Environmental
-
Coal
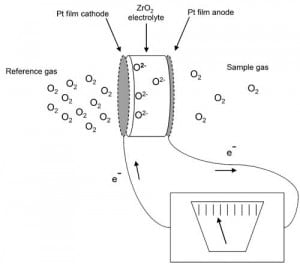
A New Instrument for In Situ SCR NOx Measurement
A zirconium oxide sensor technology originally developed for automotive applications could make in situ, simultaneous measurement of O2 and NOx a breeze for coal-fired power plants.
-
Solar
President Obama Signs Orders Aimed at Energy Independence and Economic Recovery
Following a press briefing this morning, President Barack Obama signed new executive orders intended to spur “swift action” on both U.S. economic recovery and American energy independence.
-
Coal
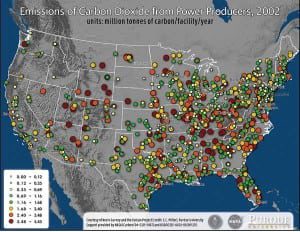
CO2 Source and Sink Tracking Improving
Many opponents of climate change policies and regulations argue that it is unfair to penalize some sectors — like power generation — more heavily than others when it’s difficult to prove precisely where specific greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are coming from, where they’re going, and what effect they are having. Toward the ends of scientific understanding and sound public policy, scientists are making progress in isolating GHG sources and sinks.
-
Environmental
Appeals Court Reinstates CAIR
Two days before Christmas, the Federal Appeals Court for the District of Columbia reinstated (PDF) the Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR) while the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) makes changes to it. Judge Judith W. Rogers said, "The parties’ persuasive demonstration, extending beyond short-term health benefits to impacts on planning by states and industry with respect to […]
-
Coal
Up in Smoke: Measuring Mercury in Stack Gases
Two types of mercury monitoring are required of coal-fired power plants: continuous emission monitoring and periodic Relative Accuracy Test Audit. One of the more attractive approaches for these analyses is provided by the Hydra-C Appendix K from Teledyne Leeman Labs.
-
Coal
California Climate Plan Touts New Renewables, Trading Allowance Schemes
In a sweeping climate change proposal that could serve as a model for the nation, two California agencies have proposed a comprehensive program for reducing the state’s greenhouse gas emissions that calls for aggressive improvements in energy efficiency, higher targets for renewable energy, and an innovative scheme for allocating emission allowances to electric utilities.
-
Coal
GAO: Lack of U.S. Greenhouse Strategy Slowing Carbon Capture
A Government Accountability Office (GAO) study released in late September concludes that technological, legal, and regulatory uncertainties—compounded by the absence of a national strategy for combating global warming—are blocking deployment of crucial technology to capture and sequester carbon dioxide from coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
“Cap and Dividend” Proposal Targets Carbon Suppliers
As senior members of Congress lay the groundwork for a new legislative debate on climate change next year, a new proposal making the rounds of Capitol Hill offices would replace the cap-and-trade approach now in vogue with one in which all carbon permits are auctioned and all auction revenues are returned to consumers.
-
Coal
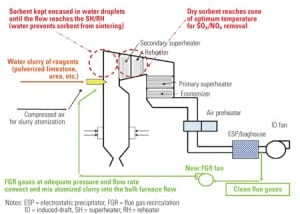
Bringing down the cost of SO2 and NOx removal
A twist on an old technique, flue gas recirculation, helps prevent slagging in the upper furnace and convective pass, according to pilot testing recently completed by APTECH CST and the Southern Research Institute. The technology—along with a companion technology for furnace sorbent and urea injection for SO2 and NOx control—could help owner/operators of smaller, older coal-fired plants meet emissions limits at a reasonable cost.
-
Coal
Computer simulation as a NOx reduction design tool
A utility evaluated various methods of obtaining a NOx reduction of at least 30%, as required by upcoming regulations for its boiler, which originally produced 0.54 lb of NOx/million Btu at 410 MW full load. Nalco Mobotec engineers performed a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation of the boiler to first understand the boiler’s combustion process and then determine the most economical method to achieve the required NOx reduction.