Instrumentation & Controls
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Monitoring Control Loop Performance
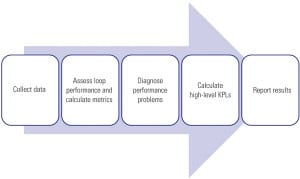
Control loop performance-monitoring software can help to improve loop performance at electric power plants by automatically collecting data, assessing several aspects of loop performance, and providing the results in reports and user interfaces.
-
Nuclear
Specifying Nuclear DCS Power Supplies
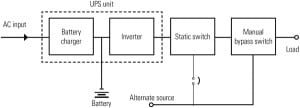
The consideration of power supplies has become critical to the success of converting analog instrumentation and control systems to digital control systems (DCSs). Careful planning is particularly necessary for nuclear power plants, where instrumentation systems are required for safely shutting down a reactor, mitigating the consequences of an accident, and performing post-accident analysis.
-
Nuclear
Crossing the Digital Divide
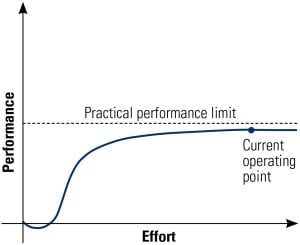
One of the great successes of the power generation industry over the past two decades has been the significant increase in nuclear plant reliability and other performance standards. However, there is reason to be concerned that the design, operation, and maintenance practices used by the current fleet of plants do not leverage all the possible advantages from a digital controls upgrade. Perhaps past success is the biggest barrier to future success.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Managing Equipment Data Through Asset Virtualization
Asset “virtualization” extends and combines the technologies of 3-D visualization and virtual reality to a new, practical level for the life-cycle management of power industry equipment. All pertinent data for a component, subsystem, or plant is associated with, stored, and accessed through as-built 3-D digital models of the actual plant that are constructed using laser scanning techniques.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
NERC CIPS Update: The Advantages of an Integrated Factory Acceptance Test
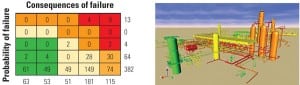
When adding, modifying, or upgrading a system, many critical infrastructures conduct a factory acceptance test (FAT). A FAT includes a customized testing procedure for systems and is completed before the final installation at the critical facility. Because it is difficult to predict the correct operation of the safety instrumented system or consequences due to failures in some parts of the system, a FAT provides a valuable check of these safety issues. Similarly, because cyber security can also impact the safety of critical systems if a system is compromised, it makes sense to integrate cyber security with the FAT.
-
O&M
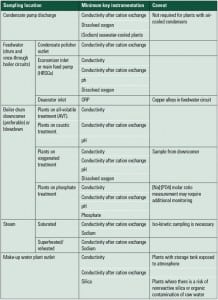
The New Water Lab
Recent advances in water laboratory instrumentation—from improved sample conditioning to advanced online instruments—have reached the market. Here’s a look at the equipment you’ll find in the best-equipped power plant laboratory this year.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Twin Pac Controls Upgraded
In November 2008, a central Texas utility commissioned HPI, a full-service turbomachinery design and construction firm based in Houston, to perform a major upgrade of its plant’s power distribution and turbine control systems.
-
O&M
Artificial Intelligence Boosts Plant IQ
Neural networks have already found practical application in many plants, and recent advancements in artificial intelligence promise to shape the design of the next generation of power plant supervisory controls. Will future plant operators be fashioned from silicon?
-
Instrumentation & Controls
K-Power Upgrades Combined- Cycle Automatic Generation Controls
Tightly managed grids require combined-cycle plants equipped with power block controls that can quickly respond to automatic generation control signals with minimal error. K-Power’s successful controls upgrade demonstrates that that goal—and more—is achievable.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Fully Automating HRSG Feedwater Pumps
Modern distributed control system platforms can provide many tools to capture best operating practices and automate them. This case study shows the steps taken to automate a hypothetical simplified feedwater pump system for a combined-cycle power plant. It describes a combination of controls automation strategies and human-machine interface techniques designed to increase the overall level of automation while improving ease of use.