Features
-
O&M
Turkey Opens Electricity Markets as Demand Grows
Turkey’s growing power market has attracted investors and project developers for over a decade, yet their plans have been dashed by unexpected political or financial crises or, worse, obstructed by a lengthy bureaucratic approval process. Now, with a more transparent retail electricity market, government regulators and investors are bullish on Turkey. Is Turkey ready to turn the power on?
-
Coal
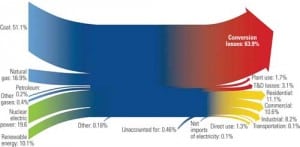
CHP: Helping to Promote Sustainable Energy
Because combined heat and power (CHP) plants optimize energy use, they cut fuel costs and pollution. Even though U.S. power plants have been using CHP for decades, today’s energy experts have a newfound appreciation for its ability to promote sustainable energy use.
-
O&M
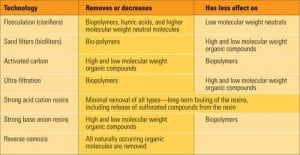
Focus on Organics in Steam
Organic compounds can enter the steam cycle from a number of sources, including water treatment chemicals, or as part of a manufacturing process. Regardless of the source of the organics, their effects range from fouling polisher resins to causing significant steam turbine damage. Conventional water pretreatment systems are available to remove organics from water, but removing organic compounds at their source is the best place to start addressing the problem.
-
O&M
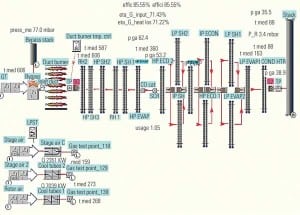
Computer Simulation of HRSGs Can Improve O&M
Obtaining accurate data about the performance of a plant’s heat-recovery steam generator is crucial to ensuring the smooth operation and maintenance of the equipment. Software designed to model and simulate HRSG operations can provide valuable information about corrosion and other operational problems.
-
O&M
Solving Fouling Problems with an HRSG Upgrade
Despite being located on the beautiful Hawaiian island of Oahu, the Kalaeloa Cogeneration Plant had trouble in paradise: Large amounts of ash from #6 low-sulfur fuel oil coated the finned tubes of its heat-recovery steam generators (HRSGs). The fouling added an extra $5 million dollars a year to the plant’s fuel bill. By retrofitting the HRSG with new panels and improved fin design, the plant overcame the fouling problems, stopped tube leaks, and cut fuel costs.
-
O&M
Lessons Learned from a Hydrogen Explosion
On January 8, 2007, a hydrogen explosion at the Muskingum River Power Plant’s 585-MW coal-fired supercritical Unit 5 caused one fatality, injuries to 10 other people, and significant damage to several buildings. The explosion occurred during a routine delivery of hydrogen when a hydrogen relief device failed, which allowed the contents of the hydrogen tank to escape and be ignited by an unknown source. This article covers the findings of the incident investigation and the actions the plant has taken to prevent a reoccurrence.
-
Coal
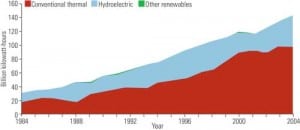
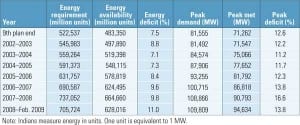
Powering the People: India’s Capacity Expansion Plans
India has become a global business power even though hundreds of millions of its citizens still live in poverty. To sustain economic growth and lift its people out of poverty, India needs more — and more reliable — power. Details of government plans for achieving those goals demonstrate that pragmatism may be in shorter supply than ambition and political will.
-
O&M
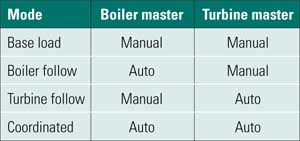
Boiler-Tuning Basics, Part II
Boilers have enormous thermal mass and are relatively slow to react. Turbines are nimble and quickly answer an operator’s command. Coordinating an entire plant requires an intimate knowledge of both systems and selecting the right logic tools to bring them together.
-
Nuclear
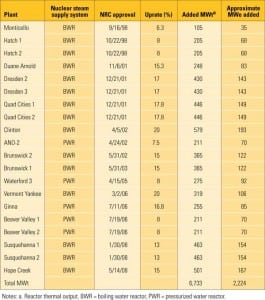
Nuclear Uprates Add Critical Capacity
New-generation nuclear plants may be having trouble getting out of the gate, but that doesn’t mean that nuclear capacity additions are at a standstill. In fact, the 104 operating nuclear units in the U.S. have added substantial new capacity in the form of reactor and plant uprates over the past 20 years. Power uprates alone have added more than 5,600 MW since 1998 — the equivalent of five new nuclear plants.
-
Nuclear
Birth Pangs of the Nuclear Renaissance
The much-ballyhooed U.S. nuclear renaissance, with a few exceptions, is running late, thanks to the usual Washington bureaucratic quagmire plus the added risk resulting from crumbling financial markets. The future doesn’t look much brighter. The poor outlook for Yucca Mountain and the new administration’s general indifference to nuclear power have made a rebirth of the nuclear industry an even higher-risk proposition than before.