-
O&M
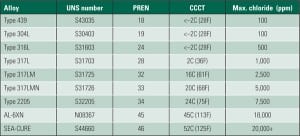
Taming Condenser Tube Leaks, Part II
In Part I of this two-part report we examined the various chemical forces at work in condenser tube leaks, the steam plant components placed at risk, and the suite of instrumentation most capable of providing early warning of a leak. Assuming you were able to repair the leak and quickly resume operation, the next step is to identify the damage mechanisms that caused the problem so you can minimize future leaks.
-
Nuclear
India Kicks Off Construction of Indigenous Nuclear Fleet
India in August began building two 700-MW indigenous nuclear power reactors at Rawatbhatta, in the desert state of Rajasthan. The two pressurized heavy water reactors (PHWRs), which will use uranium as fuel and heavy water as both moderator and coolant, are the largest to be built by the central government–run Nuclear Power Corp. of India […]
-
O&M
FBC Control Strategies for Burning Biomass
As a boiler fuel, biomass has shown great promise while suffering from a slow development history. One factor limiting its use has been the combustion system. For the most part, conventional grate-fired boilers have been the only option. Today, the most efficient approach to burning biomass to produce electricity and steam is fluidized bed combustion (FBC). Whether you choose FBC or grate, biomass presents unique challenges to control system designers.
-
-
News
Deep Excavation Support Systems Speed Plant Construction
As part of constructing the recently commissioned We Energies’ Oak Creek Power Plant Elm Road units, four remarkable below-ground structures were built. Each unique structure required creative designs and meticulous construction techniques to meet the project’s distinctive requirements.
-
Business
Lessons Learned in Reliability Standards Compliance
It has been three years and a few months since the North American Electric Reliability Council (NERC) Reliability Standards (Standards) became mandatory and noncompliance became subject to sanctions by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). You might assume that because we have had no further instances of widespread cascading outages that the Standards are working. You may also assume that—considering the database of documented noncompliance with the Standards—the industry as a whole is puzzled, unprepared, or negligent in carrying out its responsibility to keep the high-voltage electric grids reliable and secure. The truth likely lies somewhere in the middle.
-
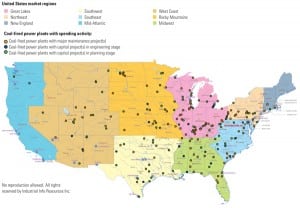
Coal
U.S. Coal-Fired Power Development: Down but Not Out
Environmentalists renewed their attacks on coal-fired power development in 2010. At the same time, Congress dithered on cap-and-trade legislation while the Environmental Protection Agency marched forward rules to reduce carbon emissions from coal-fired power plants. Couple the regulatory uncertainty with lean economic times that have flatlined electricity demand growth plus low natural gas prices, and the result is predictable: New coal-fired plant construction is in the doldrums.
-
Smart Grid
Smart Grid Cyber Security Guidelines Released
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has finalized its initial set of smart grid cyber security guidelines. NIST’s Guidelines for Smart Grid Cyber Security (NISTIR 7628) includes high-level security requirements, a framework for assessing risks, an evaluation of privacy issues in personal residences, and other information for organizations to use as they craft strategies to protect the modernizing power grid from attacks, malicious code, cascading errors, and other threats, according to NIST’s press release.
-
Commentary
The Nexus of Energy and Water
The age-old adage “water and electricity don’t mix” does not apply to 21st-century infrastructure planning. The two entities can no longer be viewed as separate commodities. The demands on both are intertwined, so solutions for meeting new and growing challenges associated with water scarcity and carbon regulations must also be integrated. Water is essential to […]
-
O&M
Innovative Cleaning of Air Preheater Coils with Pressurized Liquid Nitrogen
Cleaning air heaters in power plants or recovery boilers has traditionally involved using high-pressure water, chemicals, or steam. These techniques, though effective on moderate airside fouling of heat exchange surfaces, are usually ineffective on the more tenacious deposits that can develop in coal-fired plants. If these deposits are not removed by periodic cleaning, heat transfer in the heaters is reduced, which in turn reduces boiler efficiency and increases a unit’s heat rate. Severe fouling on air preheaters (APHs) can even reduce a unit’s power output.
Search