustion gas analyzer, the new SERVOTOUGH FluegasExact integrates Servomex’s unique Flowcube flow sensor technology to give users even more confidence in their combustion gas measurements. The analyzer features a patented zirconium oxide cell for oxygen measurement and a thick film catalytic sensor for measuring carbon monoxide (CO) […]
-
Nuclear
Germany’s Nuclear Phase-Out Has Widespread Implications
The German government in July finalized a package of bills that will phase out nuclear’s 23% contribution to the country’s power supply by 2022 and increase renewable generation from the current 17% to 35%. In August, the Federal Network Agency ( Bundesnetzagentur) said it wouldn’t rely on power from seven of the nation’s oldest reactors […]
-
Nuclear
Ling Ao 4 Starts Up While Sanmen Gets First AP1000 Reactor Vessel
In China this August, as Ling Ao Unit 4—the second unit of the Ling Ao Phase II nuclear plant—started commercial operation, Westinghouse and its consortium partners marked the milestone of receiving the reactor vessel for the Sanmen nuclear power plant—the world’s first AP1000—in China’s Zhejiang province. The start-up of Ling Ao Unit 4 in Guangdong […]
-
Coal
CWA 316(b) Update: Fish Guidance and Protection
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed new Clean Water Act section 316(b) regulations for once-through cooling water intake structures. Comments on the proposed rules closed in August, and a final rule is expected mid-2012. The EPA estimates that at least half of the power plants using once-through cooling will be required to implement a best technology available solution in coming years. That typically means barriers and screens, but you may want to consider other options.
-
Commentary
Advancing America’s Nuclear Infrastructure
It is fair to say that 2011 is bringing some uncertainty into the nuclear energy industry. The tsunami and subsequent events at Fukushima present Japan and our industry with new challenges but also serve as a catalyst for continuous improvement. In the U.S., we are learning from these events and improving our operations, designs, and emergency response approaches to make our plants safer, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly.
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Nuclear
The Fukushima Fallout: Six Months After the Nuclear Crisis
(WEB EXCLUSIVE) Much has transpired during the nearly six months following the Great East Japan Earthquake—a 3-minute, magnitude 9.0 temblor that generated a series of tsunami waves as tall as 38.9 meters (130 feet), killed more than 25,000 people, and set off the worst nuclear disaster in 25 years.