Environmental
-
Coal
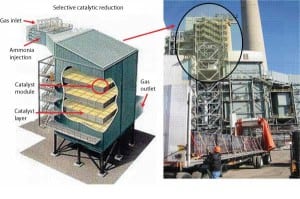
Environmentally Sound Handling of Deactivated SCR Catalyst
Selective catalytic reduction systems were introduced as a means of reducing the nitrogen oxide emissions of power generators in the 1980s. Since then, environmental issues have increased in importance, as has the value of an SCR reactor. Unfortunately, because this technology is still so new, not all users understand its full potential and proper maintenance techniques.
-
Coal
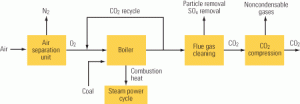
Trona Injection Reduces SO3 Emissions
Emissions of SO3 (or its hydrated form, H2SO4) have created a nagging problem for some coal-fired power generators after they’ve installed a selective catalytic reduction system. If your plant is in that unfortunate group, here’s a summary of the state of our understanding of the problem—and its solutions.
-
Commentary
Kilowatt-hour tax is fairest approach
By Jim Rogers, Duke Energy Corp. The climate change debate has been dramatized in movies, on Hollywood’s red carpets, and in documentaries featuring melting ice caps. The collective effect is extraordinary, and positive. America now stands ready to address one of its toughest challenges since the industrial revolution—decarbonizing our energy supply and economy. Now the […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Climate change: Policy via litigation?
By Steven F. Greenwald and Jeffrey P. Gray David Crane, the CEO of NRG Energy, was recently quoted in a widely disseminated publication as saying: “It is a moral imperative that we take steps to reduce CO2 concentration in the earth’s atmosphere.” One might expect those reacting to Crane’s comments (made in a February 2007 […]
-
Coal
Options for reducing a coal-fired plant’s carbon footprint, Part II
A conventional coal plant’s CO2 emissions can be reduced either after combustion (see Part I of this article in POWER, June 2008) or before. In the latter case, typified by integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants, the fuel used is synthesis gas (syngas), which contains mostly hydrogen (H2) and CO. A water-shift reactor converts the CO […]
-
Coal
Woods and power company CEOs agree: “The state of the industry is cautious”
It is rare indeed to witness, at an otherwise staid industry forum, the public rebuke of the country’s most prominent supplier to the electric power industry. But at the Keynote session and Power Industry CEO Roundtable of the 2008 ELECTRIC POWER Conference & Exhibition in Baltimore this May, Milton Lee, general manager and CEO of […]
-
Coal
Carbon Constraint Conference: Dealing with the climate change conundrum
“Once it’s enacted, the impact of climate change legislation on the electric power industry will be ten times bigger than that of the Clean Air Act,” said Dan Adamson, an attorney with the law firm of Davis Wright Tremaine and chair of the opening session at the 2nd Annual Carbon Constraint Conference (Figure 1). 1. […]
-
Water
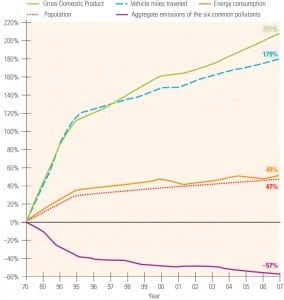
New strategies for conquering environmental challenges
No doubt some power plant engineers feel that tackling environmental problems is a lot like dealing with the Hydra, the ancient mythological serpent monster with multiple heads. When an attacker would cut off one of the Hydra’s numerous heads, two new ones would grow back in place of the head that was removed. All too […]
-
Commentary
Deadlock: Bush’s Air Policy
After almost eight years, the Bush administration’s approach to air pollution policy—including global warming—ends up with bupkus. That’s a wonderfully-useful Yiddish word meaning, literally, “nothing,” but implying less than nothing, or the meaningless result of lots of apparent, but futile, effort.
-
Coal
New Source Review Update
The mere mention of the words "New Source Review" (NSR) will immediately capture the full attention of any utility executive and might cause the cancellation of even the best power plant "upgrade" project. The effects of those three words have nothing to do with project economics or whether a project increases or decreases emissions. It’s all about the lawsuits.