Coal
-
Coal
GAO finds impediments to CCS deployment
An underdeveloped and costly CO2 capture technology, as well as regulatory and legal uncertainties over CO2 capture, injection, and storage, are the some of the more critical factors that impede carbon capture and storage (CCS) deployment in the U.S., the Government Accountability Office (GAO) — a congressional investigative arm — has reported. In its report, […]
-
O&M
Innovative Control Strategies Improve Boiler Dynamic Response
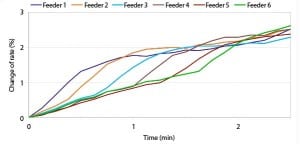
The more capable a power-generating unit is of reacting quickly to changes in load demand, the more profitably the unit can be operated. An improvement in load dynamics means that additional control response and capacity can be made available to the power grid. These characteristics are especially in demand in regions where a fast-responding unit can supply energy as ancillary services at a premium price.
-
Coal
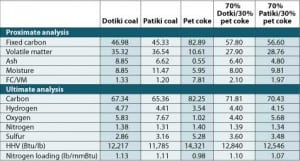
Low-NOx Retrofit for Firing Coal/Petroleum Coke Blends
Replacing existing, older-generation controlled-flow split-flame burners on Unit 1 at the Seminole Generating Station with Foster Wheeler’s new low-NOx burners and overfire air additions reduced NOx emissions. This case study provides all the details and post-installation test results.
-
Coal
Up in Smoke: Measuring Mercury in Stack Gases
Two types of mercury monitoring are required of coal-fired power plants: continuous emission monitoring and periodic Relative Accuracy Test Audit. One of the more attractive approaches for these analyses is provided by the Hydra-C Appendix K from Teledyne Leeman Labs.
-
Coal
California Climate Plan Touts New Renewables, Trading Allowance Schemes
In a sweeping climate change proposal that could serve as a model for the nation, two California agencies have proposed a comprehensive program for reducing the state’s greenhouse gas emissions that calls for aggressive improvements in energy efficiency, higher targets for renewable energy, and an innovative scheme for allocating emission allowances to electric utilities.
-
Coal
GAO: Lack of U.S. Greenhouse Strategy Slowing Carbon Capture
A Government Accountability Office (GAO) study released in late September concludes that technological, legal, and regulatory uncertainties—compounded by the absence of a national strategy for combating global warming—are blocking deployment of crucial technology to capture and sequester carbon dioxide from coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
“Cap and Dividend” Proposal Targets Carbon Suppliers
As senior members of Congress lay the groundwork for a new legislative debate on climate change next year, a new proposal making the rounds of Capitol Hill offices would replace the cap-and-trade approach now in vogue with one in which all carbon permits are auctioned and all auction revenues are returned to consumers.
-
Coal
Debunking the Chinese coal monster myth
A detailed analysis of power plants in China by researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) debunks the widespread notion that outmoded energy technology or the utter absence of government regulation is to blame for that country’s notorious air-pollution problems. The real issue, the study found, involves complicated interactions among new market forces, new […]
-
Coal
Vattenfall inaugurates first CCS pilot plant
On Sept. 9, Sweden’s Vattenfall inaugurated the world’s first demonstration plant that connects carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology in a full-chain working system. The inauguration of the pilot plant at Schwarze Pumpe in Germany, which underwent 10 years of testing, was a milestone that marked its move from the laboratory to reality, Vattenfall said. […]
-
Coal
Under construction in South Africa
This summary of power generation projects is a web-only supplement to the November 2008 special report titled “Whistling in the dark: Inside South Africa’s power crisis.”